Velocity–Time Graphs (SQA National 5 Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: X857 75
Velocity-time graphs
Speed-time graphs and velocity-time graphs are used to describe the motion of an object
Speed, or velocity, is always plotted on the vertical axis (y-axis) as it is the dependent variable
Time is always plotted on the horizontal axis (x-axis) as it is the independent variable
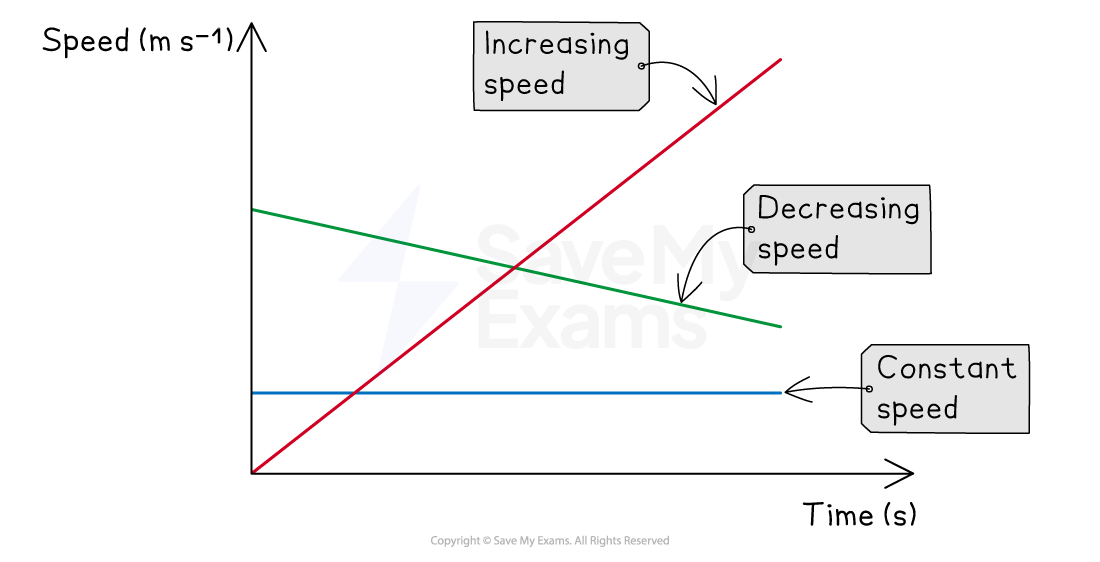
A speed-time graph shows how the speed of an object varies with time
Since speed is a scalar quantity, the values of speed will always be positive
Speed-time graph for different objects
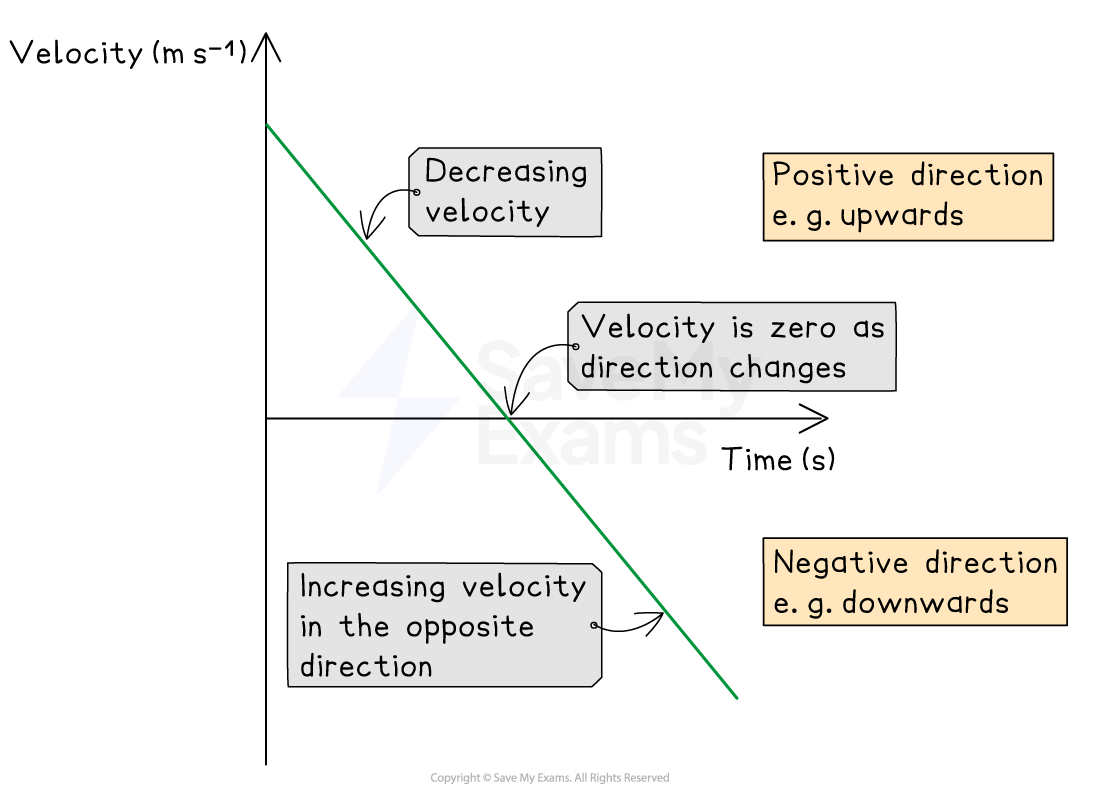
A velocity-time graph shows how the velocity of an object varies with time
This looks very similar to a speed-time graph, but since velocity is a vector quantity, the values of velocity may be positive or negative to indicate direction
