Desalination (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Environmental Management): Revision Note
Exam code: 0680
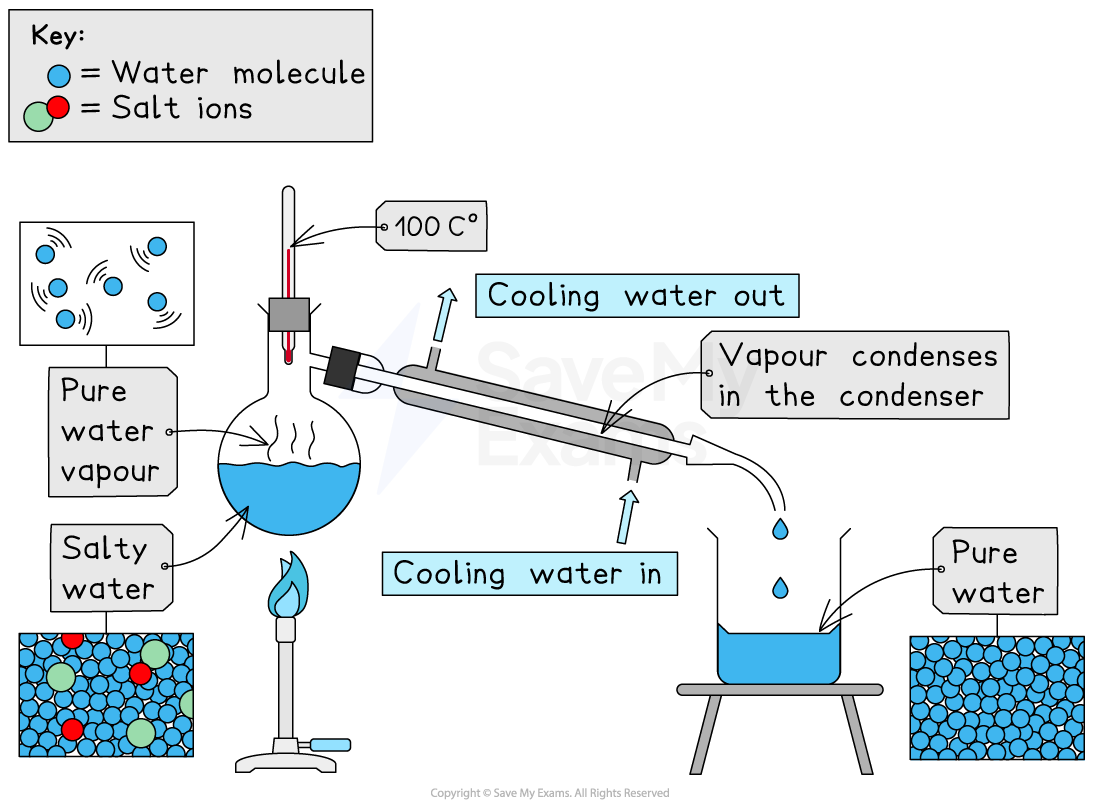
Desalination: distillation
Desalination is the process of removing salt from seawater to produce potable (safe-to-drink) water
Two main methods are used:
Distillation
Reverse osmosis
Distillation involves heating seawater until it boils
Salt and impurities do not evaporate and remain in the liquid
The water turns into steam, which is pure water vapour
Steam rises and leaves the salty water behind
The steam is then cooled and condensed
Turns back into liquid fresh water
Produces potable water, safe for drinking
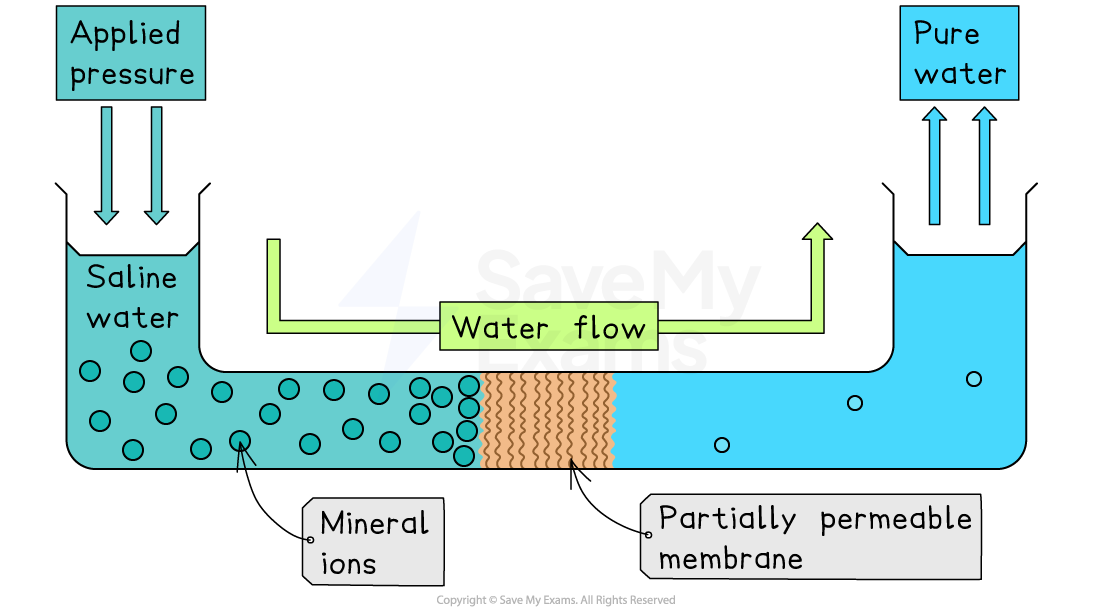
Desalination: reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis involves forcing seawater through a semipermeable membrane using high pressure
The membrane allows small water molecules to pass through
It blocks salt ions and most other dissolved substances
