Reading Scales (SQA National 5 Applications of Mathematics): Revision Note
Exam code: X844 75
Reading scales
How do I find the small divisions on a scale?
You will be given at least two values on a scale
The gap between them will be split into scale divisions
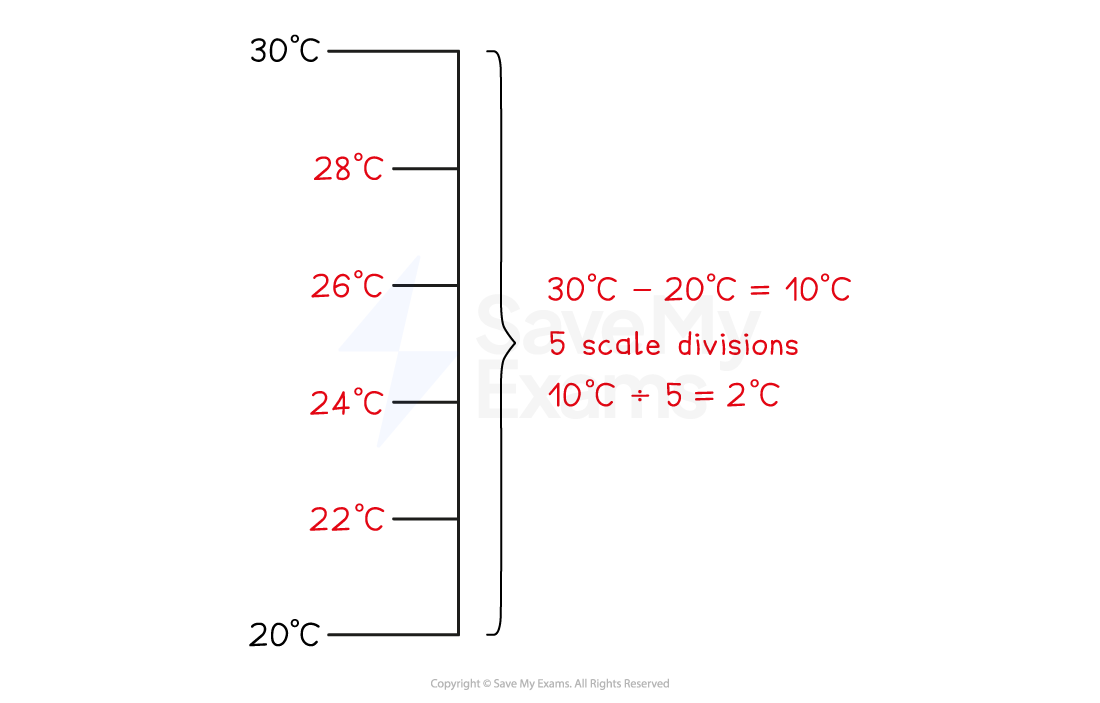
STEP 1
Find the difference between any pair of values on the scaleSTEP 2
Count the number of scale divisions between the pair of valuesUsually there are 5, 10 or 20 divisions
STEP 3
Divide the difference between the pair by the number of scale divisionsThis tells you how much each scale division is worth
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A scale might have multiple sets of scale divisions. For example, a scale might have:
major divisions going up in 20s
subdivisions going up in 5s
minor divisions going up in 1s
How do I read a scale?
