Area of Standard Shapes (SQA National 5 Applications of Mathematics): Revision Note
Exam code: X844 75
Area of rectangles, triangles and circles
How do I find the area of a rectangle?
The formula for the area of a rectangle is
Multiply together the base and the height
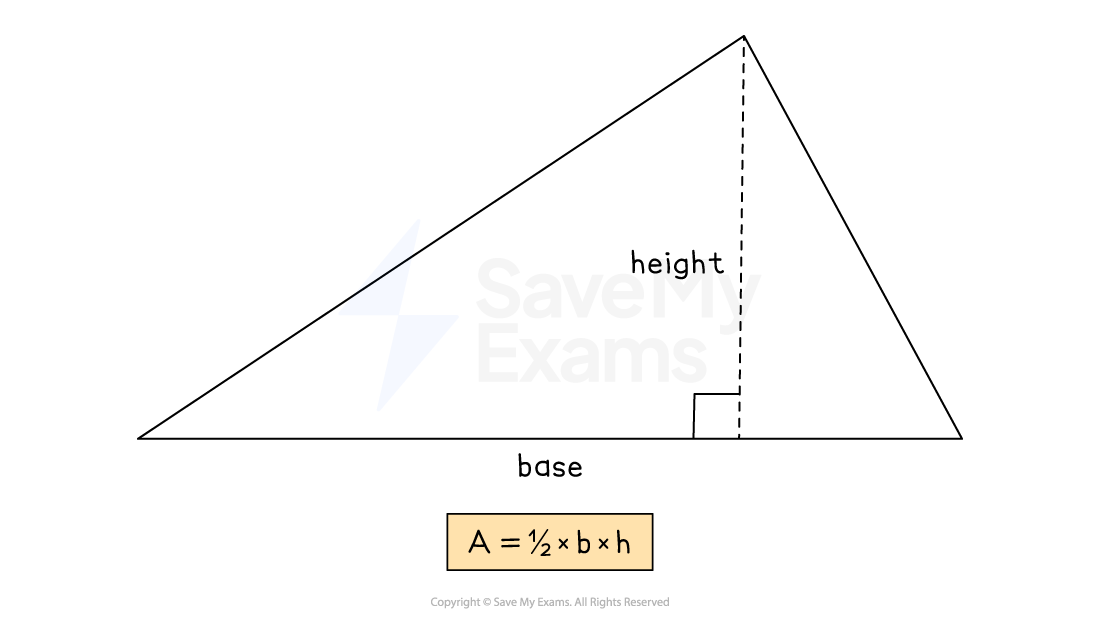
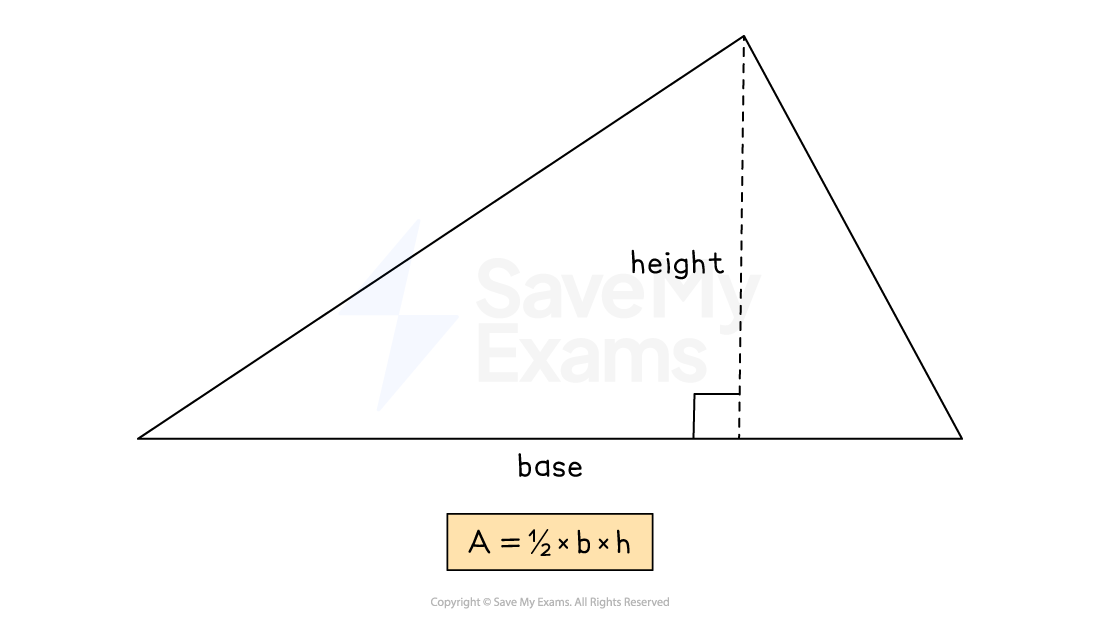
How do I find the area of a triangle?
The formula for the area of a triangle is
Multiply together the base and the perpendicular height
Halve the answer
The perpendicular height may not be the length of one of the sides of the triangle
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You might have to use Pythagoras' theorem to find the perpendicular height.
