Measuring Acceleration (SQA National 5 Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: X857 75
Measuring acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity, or the change in velocity per unit time
The quantities required to determine the acceleration of a moving object are
the initial velocity
of the object
the final velocity
of the object
the time interval
between these velocities
The experimental methods for measuring acceleration are similar to those used for measuring speed
Apparatus for measuring acceleration:
Trolley
Ramp
Card with one or two sections attached to the trolley
Ruler
Stop clock
One or two light gates connected to a computer or electronic timers
Measuring acceleration with one light gate
Acceleration from rest
This method uses one light gate and a single card to measure acceleration
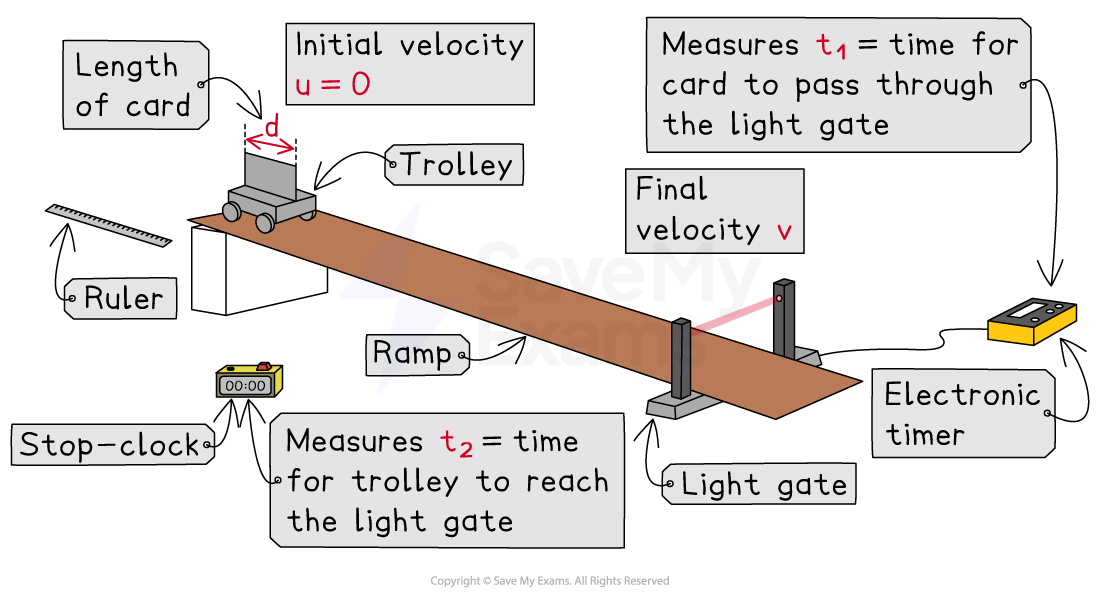
Method:
Set up the ramp with one light gate (attached to a computer or timer) at the bottom of the ramp
Measure the length of the card
using a ruler
Release the trolley from rest (initial velocity
) at the top of the ramp and start the stop clock
As the trolley passes the light gate, the timer records the time
the card blocks the light beam
Use the stop clock to measure the time
for the trolley to reach the light gate
Calculate the final velocity
using the equation:
Calculate the acceleration
of the trolley using the equation:
Acceleration at a point
This method uses one light gate and a double card (two sections separated by a gap) to measure acceleration at a single point
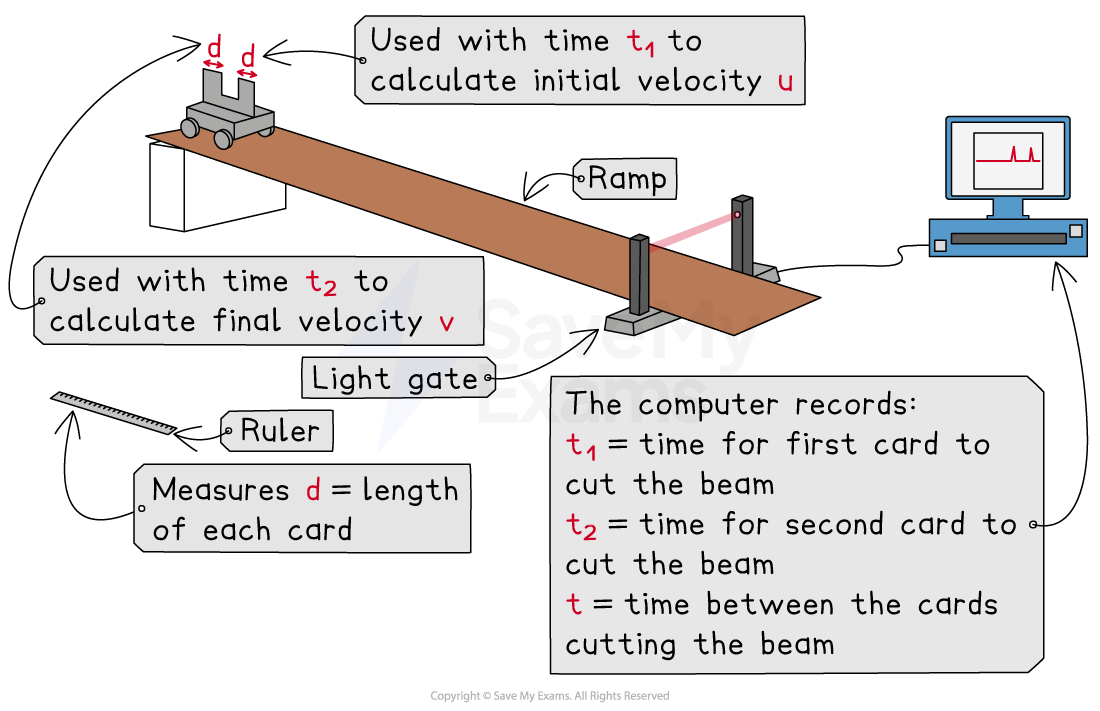
Method:
Set up the ramp with one light gate (attached to a computer) at any point
Measure the length
of each mask using a ruler (ideally, these should be the same length)
Release the trolley from rest at the top of the ramp
As the trolley passes the light gate, the computer records the time
that the first card blocks the light beam and the time
that the second card blocks the light beam
