Casper has decided to purchase a new television.
Explain one possible opportunity cost for Casper of this decision.
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: 4EC1
Casper has decided to purchase a new television.
Explain one possible opportunity cost for Casper of this decision.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A firm has decided to purchase a new delivery vehicle.
Explain one possible opportunity cost for the firm of this decision.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Which one of the following is a definition of opportunity cost?
Rivalry that exists between firms
Investment in capital goods
The next best alternative given up
Unused resources
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
In the box below, draw a production possibility curve (PPC) for a firm that can produce shampoo and/or toothpaste. On your PPC, draw and label what would happen if production of toothpaste was increased.
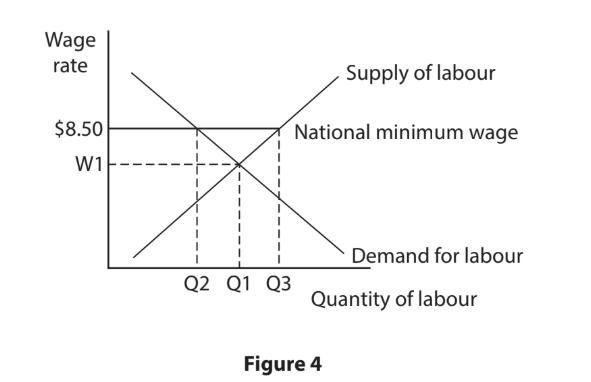
In 2021, the national minimum wage in Barbados was increased from $6.25 per hour to $8.50 per hour.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Which one of the following could be described as an economic need?
Haircut
Holiday
Shelter
Smartphone
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Figure 4 shows the Production Possibility Curve (PPC) for an economy making capital goods and consumer goods.
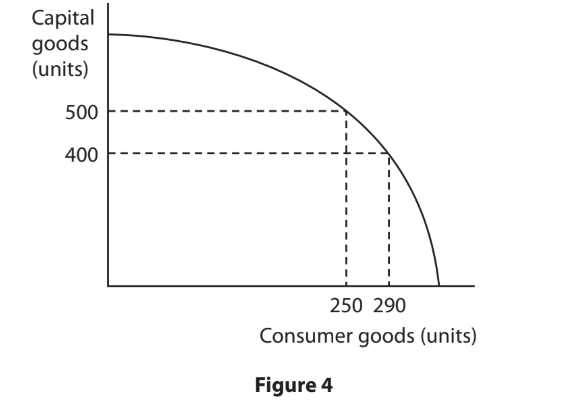
When the current level of output is 250 units of consumer goods, calculate the opportunity cost of producing an additional 40 units of consumer goods. You are advised to show your working.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
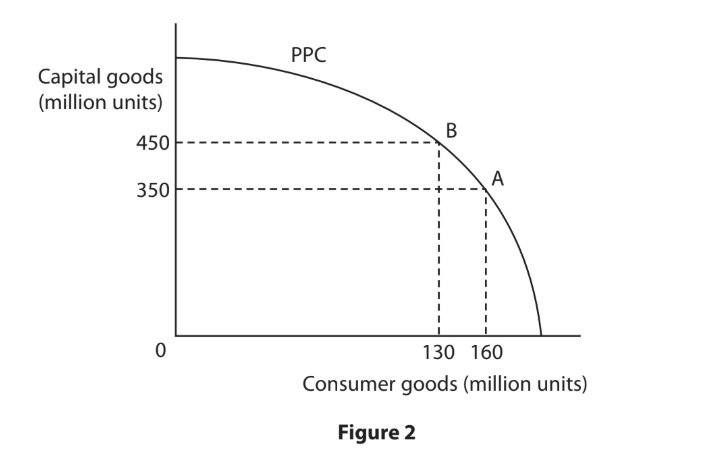
Figure 2 shows the production possibility curve (PPC) for an economy.
With reference to the data above and your knowledge of economics, analyse the impact on the economy after a movement from A to B on the production possibility curve (PPC).
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
What is meant by the term opportunity cost?
