The Reflex Arc (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
The reflex arc
Simple reflexes allow rapid, automatic responses to stimuli, the purpose of which is to protect an organism from harm, e.g.:
the pupil reflex prevents bright light from damaging the retina
the coughing reflex prevents obstructions from entering the airways
Reflex nerve pathways are known as reflex arcs
Reflex arcs do not involve conscious parts of the brain, meaning that reflexes are faster than any other type of nervous response
The structure of a reflex arc
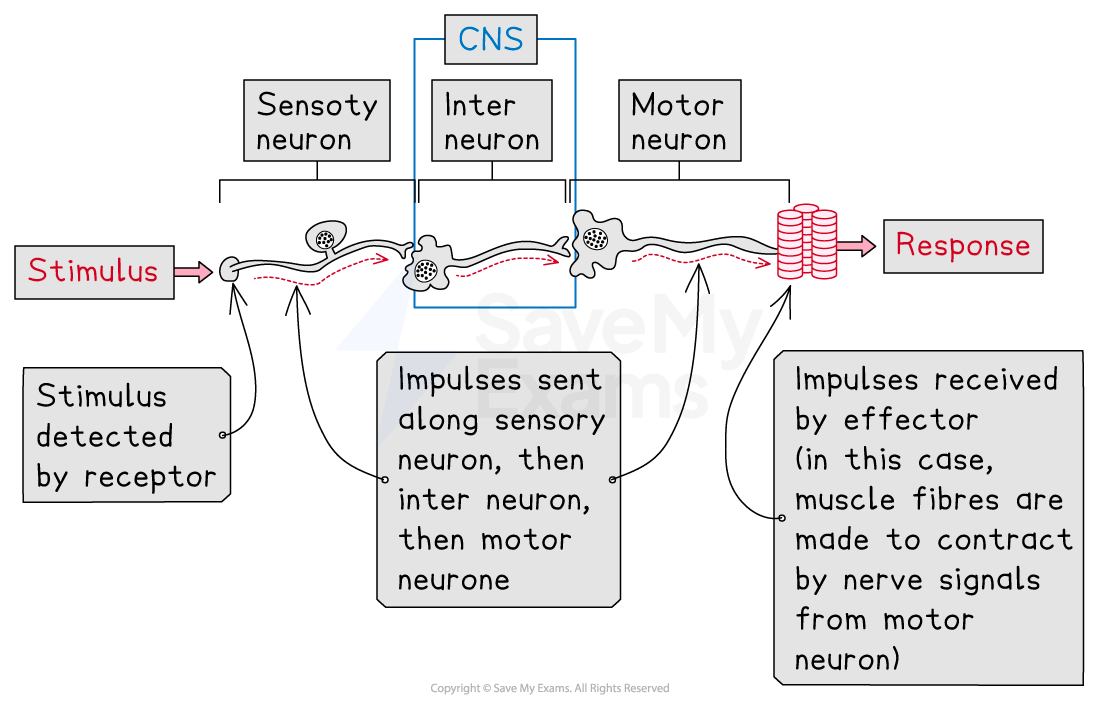
In a reflex arc, a stimulus brings about a response when a nerve impulse is sent as follows:
receptor → sensory neuron → inter neuron → motor neuron → effector
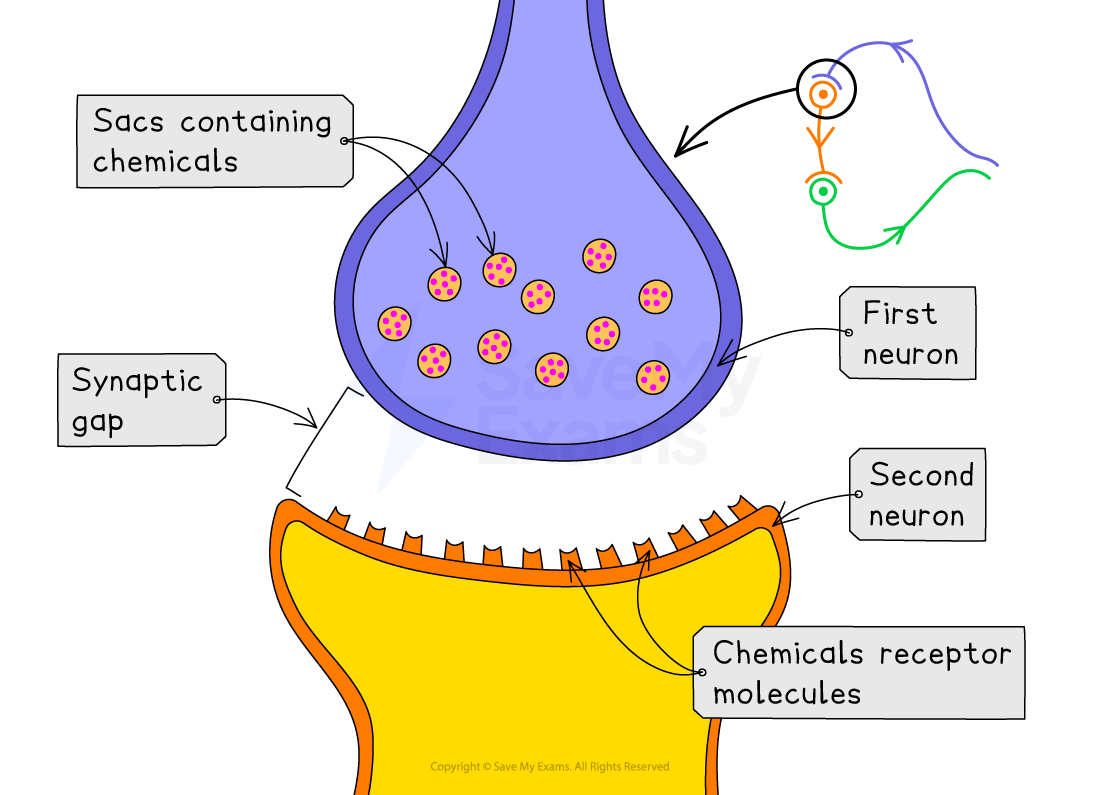
The synapse
Neurons never touch each other
The junctions (gaps) in between them are called synapses
The electrical impulse travels along the first neuron and triggers the release of chemicals from small sacs at the nerve ending
The chemicals diffuse across the synaptic gap and bind with receptor molecules on the membrane of the second neuron
This initiates the continuation of the electrical impulse in the second neuron

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