The computer also records the time
between each card passing through the light beam
Calculate the initial velocity
using the equation:
Calculate the final velocity
using the equation:
Calculate the acceleration
of the trolley at a point using the equation:
Measuring acceleration with two light gates
This method uses two light gates and a single card to measure the average acceleration between two points
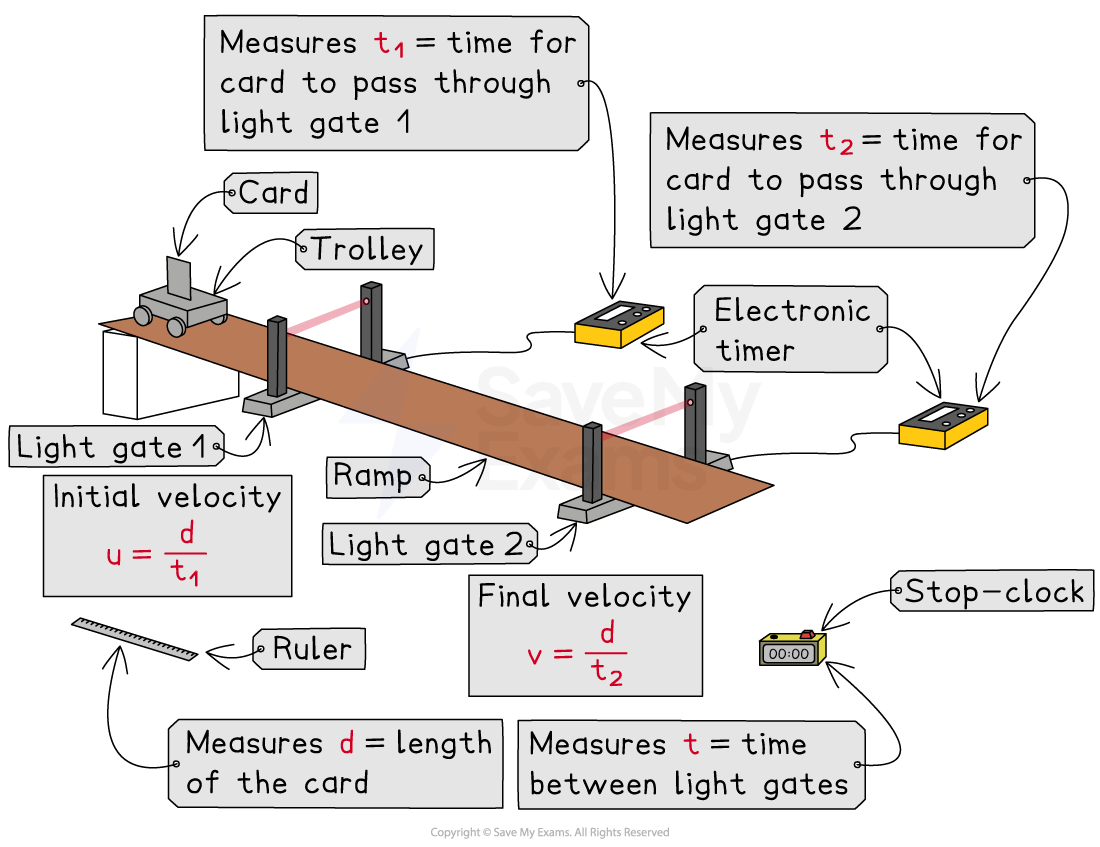
Method:
Set up the ramp with two light gates (attached to a computer or timers) at the bottom of the ramp
Measure the length of the card
using a ruler
Release the trolley from rest at the top of the ramp
As the trolley passes through light gate 1 and light gate 2, times
and
are recorded, respectively, as the card blocks the light beam
Use the stop clock to measure the time
for the trolley to pass between the light gates
Calculate the initial velocity
using the equation:
Calculate the final velocity
using the equation:
Calculate the average acceleration
of the trolley using the equation:
Evaluating the experiment
The main source of error in these experiments arises from human error in the measurements of
distance, when using a ruler
time, when using a stop clock
The experiments could be improved by
using an electronic timer instead of a stop clock to record the time
between the gates
releasing the trolley from the same point each time
taking repeat readings and averaging the results
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Exam questions about experimental procedures tend to focus on identifying required measurements for an investigation. For the measurement of acceleration, these are
the length of the card attached to the trolley
the time for the card to pass through the light gates (to calculate instantaneous speed)
the time between positions of initial and final velocities (this depends on the method used)

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