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
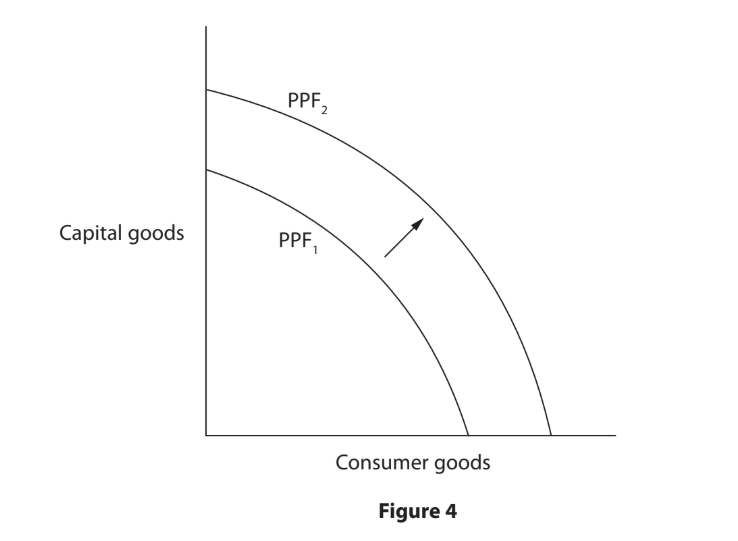
Figure 4 shows an outward shift in the production possibility frontier (PPF) for Zambia in 2019. Agriculture, construction and copper production are some of the main areas that contribute to the economy of Zambia.
With reference to the data above and your knowledge of economics, analyse why the economy has moved from PPF1 to PPF2.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Describe one reason why infinite wants lead to scarcity.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
In the box below, draw a production possibility frontier (PPF) for a firm that can produce tables and/or chairs. On your PPF, draw what would happen if the production of chairs decreased and tables increased.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Which one of the following means having more of one thing but less of another thing?
Menu costs
Trade-off
Opportunity cost
Trading bloc
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which one of the following does a point on a production possibility curve (PPC) represent?
Where capital goods should be produced
How the production of all goods can be increased
Government revenue from production
A given amount of resources being fully employed
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A country is able to produce agricultural and non-agricultural goods with a given amount of resources. Its production possibility curve (PPC) is shown in Figure 2.
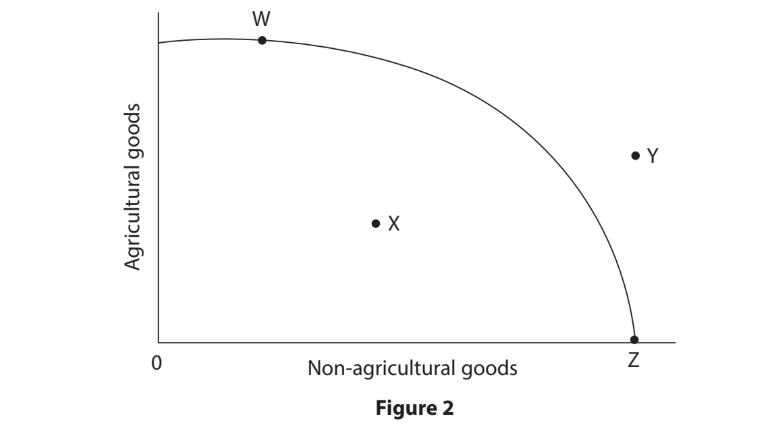
Which one of the following points shows unemployed resources?
W
X
Y
Z
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The government of a country has decided to build a new hospital.
Explain one possible opportunity cost for the government of this decision.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Using the axes below, draw two production possibility curves (PPC) to show an
economy moving from PPC1 to PPC2. Label both production possibility curves and the axes.
Technology has been used to perform some of the jobs previously done for many years by humans, for example, robots in factories and self-checkout machines. This substitution of capital for labour is likely to increase as technology advances. At most call centres, humans currently respond to customer queries but Google has developed an automated assistant. Many telecom firms have switched to using calls made by these automated assistants.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A firm has decided to purchase a new computer system.
Explain one possible opportunity cost for the firm of this decision.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Which one of the following is the term for the next best alternative given up when a choice is made?
Business competition
Capital investment
Opportunity cost
Spare capacity
Choose your answer
The problem of scarcity is that there are unlimited wants and finite resources.
