Sources of Fresh Water (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Environmental Management): Revision Note
Exam code: 0680
What are the main sources of fresh water?
Fresh water refers to water with low salt content, used by people for drinking, washing, farming and industry
Only a small percentage of Earth’s water is fresh water

People obtain fresh water from four main sources:
Atmosphere
Surface water
Groundwater
Desalinated ocean water
Atmosphere: rain and snow
Rain and snow come from precipitation, when water vapour in the atmosphere cools and falls to the Earth
Used directly by plants and stored in rivers, lakes and groundwater
Many regions depend on seasonal rainfall for drinking water, farming and filling reservoirs
Snow in mountains melts in warmer seasons
Meltwater feeds rivers and provides water during dry periods
Surface water: rivers, lakes and reservoirs
Surface water is fresh water found above ground
Rivers
Flow across the land and collect rainfall and meltwater
Used for drinking water, irrigation and hydroelectric power
Lakes
Store large amounts of water in natural basins
Provide a reliable supply throughout the year
Reservoirs
Reservoirs—artificial lakes created by building dams
Store water for cities, agriculture and industry
Help control flooding and maintain water supply during droughts
Groundwater: aquifers and wells
Groundwater is stored below the Earth’s surface in soil and rock
Aquifers
Aquifers—underground layers of rock that hold water
Filled by rainwater soaking into the ground
Provide clean, filtered water for drinking but hard to access
Wells
Wells are holes dug or drilled into the ground to reach aquifers
Communities pump water to the surface for home use, farming and livestock
Oceans: desalination plants
Oceans contain salt water, which is not safe to drink
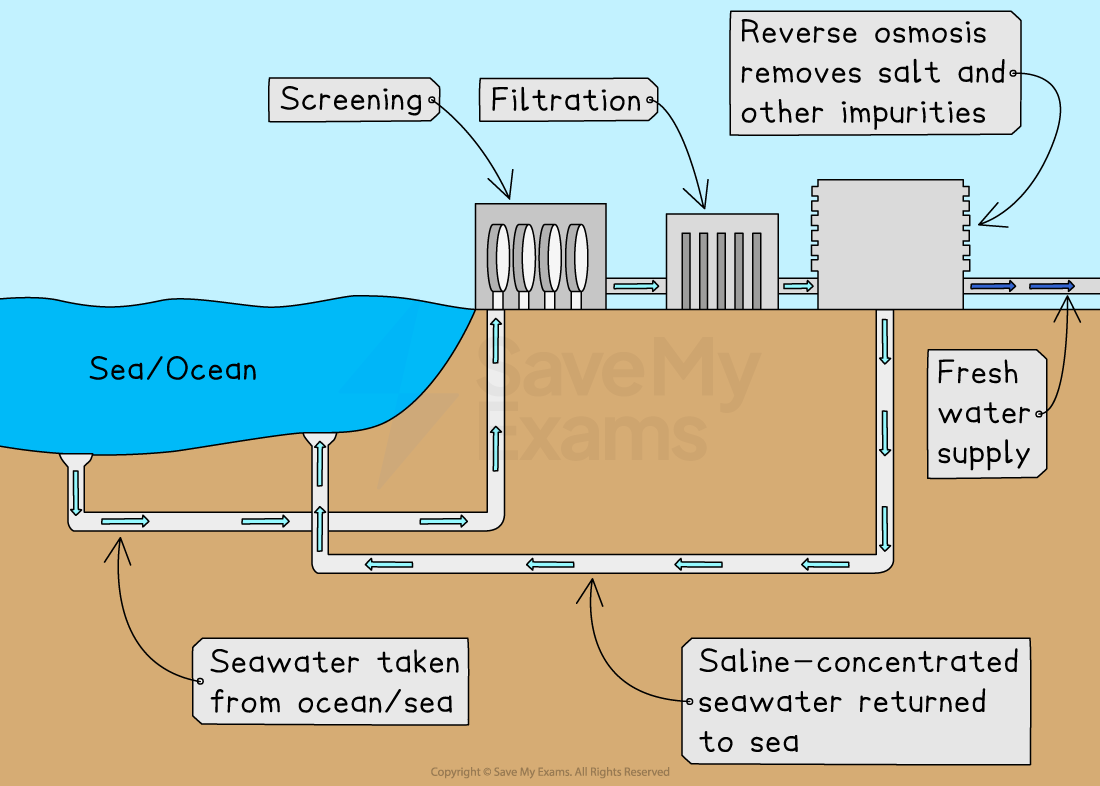
Desalination is the process of removing salt from seawater to make fresh water
This can be done using heat (distillation) or membranes (reverse osmosis)
A desalination plant is a large facility where machines remove salt from seawater to produce fresh drinking water
They are usually found in coastal areas where freshwater supplies are limited
They are useful in dry countries with little rainfall
Provides a reliable supply but uses large amounts of energy
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You need to be able to describe how desalination plants actually work (i.e. how they use distillation or reverse osmosis) to turn seawater into fresh water. This is covered in detail in our revision note page on desalination.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
