Protein Structure & Function (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
Protein structure
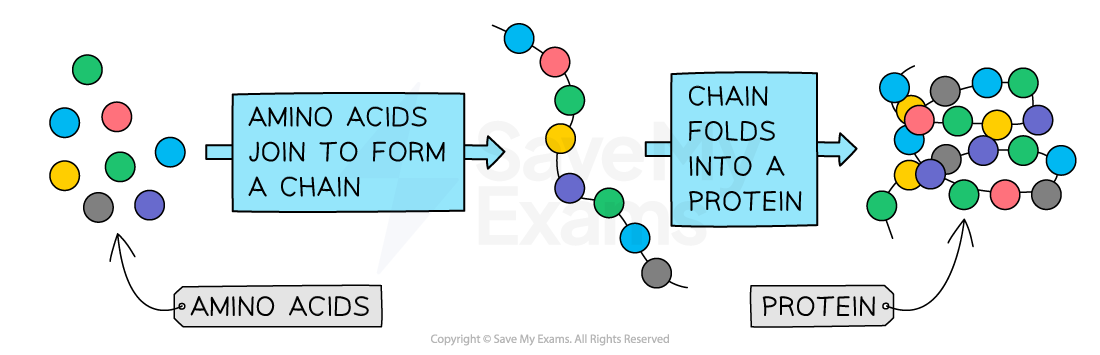
Proteins are molecules made from individual units called amino acids
The sequence of amino acids bonded together forms the basic structure, which is is specific for each protein
A single alteration in the sequence of amino acids can affect the function of the protein
Amino acid chains then fold and form additional bonds between the amino acids, creating a final three-dimensional shape
The final shape of a protein determines its function
Proteins with different shapes will carry out different roles within cells
Protein function
Proteins perform a wide range of essential roles in all living organisms
Examples of protein function include:
structure: structural proteins provide support, e.g. within tendons, ligaments and skin
enzymes: enzymes are proteins that function as biological catalysts, e.g. pepsin and amylase in digestion
hormones: these proteins travel around in the blood and transmit chemical signals to target cells, e.g. insulin
antibodies: immune proteins that recognise and neutralise pathogens
receptors: proteins embedded in the cell membrane that bind to specific signals, e.g. hormones, and allow cells to respond

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