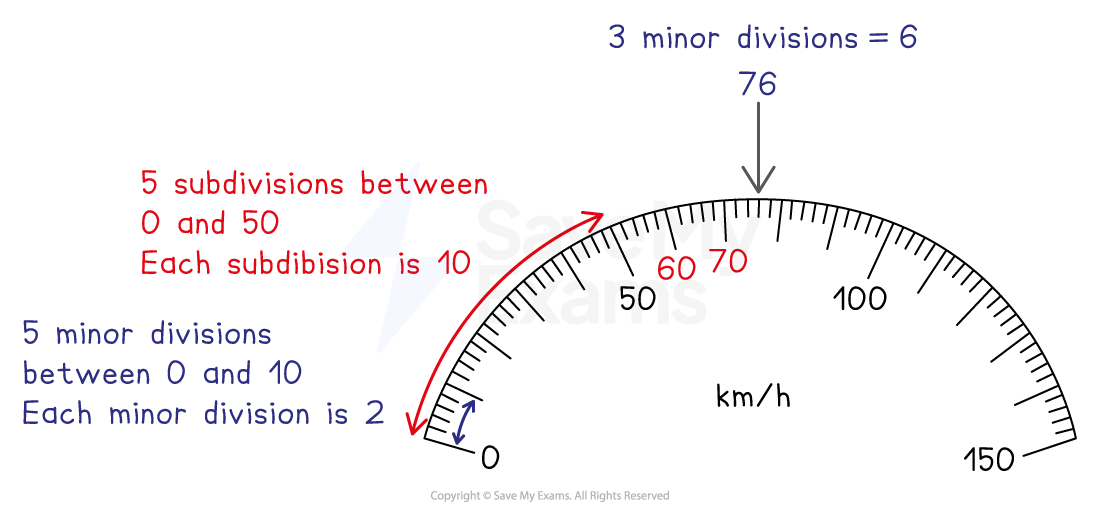
STEP 1
Find the value of each scale divisionSTEP 2
Identify the direction of the scaleUse the direction in which the numbers are increasing
STEP 3
Count the number of scale divisions from the last major divisionThere are normally major divisions at multiples of 10 or 20
STEP 4
Use the value of each scale division to find the value
How do I use measuring equipment with two units?
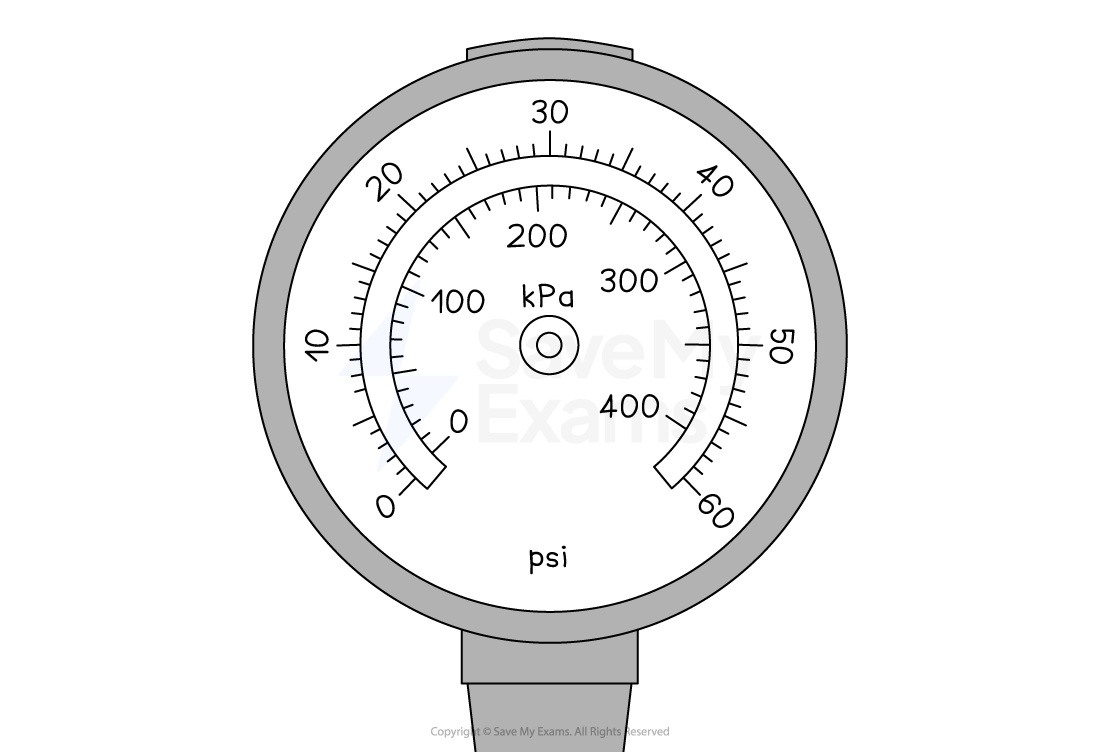
Some measuring tools include two different units
Examples include
