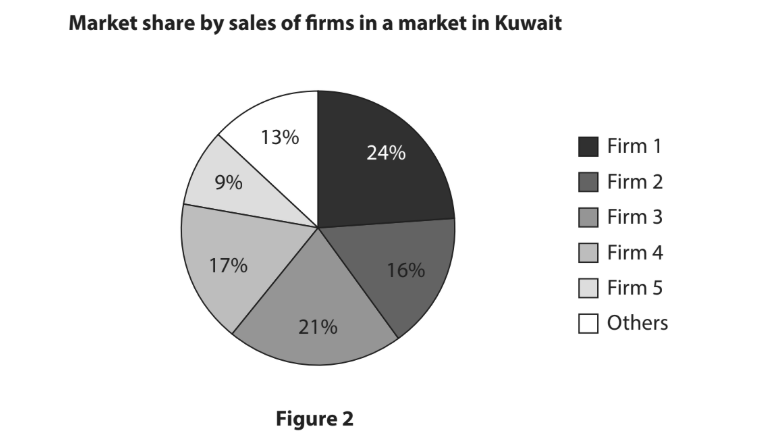
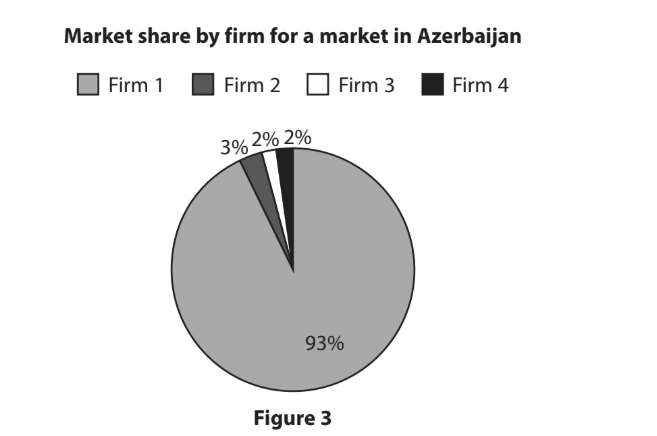
McAfee is a US-based global computer software security company. In 2017, its revenue was over $2.5bn. The company operates a ‘fundraising match programme’. This means when one of its 7,600 employees participates in a fundraising activity, such as a walk, run or cycle event, the company will contribute an equal amount. For every $1 raised for charity by an employee, the company will also contribute $1 to the charity, up to a maximum of $1 000 per person.
(Source adapted from: https://doublethedonation.com/ (opens in a new tab)tips/companies-that-donate-to-nonprofits/#match)
With reference to the data above and your knowledge of economics, analyse the possible reasons why McAfee chooses not to profit maximise but instead operates the fundraising match programme.