The Alternate Segment Theorem (AQA GCSE Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 8300
Did this video help you?
Alternate segment theorem
Circle theorem: The alternate segment theorem
The angle between a chord and a tangent is equal to the angle in the alternate segment
The alternate segment is the region on the opposite side of a chord from a given angle formed between that chord and a tangent line
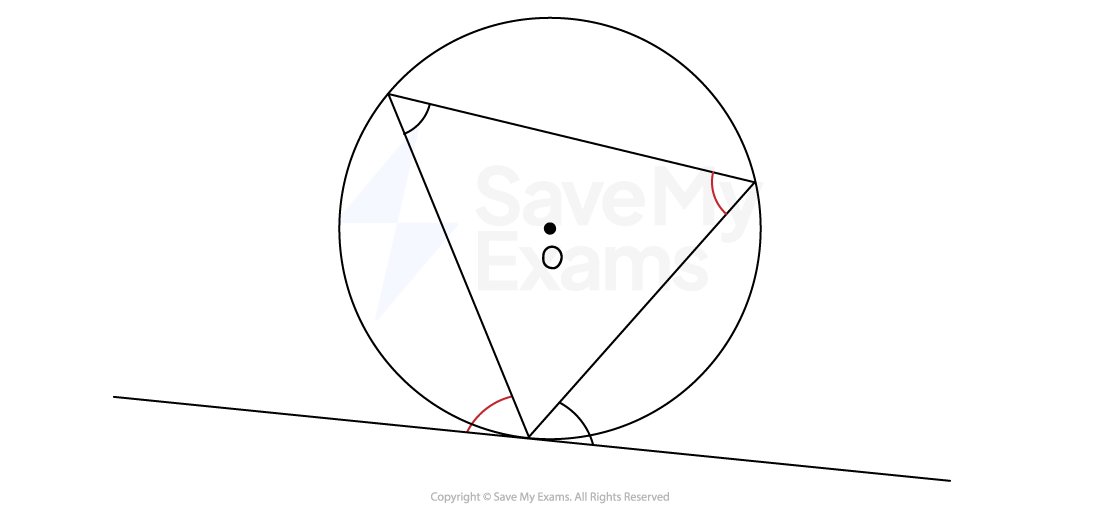
To spot this circle theorem on a diagram
look for a cyclic triangle
where all three vertices of the triangle lie on the circumference
one vertex of the triangle meets a tangent
To identify which angles are equal
mark the angle between the tangent and the side of the cyclic triangle
the angle inside the triangle at the corner opposite the side of the triangle that forms the first angle is the equal angle
When explaining this theorem in an exam you can just say the phrase:
The Alternate segment theorem
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Look for cyclic triangles and tangents in busy diagrams.
Questions involving the alternate segment theorem frequently appear in exams!
Worked Example
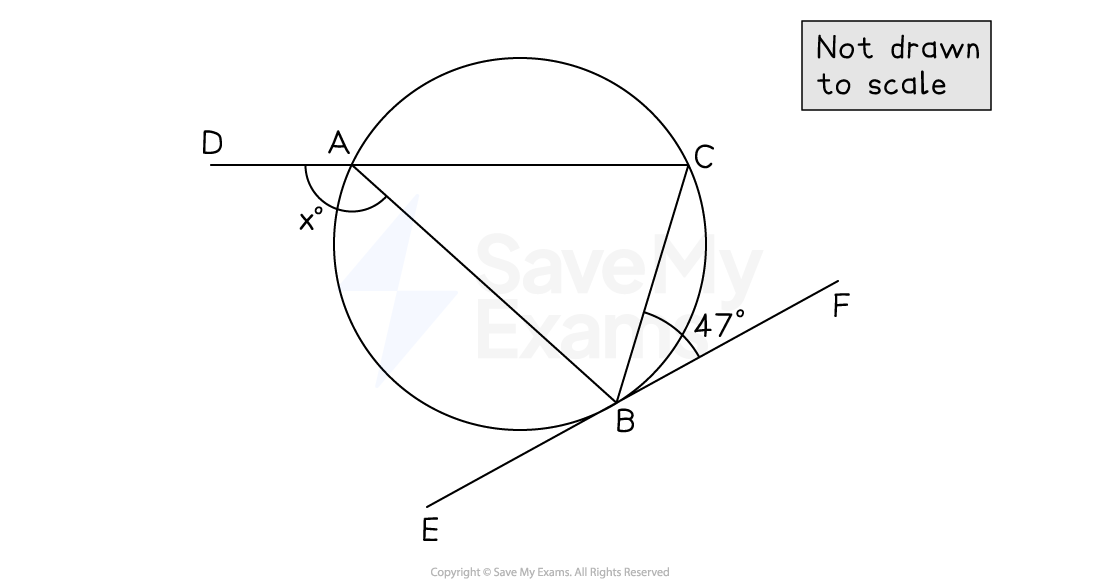
,
and
are points on a circle.
is a straight line.
is a tangent to the circle.
Find the value of .
Answer:
One vertex of this triangle meets a tangent at point B
The angle between one of its sides (BC) and the tangent is given
Find the angle inside the triangle, opposite to the same side (BC)
Angle CBF = Angle CAB by the alternate segment theorem
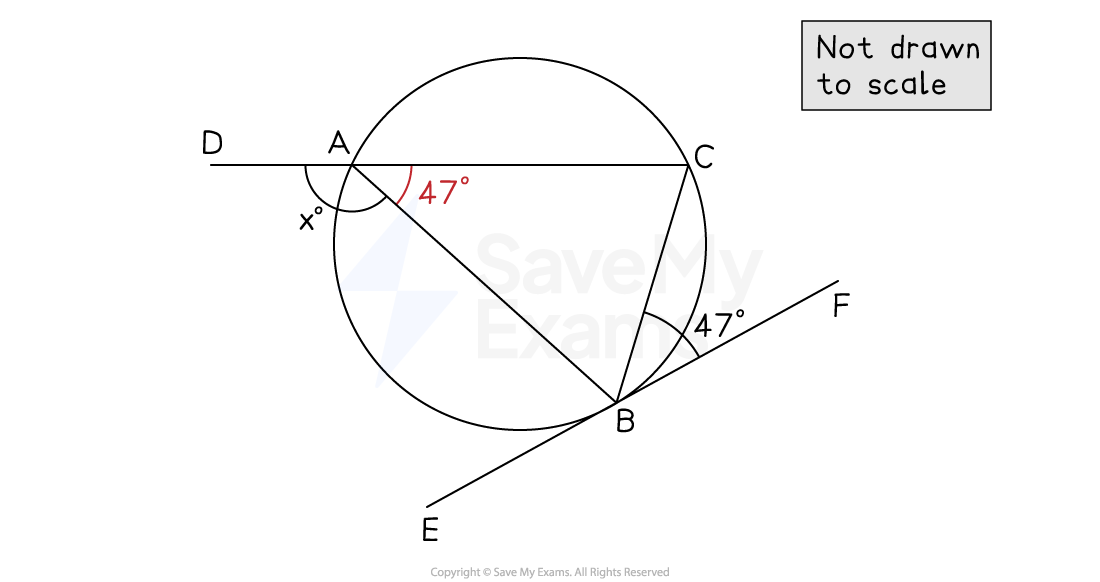
Angle and angle CAB form a straight lie

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