thermometers which measure using degrees Celsius and degrees Fahrenheit
pressure gauges which measure using kPa and psi
speedometers which measure using mph and km/h
Treat each scale separately and find the values of their scale divisions
You can use these measuring devices to:
convert between units
compare two measurements using different units
Worked Example
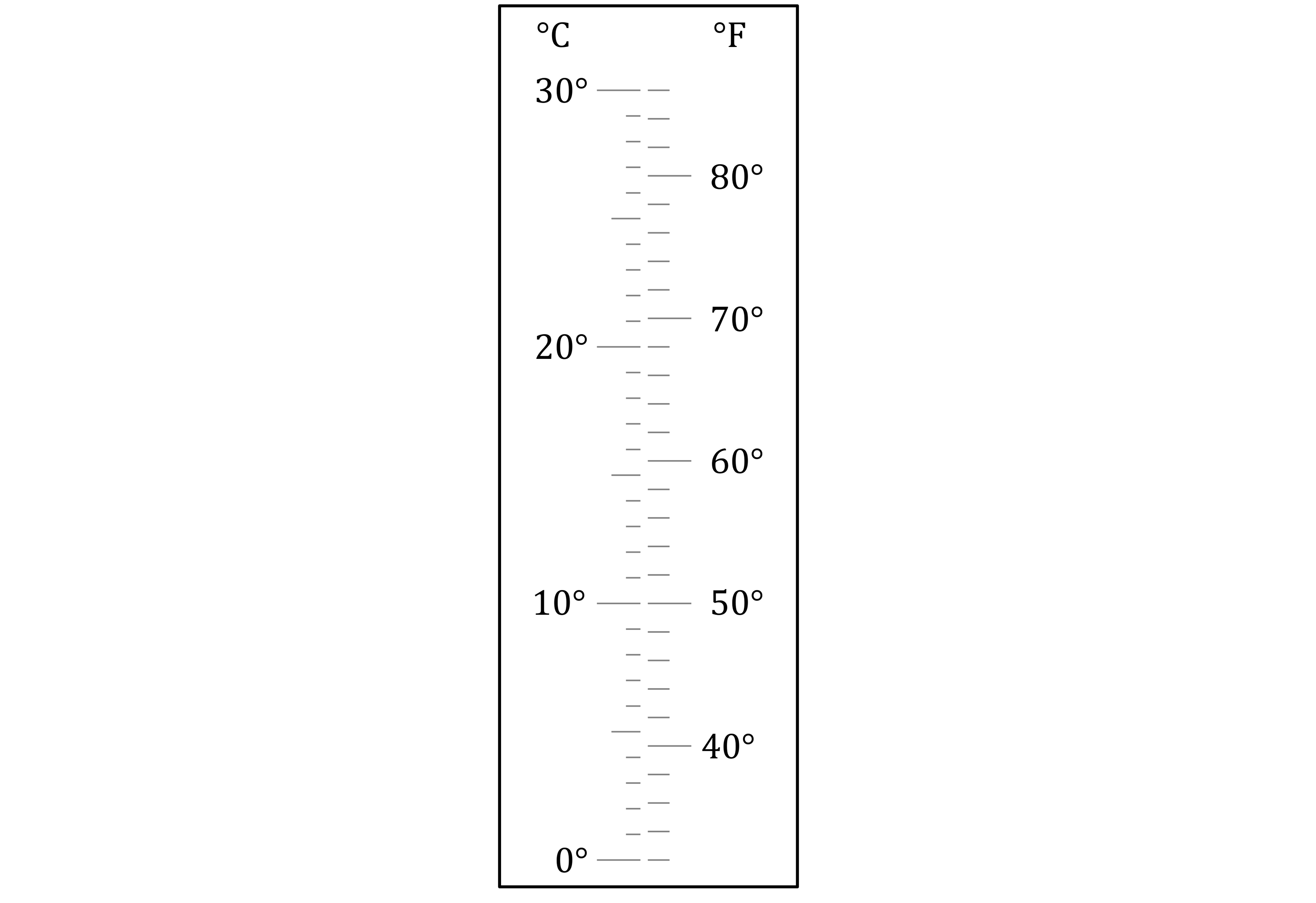
On Monday, the temperature was 18.5°C.
On Tuesday, the temperature was 64°F.
Use the thermometer to determine which day had the higher temperature.
