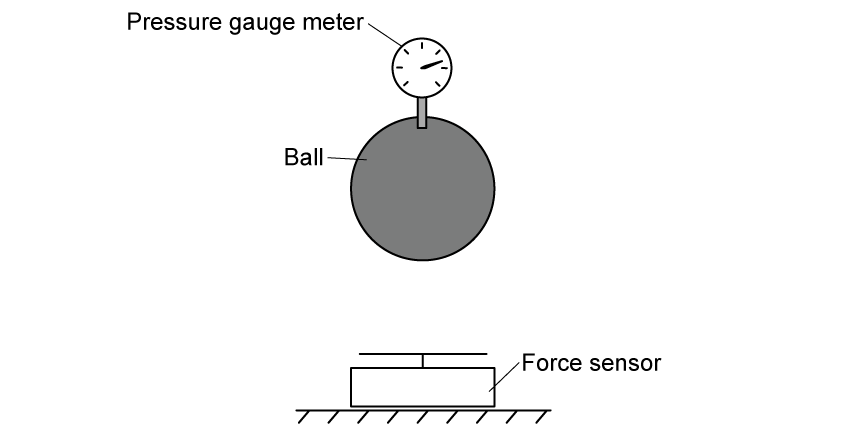
A resistance wire is coiled around a thermistor. The coil of wire will warm the thermistor.
It is suggested that the relationship between the power P dissipated in the coiled wire and the stable resistance R of the thermistor is given by the expression P = kRn, where k and n are constants.
Describe how an experiment can be conducted to assess the validity of this expression and how the data collected can be analysed to determine k and n.
Use the space below for a circuit diagram.
Was this exam question helpful?