A student uses four electrical appliances for different lengths of time.
Look at the table.
Appliance | Power (W) | Time used (hours) |
Hair dryer | 1500 | 0.3 |
TV | 100 | 5 |
Toaster | 2000 | 0.2 |
Light blub | 10 | 12 |
i) Which appliance uses the most energy?
[1]
ii) Which appliance uses the least energy?
[1]
Here are three different components and their use in the home.
Match the component to its correct use.
One has been done for you.

A charge of 44 000 C flows through a light bulb. The potential difference is 230 V.
Calculate the energy transferred.
Use the equation: Charge = Energy ÷ Potential difference
Record your answer to 2 significant figures.
Answer = ...................................................... J
i) A student has completed her homework on static electricity.
Look at her homework.
1 Static charge only builds up on insulators. 2 Opposite charges attract. 3 Like charges repel. 4 Only positive charges can move. |
Identify the student’s mistake and correct it.
[2]
ii) When charges move, a current flows.
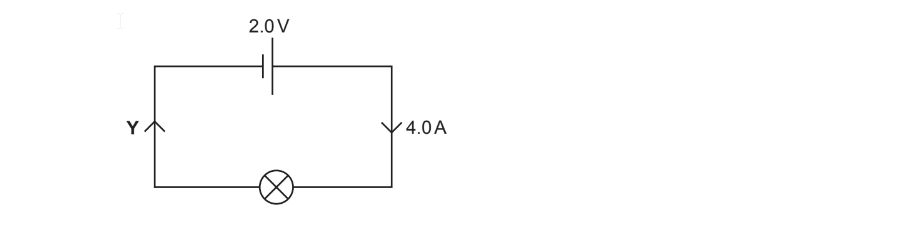
Write down the current flowing at point Y in the circuit.
Answer = .......................................................A [1]
Was this exam question helpful?