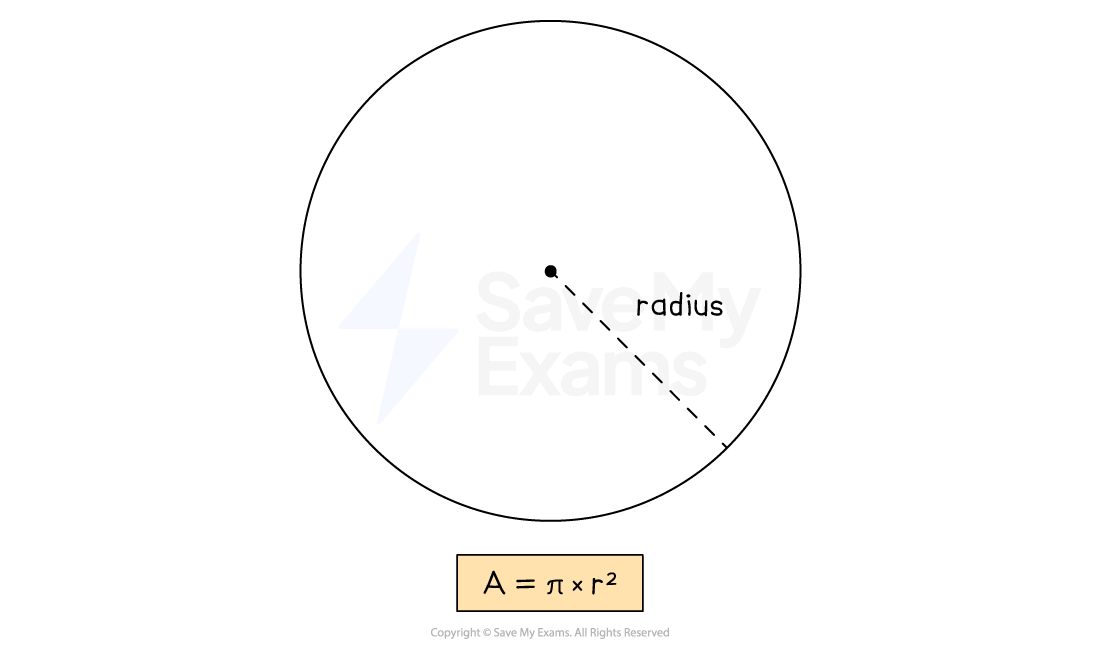
How do I find the area of a circle?
The formula for the area of a circle is
Identify the radius
This is half the length of the diameter
Square the radius
Multiply the radius squared by π
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are given this formula in the exam.
Worked Example
Chrissy is deciding between two shapes for her new logo. One is a circle with a diameter of 8 cm. The other is an isosceles triangle with dimensions as shown below.
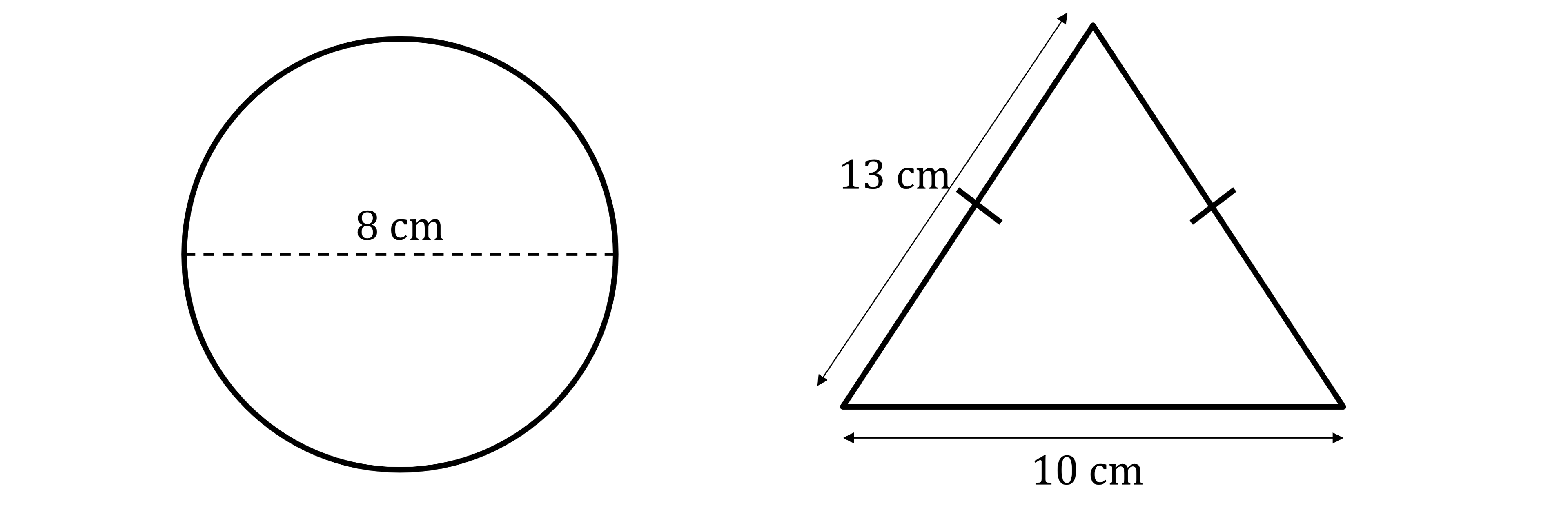
Chrissy wants to choose the shape with the greatest area. Which shape should Chrissy choose?
Answer:
Find the area of both shapes
Circle
Halve the diameter to find the radius
Use
Triangle
Use Pythagoras' theorem to find the perpendicular height
Halve the base
Subtract the squares as you are finding a shorter side
Use
Compare the areas and choose the shape with the greatest area
50.26... < 60
Triangle

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