Velocity-time graph for a ball thrown upwards
Interpreting velocity-time graphs
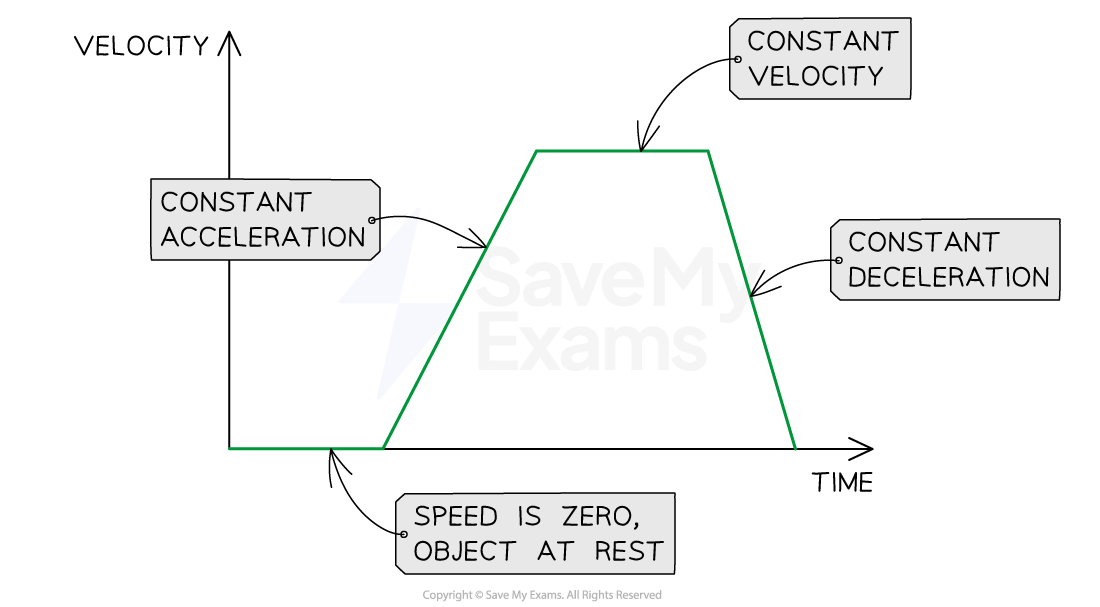
The slope of the line on a velocity-time graph represents the magnitude of acceleration
The steeper the slope, the larger the acceleration
The object's speed changes very quickly
The shallower the slope, the smaller the acceleration
The object's speed changes very gradually
A positive slope indicates increasing velocity
The object is accelerating
A negative slope indicates decreasing velocity
The object is decelerating
A horizontal (flat) line means the acceleration is zero
The object is moving with a constant velocity
Constant acceleration and constant velocity on a velocity-time graph

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
