The Kinetic Model (SQA National 5 Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: X857 75
The kinetic model
The kinetic model is used in physics to explain the motion of particles
The kinetic model is the idea that all matter is made up of particles that are always moving
This model explains the properties of solids, liquids and gases
The kinetic model and gases
Particles in a gas are in constant random motion at high speeds
Random motion means that the molecules are travelling in no specific path and undergo sudden changes in their motion if they collide, either with:
the walls of its container
other particles
Pressure in a gas is caused by the collisions of particles with the walls of the container
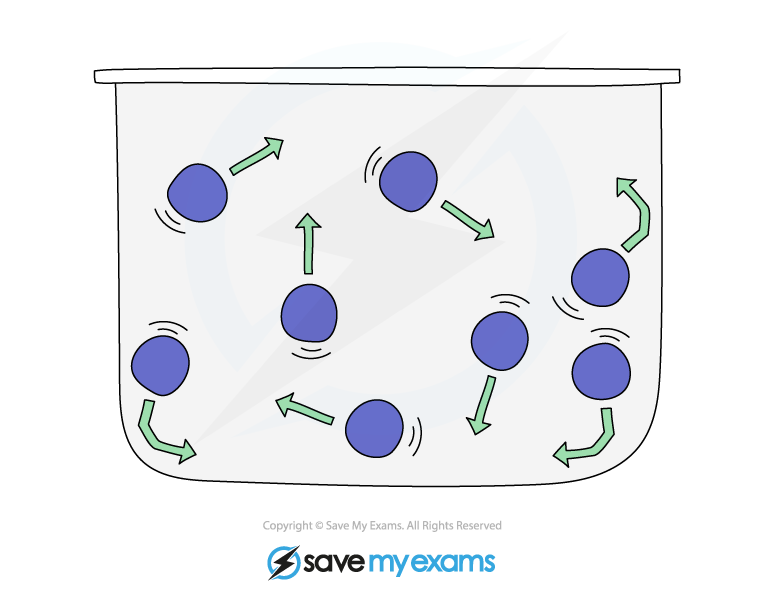
Gas pressure
When a gas is held in a container, there is a constant force applied by the gas to the container
The gas particles collide with the container walls
In each collision, the gas particle exerts a tiny force upon impact which acts at right angles to the surface
The net effect of many such collisions is a constant force on the surface area of the container
Since pressure is force per unit area, the gas can be said to exert pressure on the container
When the particles travel faster (e.g. at a higher temperature), they collide with walls more frequently
This means the gas exerts a greater pressure

Worked Example
The particles in a gas exert a force of 0.30 N on a surface of 0.025 m2.
Calculate the pressure exerted on the surface by the gas.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Force, F = 0.30 N
Area, A = 0.025 m2
Step 2: Write out the relationship for pressure
Step 3: Substitute in the known values to calculate
The least precise input value is 2 s.f.
The answer is to 2 s.f.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When explaining gas pressure in your exam, be sure to include the gas particles colliding with the surface of the container, exerting a force on the surface of the container.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
