Diffusion (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
Passive transport
All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane, which separates the inside of a cell from its outside environment
Cells must move substances across their membranes in order to:
take in nutrients and gases
remove waste
Membrane transport can be either passive or active
Passive transport can be defined as follows:
membrane transport that occurs down a concentration gradient and does not require energy
Examples of passive transport include:
diffusion
osmosis
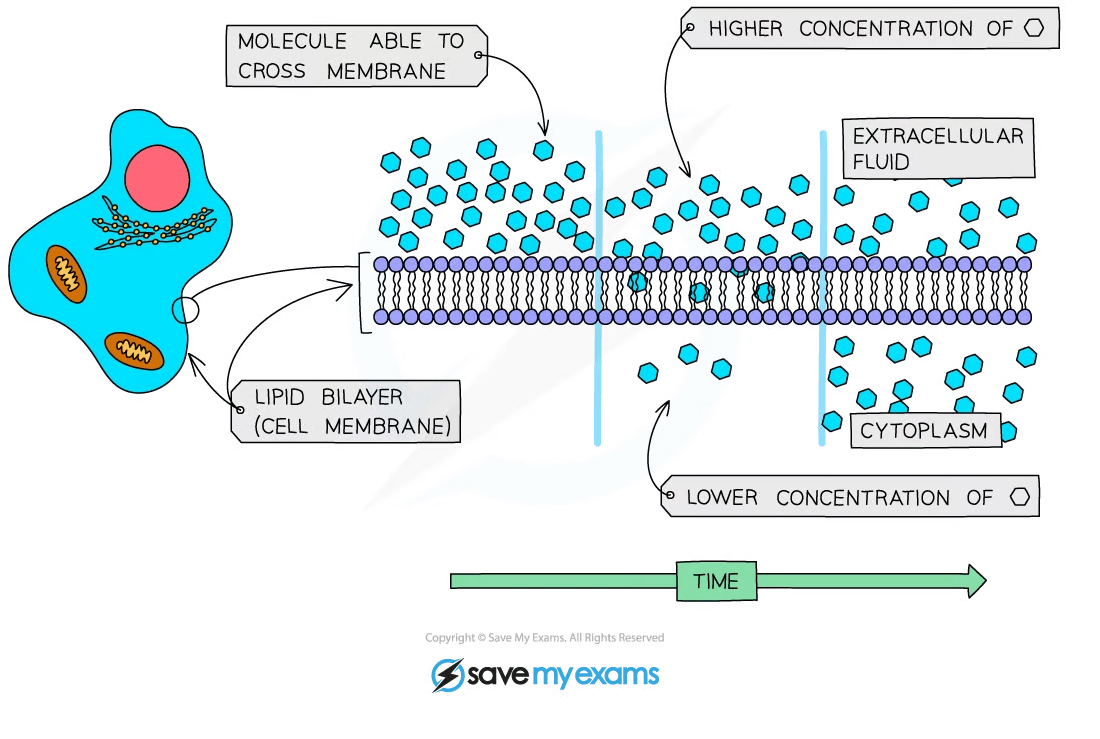
The process of diffusion
Diffusion can be defined as:
the movement of molecules down a concentration gradient from a higher to a lower concentration
This movement continues until the concentration of substances is equal
Note that diffusion occurs as a result of the random movement of molecules
Substances can diffuse through the cell membrane to enter or exit a cell
E.g. oxygen and carbon dioxide can diffuse across cell membranes during gas exchange

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