Produces fresh water on one side of the membrane
Leftover salty water (brine) must be safely disposed of
Benefits & limitations of desalination
Benefits of desalination
Provides a reliable source of drinking water in dry or water-poor regions
Useful where rainfall is low or rivers and lakes are limited
Not affected by drought, because the ocean is a constant supply
Can supply large populations, including major cities
Helps countries reduce dependence on imported water or overused rivers

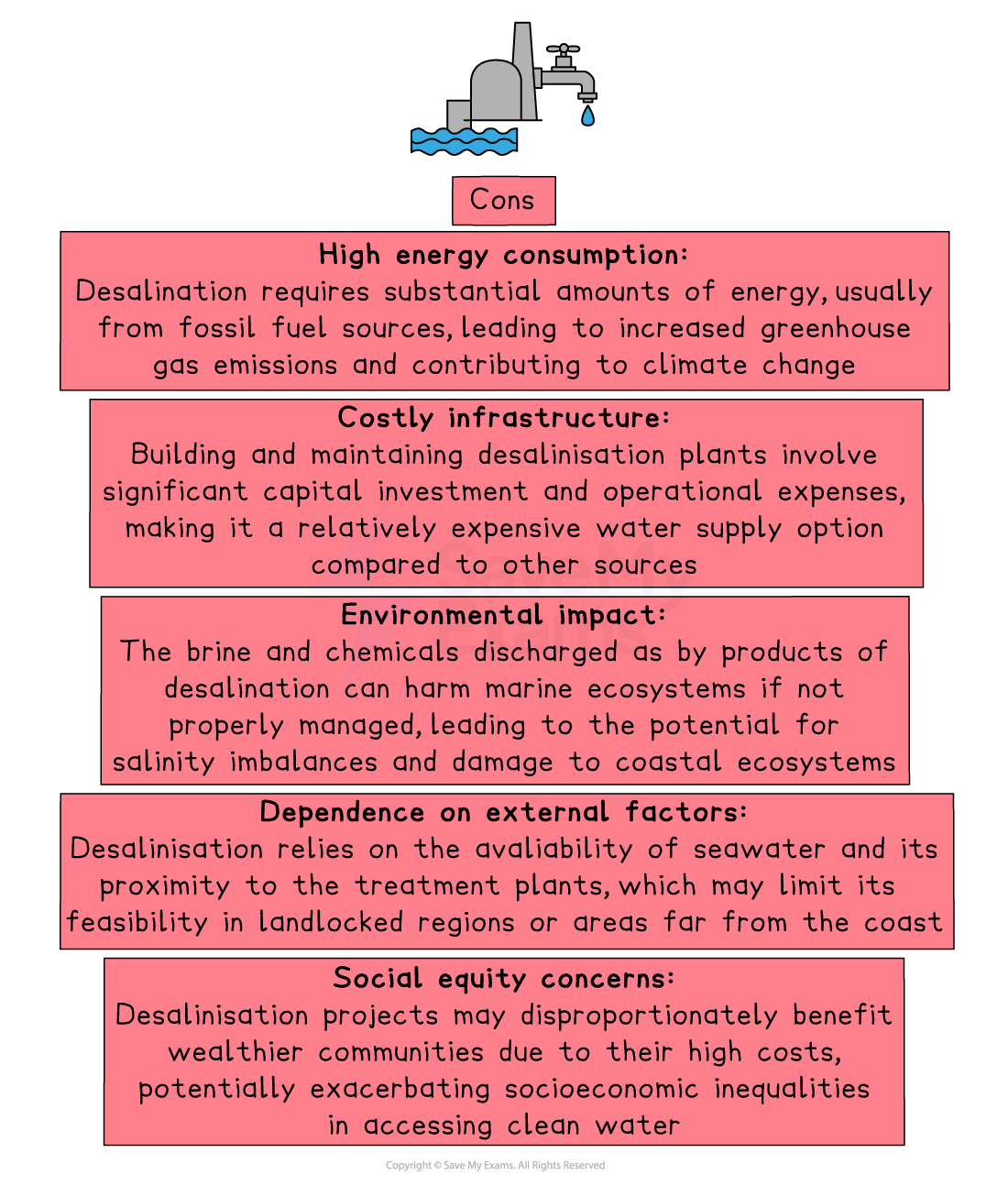
Limitations of desalination
Requires large amounts of energy, making it expensive to run
Especially for distillation, which involves heating water
Produces brine, a very salty waste product
Must be disposed of carefully to avoid harming marine ecosystems
Building and maintaining desalination plants is costly
Not all countries can afford the infrastructure needed
Reverse osmosis membranes need regular cleaning or replacing, increasing costs

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