Define the term wants.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
In the box below, draw a production possibility frontier (PPF) for a firm that can produce diaries and/or calendars. On your PPF, draw what would happen if production of calendars increased.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Figure 6 shows the Production Possibility Curve (PPC) for an economy making consumer goods and capital goods.
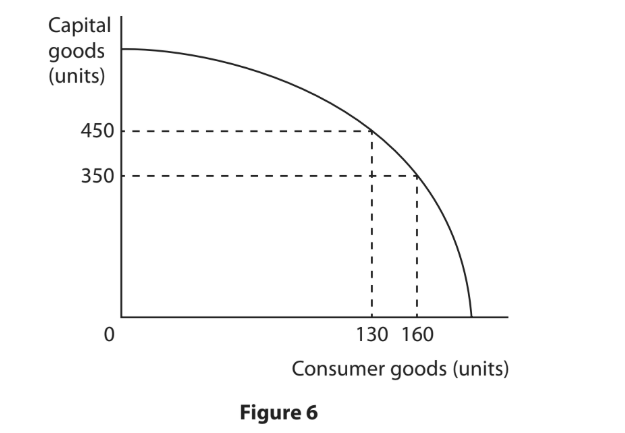
When the current level of output is 350 units of capital goods, calculate the opportunity cost of producing an additional 100 units of capital goods. You are advised to show your working.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A country is able to produce agricultural and non-agricultural goods. Its production possibility curve is shown in Figure 3.
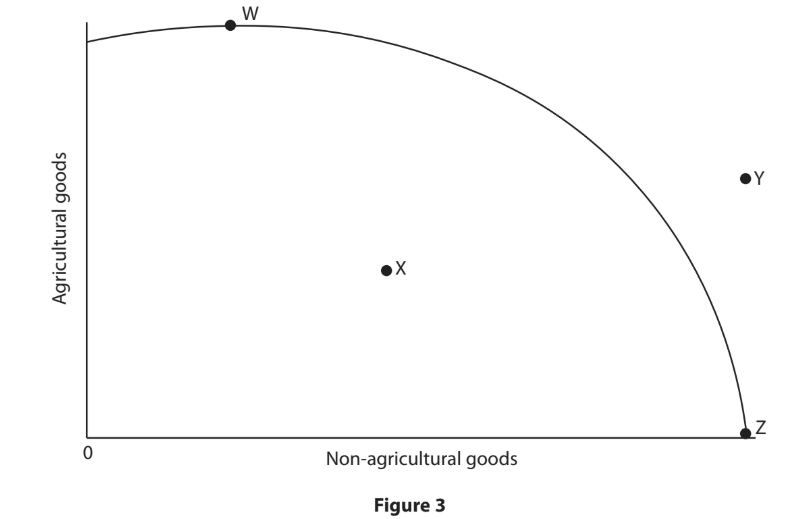
Which one of the following points is not achievable?
W
X
Y
Z
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which one of the following is an example of an economic want?
Food
Water
Shelter
Education
Choose your answer
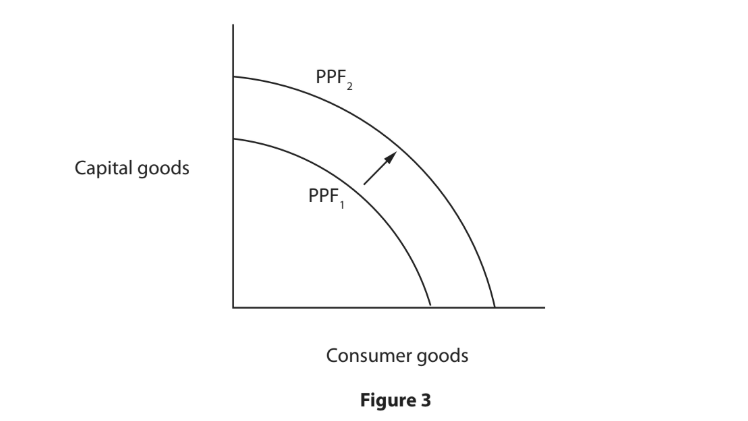
Figure 3 shows an outward shift in the production possibility frontier (PPF) for an economy.
Analyse why the economy has moved from PPF1 to PPF2.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?