The Process of Photosynthesis (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
The light reactions
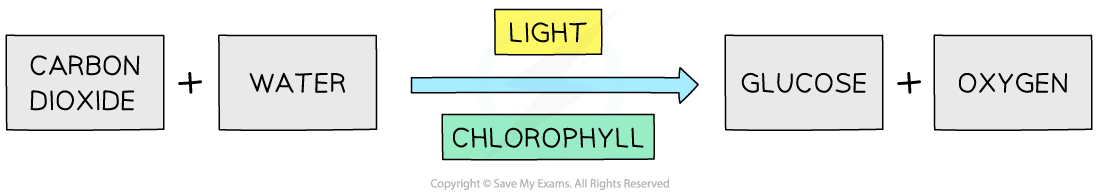
Photosynthesis is the process used by plants to produce their own biological molecules; it can be summarised as:
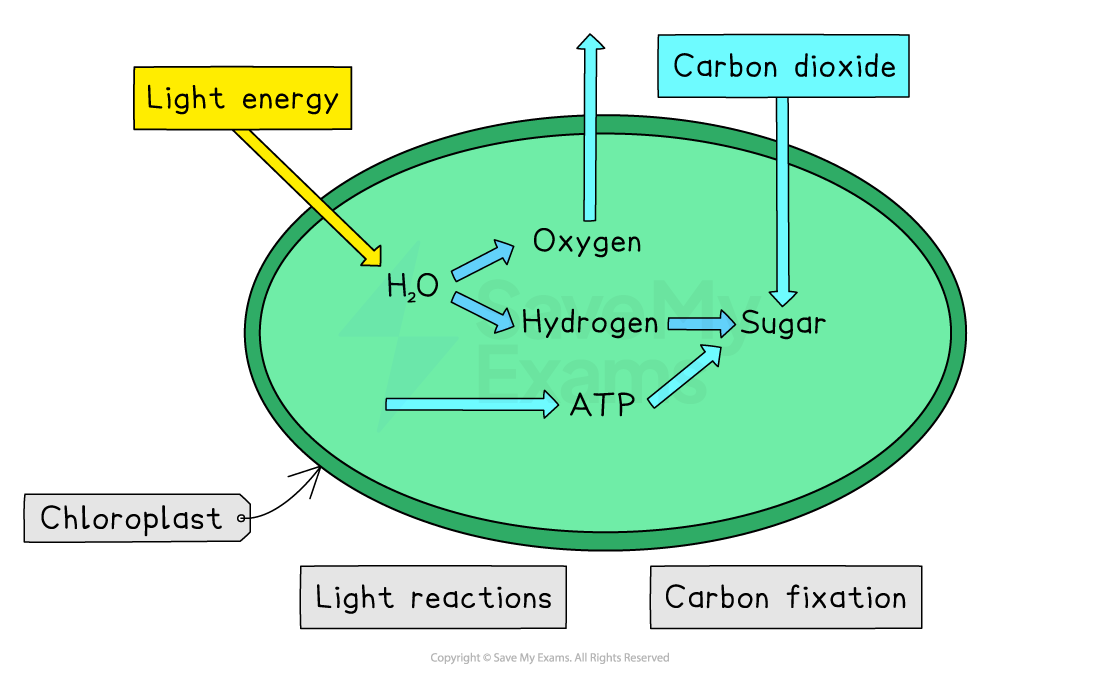
The reactions of photosynthesis can be divided into two stages:
the light reactions: light energy from the sun is captured
carbon fixation: carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is used to produce sugar
During the light reactions, light energy from the sun is trapped by chlorophyll, a green pigment found inside chloroplasts
The light energy:
is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP
splits water, releasing hydrogen and oxygen
Products of the light reactions are therefore:
ATP: passed to the next stage of photosynthesis
hydrogen: also passed to the next stage of photosynthesis
oxygen: diffuses out of the cell as a waste product
Carbon fixation
The second stage of photosynthesis involves a series of enzyme-controlled reactions
Enzyme activity is affected by temperature, so the carbon fixation reactions are temperature-dependent
These reactions require:
hydrogen and ATP from the light reactions
carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
Hydrogen, ATP and carbon dioxide are used to produce sugar

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
