Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions (Edexcel GCSE Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 1CH0
Written by: Stewart Hird
Updated on
Did this video help you?
Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions
Rules:
Aqueous solutions will always have water present
Some water molecules split up into hydrogen and hydroxide ions, H+ and OH–, which participate in the electrolysis reactions
Positive electrode (anode)
Negatively charged OH– ions and non-metal ions are attracted to the positive electrode (anode)
If halide ions (Cl-, Br-, I-) and OH- are present:
The halide ion is discharged at the anode
It loses electrons and forms the halogen (chlorine, bromine or iodine)
If no halide ions are present:
OH- is discharged at the anode
It loses electrons and forms oxygen gas
In both cases, the other negative ion remains in solution
Negative electrode (cathode)
H+ ions and metal ions are attracted to the negative electrode (cathode)
But only one will gain electrons
So, either hydrogen or a metal will be produced
If the metal is above hydrogen in reactivity series, hydrogen will be produced
This is seen as bubbling at the cathode
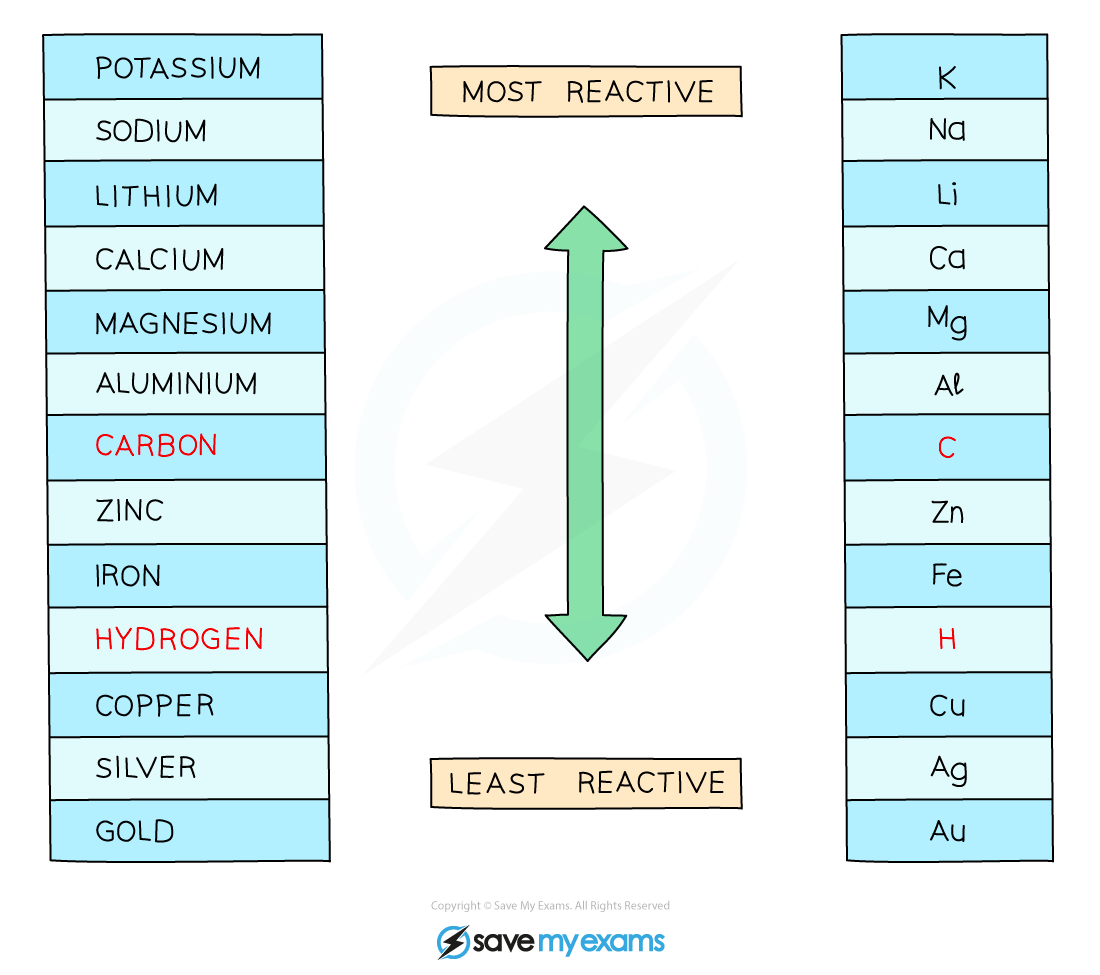
The reactivity series of metals enables chemists to predict the products at the cathode in the electrolysis of aqueous solutions
Electrolysing aqueous solution where there are gaseous products
The apparatus can be modified for the collection of gases by using inverted test tubes over the electrodes
The electrodes are made from graphite
Graphite is used because it is inert and does not interfere with the electrolysis reactions

The electrolysis of aqueous solutions using inverted test tubes to collect gases at the electrodes
Using named electrolytes
The products at the electrodes from solutions of copper chloride, sodium chloride, sodium sulfate and water acidified with sulfuric acid are:
Aqueous solution | Product at positive electrode (anode) | Product at negative electrode (cathode) |
|---|---|---|
Sodium chloride (NaCl) | Chlorine gas | Hydrogen gas |
Copper(II) chloride (CuCl2) | Chlorine gas | Copper |
Sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) | Oxygen gas | Hydrogen gas |
Dilute sulfuric acid (H2SO4) | Oxygen gas | Hydrogen gas |
Explaining the products
Sodium chloride:
Sodium is above hydrogen in the reactivity series
This means that hydrogen ions are preferentially discharged at the negative electrode (cathode)
Chlorine is a halogen
This means that it is preferentially discharged at the positive electrode (anode)
Copper chloride:
Copper is below hydrogen in the reactivity series
This means that copper(II) ions are preferentially discharged at the negative electrode (cathode)
Chlorine is a halogen
This means that it is preferentially discharged at the positive electrode (anode)
Sodium sulfate:
Sodium is above hydrogen in the reactivity series
This means that hydrogen ions are preferentially discharged at the negative electrode (cathode)
Hydroxide ions are preferentially discharged over sulfate ions
This means that oxygen is produced at the positive electrode (anode)
Dilute sulfuric acid (acidified water):
Hydrogen ions are discharged at the negative electrode (cathode)
Oxygen from water molecules is preferentially discharged at the positive electrode (anode)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Once you have identified the ions, the next step is to decide towards which electrode will they be drawn and identify the product formed.
It helps if you recall the reactivity series.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
