Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Types of farming (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Geography): Revision Note
Exam code: 0460 & 0976
Specification link
This page covers section 10.1.1 of the CIE IGCSE specification .
10.1.1 - Farming types: subsistence, commercial, arable, pastoral, mixed, aeroponics, aquaponics, hydroponics.
What are the different types of farming?
To obtain food, humans use and modify the ecosystems through farming
There are four groupings commonly used to categorise farming:
By inputs:
Intensive farming use large amounts of labour, machines, technology or money often resulting in high yields per acre/hectare
Extensive farming uses low levels of labour, machines, technology or money often resulting in low yields per acre/hectare
By what is grown/raised (processes):
Arable is the cultivation of crops
Pastoral is the rearing of livestock
Mixed is a combination of arable and pastoral
By the outputs:
Commercial farming is growing crops or rearing livestock for profit
Subsistence farming is when crops are grown and livestock is raised to feed the farmer and their family
Classification of farms is not easy because:
each type of farm belongs in more than one category
a sheep farm is commercial, extensive and pastoral
activities within the farm are subject to change
If a subsistence farmer has a particularly good harvest then they will sell some of the crops for profit
As well as the main categories farming can also be categorised by location
Nomadic farming occurs where farmers move from one place to another
This usually happens in areas where farmers need to search for grassland for grazing their livestock
Sedentary farms are located in one place and do not move
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember, farms do fit into more than one category. For example, a sheep farm in Cumbria. The UK would be categorised as arable, commercial, extensive and sedentary
Other types of farming
Vertical farming
Vertical farming is the growth of crops vertically (upwards), in layers
This type of farming usually occurs in large buildings, greenhouses or shipping containers to reduce land use
The systems produce more food for the land available
Examples include:
Aeroponics - crops hang in the air, with their roots exposed. A nutrient-rich condensed mist waters the plants
Hydroponics - growing plants without soil, using mineral nutrient-rich water instead
Aquaponics - using aquaculture with hydroponics. Waste from marine animals nourishes the water used for crop growth
Vertical farming is seen in countries across the world, from Germany and the Netherlands to Japan and Singapore
Examples of vertically farmed foods include:
Lettuce, kale, broccoli, garlic
Strawberries
Tree seedlings
Plants used for medicine
Fish
Aeroponics
This method involves growing plants inside using a mist system
The plants are not grow in soil but are suspended in the air and the roots take in the nutrients and water they need from the mist
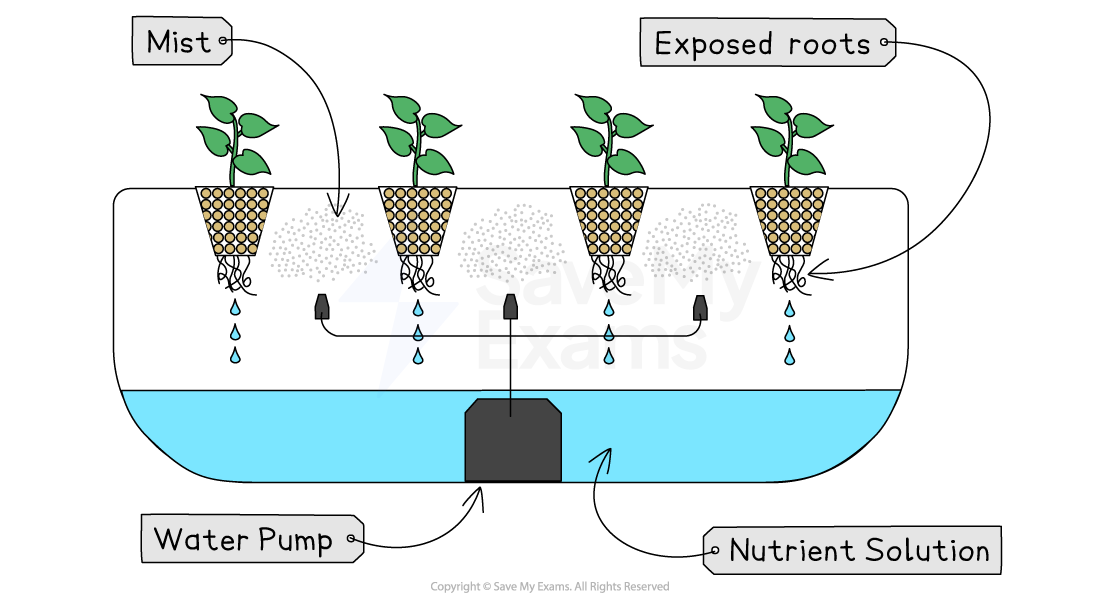
Costs of aeroponic systems are high
The system is only suitable for some crops such as:
lettuce
kale
strawberries
tomatoes
Aeroponics uses less water than traditional systems
It may also produce higher yields
Hydroponics
In a hydroponic system plants are grown in a nutrient rich liquid
Unlike aeroponics where the roots are suspended in the air, in hydroponics the roots sit in the liquid
Aquaponics
An aquaponic system combines aquaculture and hydroponics
As in hydroponics the plant roots sit in a nutrient rich water
The difference is that in aquaponics the water is an environment for fish
The fish waste provides nutrients for the plant growth
The plants remove nitrates from the water which filters it, keeping it clean for the fish

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?