Area of Composite Shapes (SQA National 5 Applications of Mathematics): Revision Note
Exam code: X844 75
Area of composite shapes
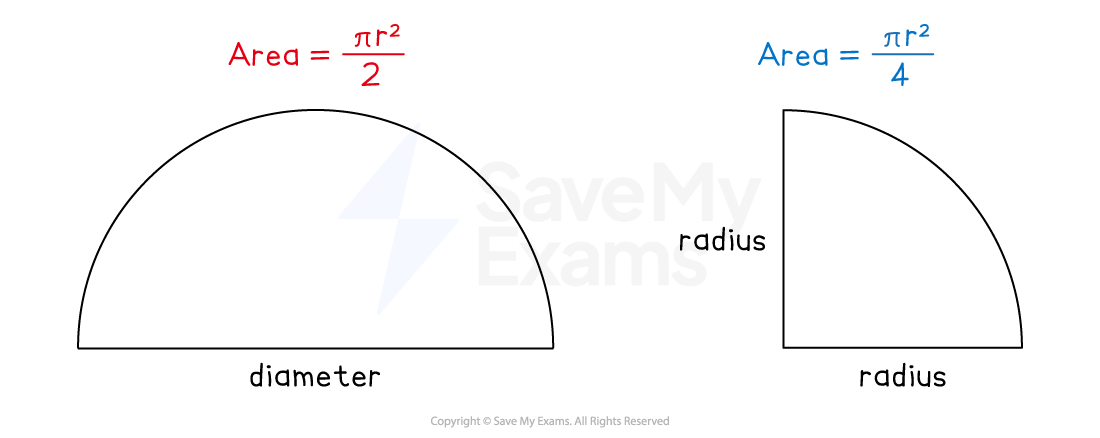
How do I find the area of parts of circles?
Identify the radius of the full circle
You might have to halve the diameter
Calculate the area of the full circle
Divide the area by:
2 if it is a semicircle
4 if it is a quarter circle
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You can put parts of circles together to make your calculation easier. For example, if the shape contains two equal semicircles, then you can just find the area of the full circle. This gives the same answer as halving it (to find the area of one semicircle) and then doubling it.
What is a composite shape?
Sometimes you will have a shape that is not a standard shape such as a rectangle, triangle or circle
These are called composite shapes
You can split the non-standard shape into standard shapes
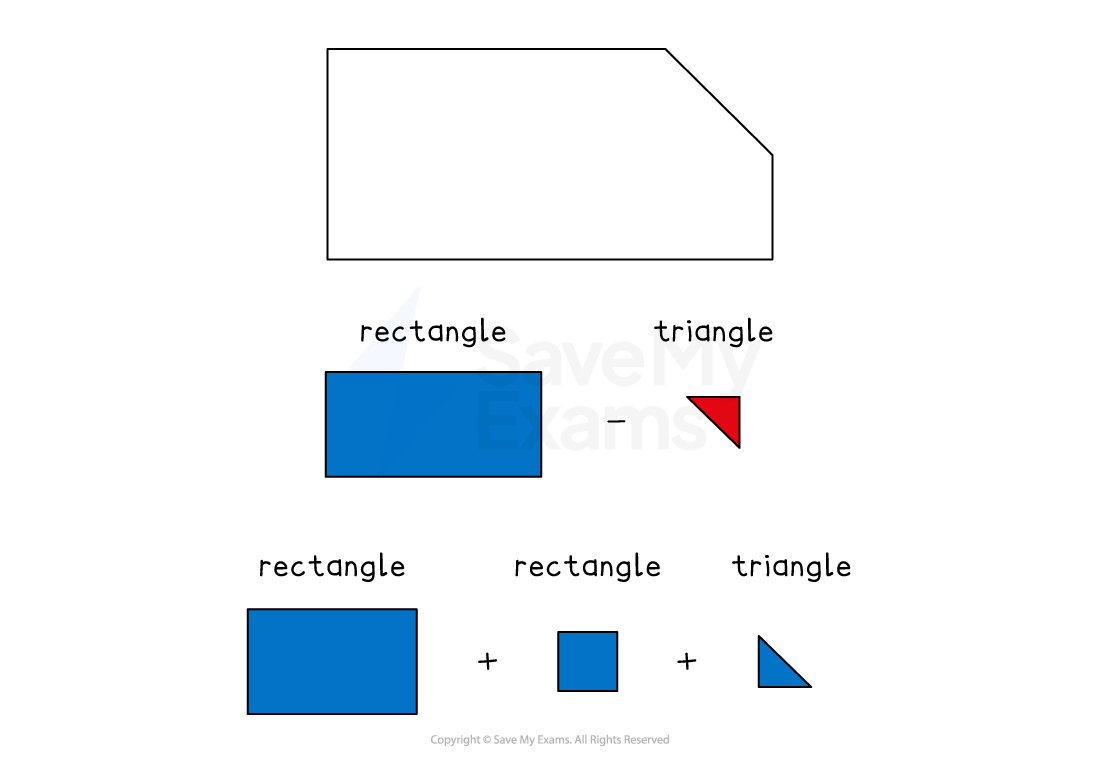
How do I find the area of a composite shape?
