Fibrous Proteins (OCR A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: H420
Fibrous Proteins
Fibrous proteins are long strands of polypeptide chains that have cross-linkages due to hydrogen bonds
These proteins have little or no tertiary structure
Due to a large number of hydrophobic R groups, fibrous proteins are insoluble in water
Fibrous proteins have a limited number of amino acids with the sequence usually being highly repetitive
The highly repetitive sequence creates very organised structures that are strong and this along with their insolubility property, makes fibrous proteins very suitable for structural roles
Examples of fibrous proteins:
Keratin makes up hair, nails, horns and feathers (it is a very tough fibrous protein)
Elastin is found in connective tissue, tendons, skin and bone (it can stretch and then return to its original shape)
Collagen is a connective tissue found in skin, tendons and ligaments
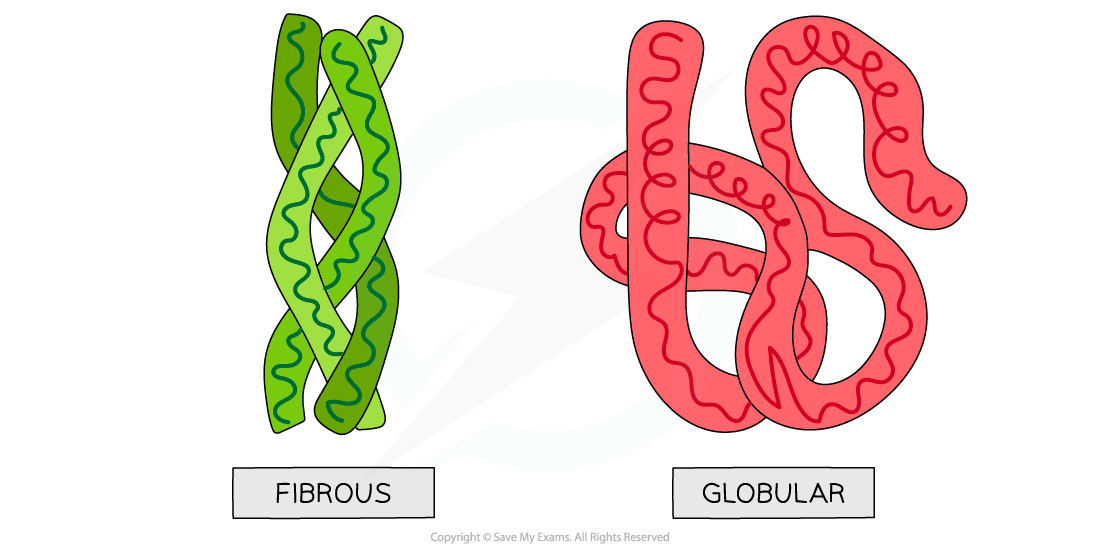
Globular and fibrous protein models illustrating the roughly spherical shape of globular proteins and the long, stranded shape of fibrous proteins
Comparison of Globular & Fibrous Tertiary Proteins Table

Collagen
Collagen is the most common structural protein found in vertebrates
It provides structural support
In vertebrates it is the component of connective tissue which forms:
Tendons
Cartilage
Ligaments
Bones
Teeth
Skin
Walls of blood vessels
Cornea of the eye
Function of collagen
Collagen is a flexible structural protein forming connective tissues
The presence of the many hydrogen bonds within the triple helix structure of collagen results in great tensile strength. This enables collagen to be able to withstand large pulling forces without stretching or breaking
The staggered ends of the collagen molecules within the fibrils provide strength
Collagen is a stable protein due to the high proportion of proline and hydroxyproline amino acids present. These amino acids increase stability as their R groups repel each other
The length of collagen molecules means they take too long to dissolve in water (making it insoluble in water)
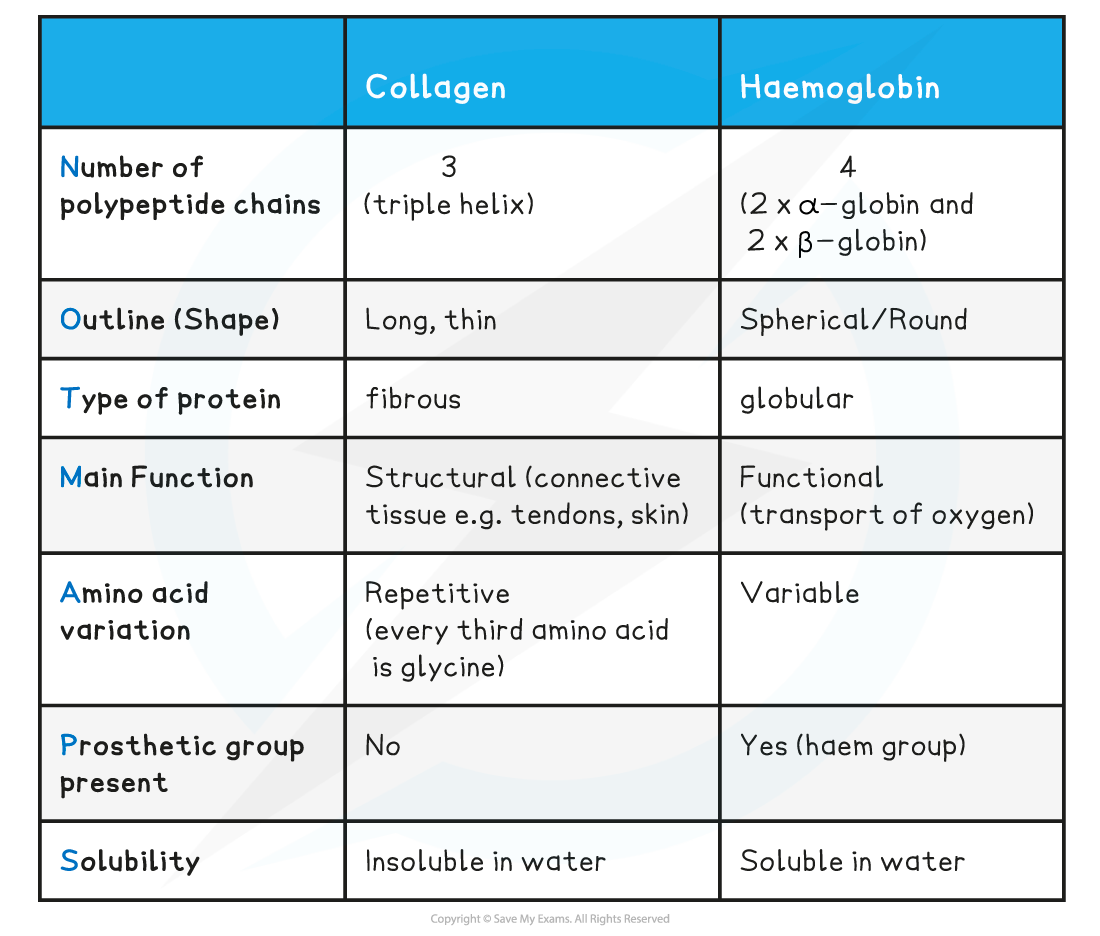
Comparison between Collagen & Haemoglobin Table
Examiner Tips and Tricks
To distinguish between proteins, learn SAFES (Shape, Amino acid sequence, Function, Examples and Solubility).You may also be asked to compare the structure and function of haemoglobin and collagen in the exam.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
