Conservation of Energy (SQA National 5 Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: X857 75
Conservation of energy
The principle of conservation of energy states that:
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be converted from one form to another
This means the total amount of energy in a closed system remains constant
The total energy transferred in to a system must be equal to the total energy transferred out of the system

Therefore, energy is never 'lost', but it can be transferred to the surroundings
Energy can be dissipated (spread out) to the surroundings by heating and radiation
Dissipated energy transfers are often not useful and can then be described as wasted energy
Energy transfers
Energy is a property of an object that is stored or transferred
Energy must be transferred to an object to perform work on or heat up that object
Energy is measured in units of joules (J)
Applications of energy conservation
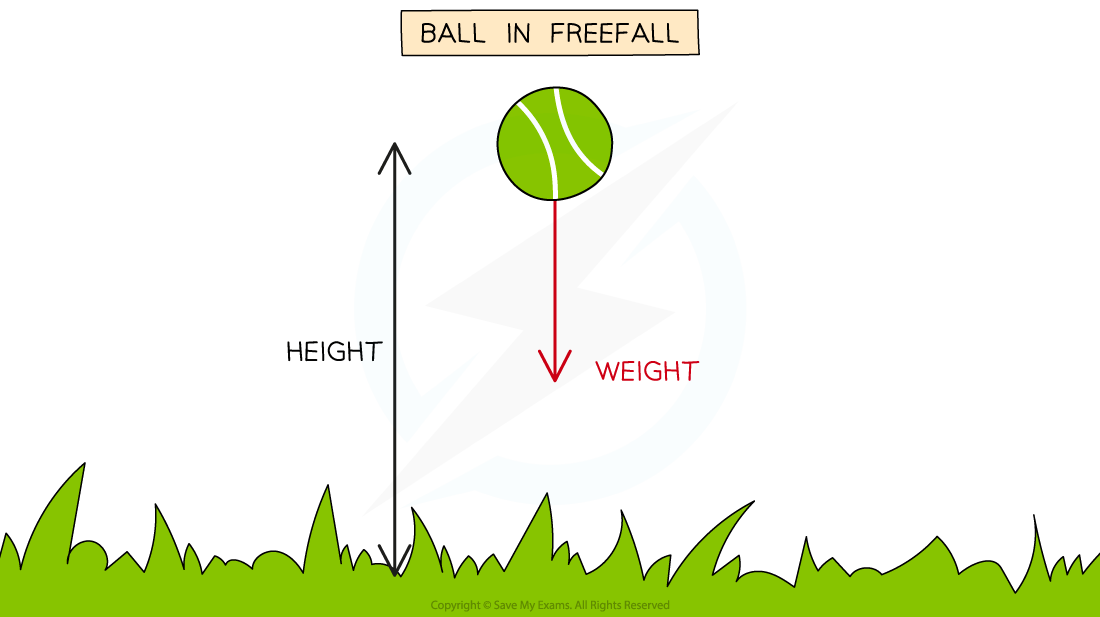
An example of an energy transfer between gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy is a ball dropped from a height
Before it is dropped, the ball has zero kinetic energy because it is stationary but has maximum gravitational potential energy
As it is dropped, the gravitational potential energy is converted into kinetic energy
As the ball loses gravitational potential energy, it gains kinetic energy
Assuming there are no energy losses to the surroundings, the gravitational potential energy lost, will be equal to the kinetic energy grained
Energy Transfer on a Ball
Energy losses to the surroundings include:
Heating by air resistance, or friction
Sound
Light
Worked Example
155 000 J of electrical energy is transferred to an iron to heat its soleplate to its maximum operating temperature of 240°C.
However, the soleplate only reaches 232°C.
Explain why the iron fails to heat its soleplate to 240°C.
Answer:
The electrical energy is the total energy transferred in to the iron
The principle of conservation of energy states that total energy in = total energy out
Not all the energy in is transferred to the soleplate
Some of the energy is transferred away from the iron by heating the surrounding air and the plastic casing of the iron
Therefore, the iron cannot reach its maximum operating temperature of 240°C

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
