Alcohols (SQA National 5 Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: X813 75
The alcohols
What are alcohols?
Alcohols are a family of organic compounds
They are not hydrocarbons because they contain oxygen
For a full table of the first alcohols and their structures, see the Full & shortened structural formulae
Alcohols are a homologous series with four key facts:
1. They contain the -OH (hydroxyl) functional group
All alcohols contain a hydroxyl group
This is an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom (-OH)
This is the functional group that gives alcohols their characteristic properties
2. They are represented by a general formula
The general formula for the alcohol homologous series is CnH2n+1OH
This formula applies to saturated, straight-chain alcohols
For example:
If an alcohol has 2 carbon atoms, n = 2
So, its formula will be C2H(2 x 2) + 1OH = C2H5OH
3. They are used as fuels
Alcohols are highly flammable and burn with very clean flames, releasing large amounts of energy
They are used as:
Fuels in spirit burners and camping stoves
Biofuels for cars
4. They are used as solvents
Alcohols are excellent solvents because they can dissolve many substances that water cannot
They are used as solvents in many products, including:
Perfumes
Deodorants
Hand sanitisers
Names & formulae of alcohols
Like other organic compounds, alcohols are named systematically
There are three skills for alcohols:
Naming alcohols from their structure
Drawing alcohols from their name
Determining the formula of an alcohol
1. Naming alcohols
The name of a straight-chain alcohol is made of three parts:
A prefix to show the number of carbon atoms
A number to show which carbon the -OH group is attached to
The ending -ol to show it is an alcohol
The rules for naming alcohols:
Find the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms
This chain must contain the -OH group
The -OH group means that the name ends with "-ol"
Number the carbon atoms
This is only needed if there are 3 or more carbon atoms
Start from the end closest to the -OH group, to give the functional group the lowest possible number
Combine the parts to make the full name
Write the main chain prefix
Add a hyphen
Write the number of the carbon that the -OH group is attached to
Add a hyphen
Write the "-ol" ending for an alcohol
If there are branches, you name them in the same way as for alkanes
Worked Example
Name the following molecule.
[1]
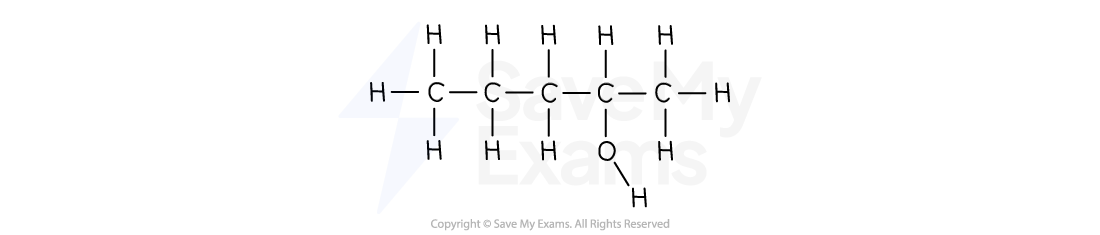
Answer:
Main chain:
The main chain containing the -OH group has 5 carbon atoms
So, the name starts with pentan-
The -OH group:
Numbering from left to right, the -OH group is on carbon 4
Numbering from right to left, the -OH group is on carbon 2
The lowest number is 2
So, the name contains -2- and ends in -ol
Combine the parts:
The full name is pentan-2-ol [1 mark]
2. Drawing alcohols
You can work backwards from the name to draw the structure of an alcohol
The rules for drawing alcohols:
Identify the longest carbon chain
Identify the number of carbons in the longest chain
For example, "propan" means a 3-carbon chain with carbon-carbon single bonds, C-C
Draw the main carbon chain
Identify the -OH group:
Identify the carbon with the -OH group attached
For example, "-1-" means the -OH group is attached to carbon 1
Add the -OH group
Add the hydrogens to complete the structure
Make sure every carbon atom has exactly four bonds
Worked Example
Draw the full structural formula for butan-2-ol.
[1]
Answer:
Main chain:
"butan-" means a chain of 4 carbons
The -OH group:
"-2-ol" means that the -OH group is attached to carbon number 2.
So, the full structural formula for butan-2-ol is:

[1 mark]
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When drawing the full structural formula of an alcohol, you must show the bond between the oxygen and the hydrogen (-O-H)
Just writing -OH is not a full structural formula and could lose you a mark

3. The molecular formula of alcohols
The general formula of alcohols can be used to determine the molecular formula
Worked Example
State the formula of heptan-2-ol.
[1]
Answer:
The general formula of an alcohol is CnH2n+1OH
Hept means that n = 7
So, the formula of heptan-2-ol is C7H(2 x 7) + 1OH = C7H15OH [1 mark]

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