Split the composite shape into standard shapes
This might be
two or more shapes joined together
a shape removed from a bigger shape
Find the areas of the standard shapes
Add or subtract these
Add if a shape is joined to another shape
Subtract if a shape is removed from another shape
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Take a moment to think about how to split up the shape into the easiest shapes possible – there will probably be more than one way to do it!
Worked Example
Kia has a garden in the shape of semicircle. Kia forms an isosceles triangle using the diameter of the semicircle and a third point on the edge of the semicircle, as shown in the diagram below.
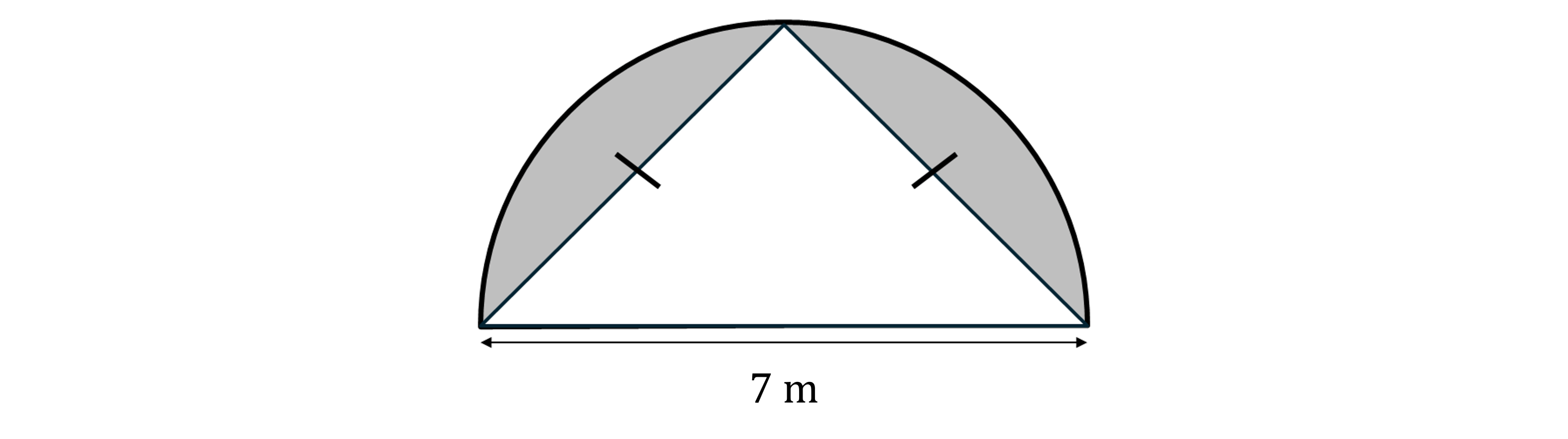
Kia fills the triangle with grass and fills the remaining space with stones.
Calculate the area of the space that is filled with stones.
Answer:
Find the area of the semicircle
Halve the diameter to find the radius
Use
to find the area of the full circle
Halve the area
Find the area of the triangle
The perpendicular height is just the radius of the circle
Use
Subtract the area of the triangle from the area of the semicircle
Include the units
6.99 m2

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
