Calculating Specific Latent Heat (SQA National 5 Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: X857 75
Calculating specific latent heat
Specific latent heat is defined as:
The amount of energy required to change the state of 1 kg of a substance with no change in temperature
The specific latent heat of a substance can be calculated using the following relationship:
Where:
= heat energy required for a change in state, in joules (J)
= mass, in kilograms (kg)
= specific latent heat, in joules per kilogram (J kg-1)
This relationship can be rearranged with the help of a triangle
See Motion Equations for instructions on how to use a relationship triangle
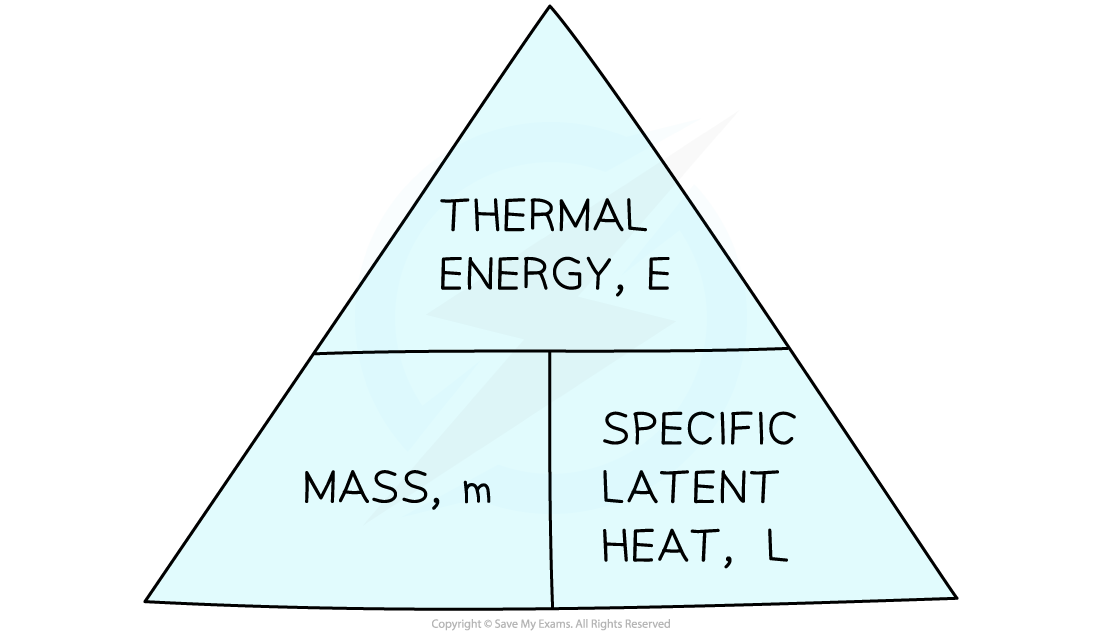
The same relationship is used for both the specific latent heat of fusion and the specific latent heat of vaporisation
However, the numerical values of
are very different, so be sure to use the correct values from the data sheet in calculations
For example, the values of latent heat for water are:
Specific latent heat of fusion =
Specific latent heat of vaporisation =
Therefore, evaporating 1 kg of water requires roughly seven times more energy than melting the same amount of ice to form water
Worked Example
Water ice melts and freezes at its melting point.
Specific latent heat of fusion of water =
Specific latent heat of vaporisation of
(i) Calculate the minimum amount of energy required to melt 1.3 kg of water ice at its melting point.
(ii) State the amount of heat energy given out as 1.3 kg of water freezes into ice at its melting point.
Answer (i):
Step 1: Write down the relevant relationship
Step 2: Substitute in the known values to calculate
Melting ice is changing state from a solid to a liquid
Therefore, the value for specific latent heat of fusion is used
Step 3: Round to an appropriate number of significant figures
The least precise data point is 2 s.f. (1.3 kg)
Therefore, the answer must be given to the same precision
Answer (ii):
If
of heat energy is required to melt 1.3 kg of ice into liquid water, then the same amount of heat energy is given out when 1.3 kg of liquid water freezes into ice at its melting point
Therefore,
is given out
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Both the relationship and the latent heat values will be provided to you in the exam. You do not need to remember any of the specific values.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