Answer:
The °C scale
10 divisions between 0 and 10
Each division is 1°C
18.5°C is 3 and a half divisions above 15°C
It is between 18°C and 19°C
The °F scale
5 divisions between 40 and 50
Each division is 2°F
64°F is 2 divisions above 60°C
Label both temperatures on the scale
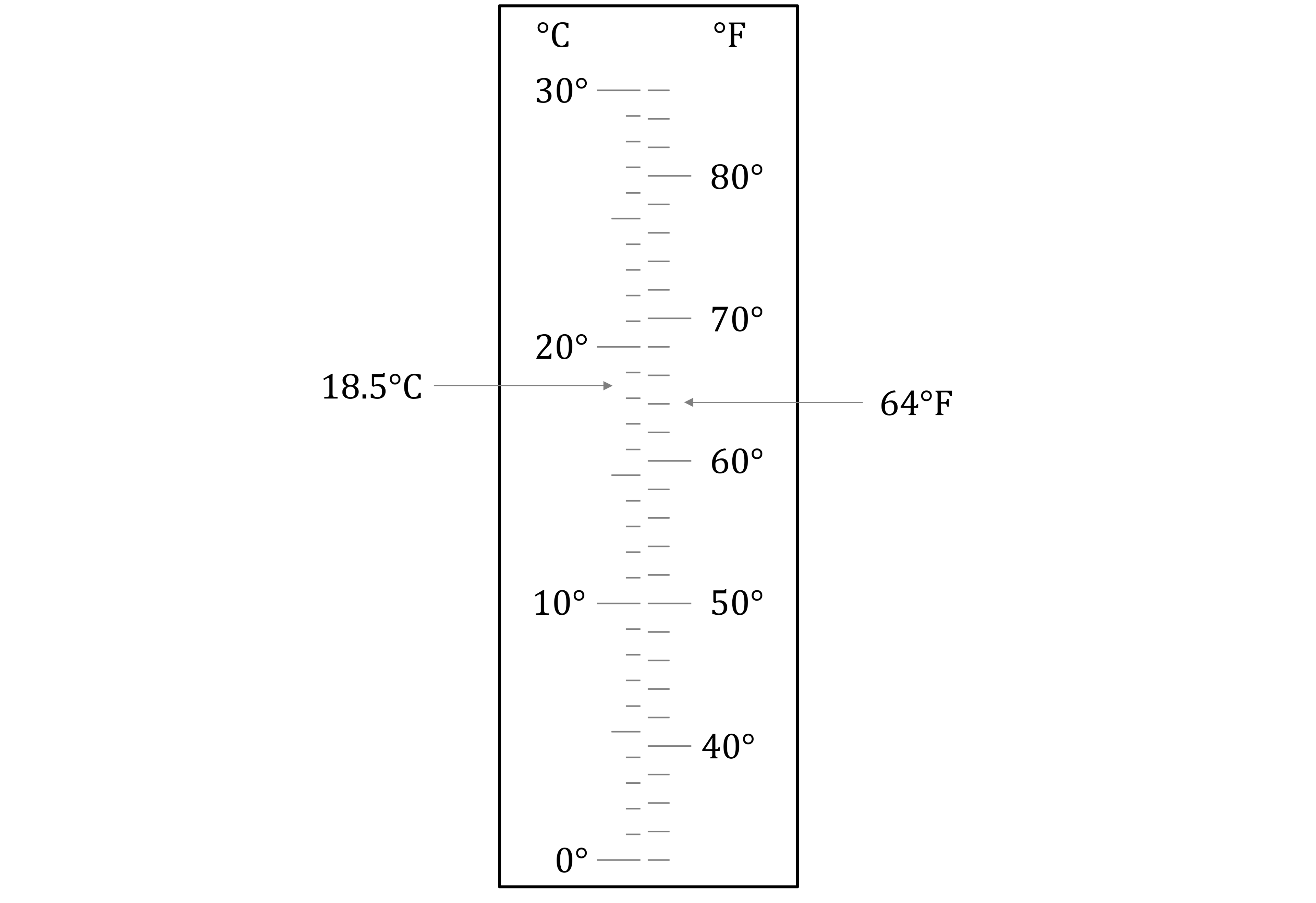
Monday had the higher temperature

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
