The Big Bang Theory (SQA National 5 Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: X857 75
The Big Bang theory
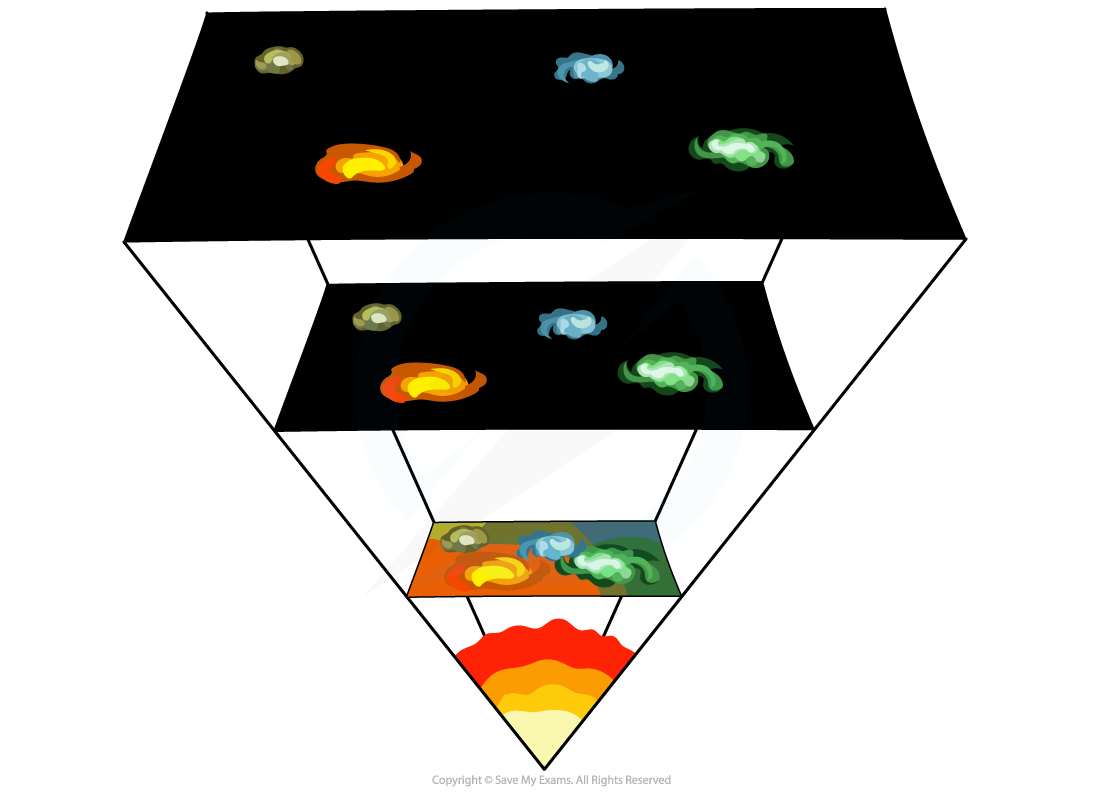
Scientists describe the origin of the universe using the Big Bang theory
The universe began from a single point that was extremely hot and dense
A giant explosion, known as the Big Bang, caused the universe to expand outwards
As each point moved away from the others, the universe began to cool
As a result of the initial explosion, the universe continues to expand
The Big Bang origin of the universe
The age of the universe
The current estimate for the age of the universe is 13.8 billion years old
This is based on data collected by modern space probes and telescopes studying the motion of galaxies
Evidence for the Big Bang theory
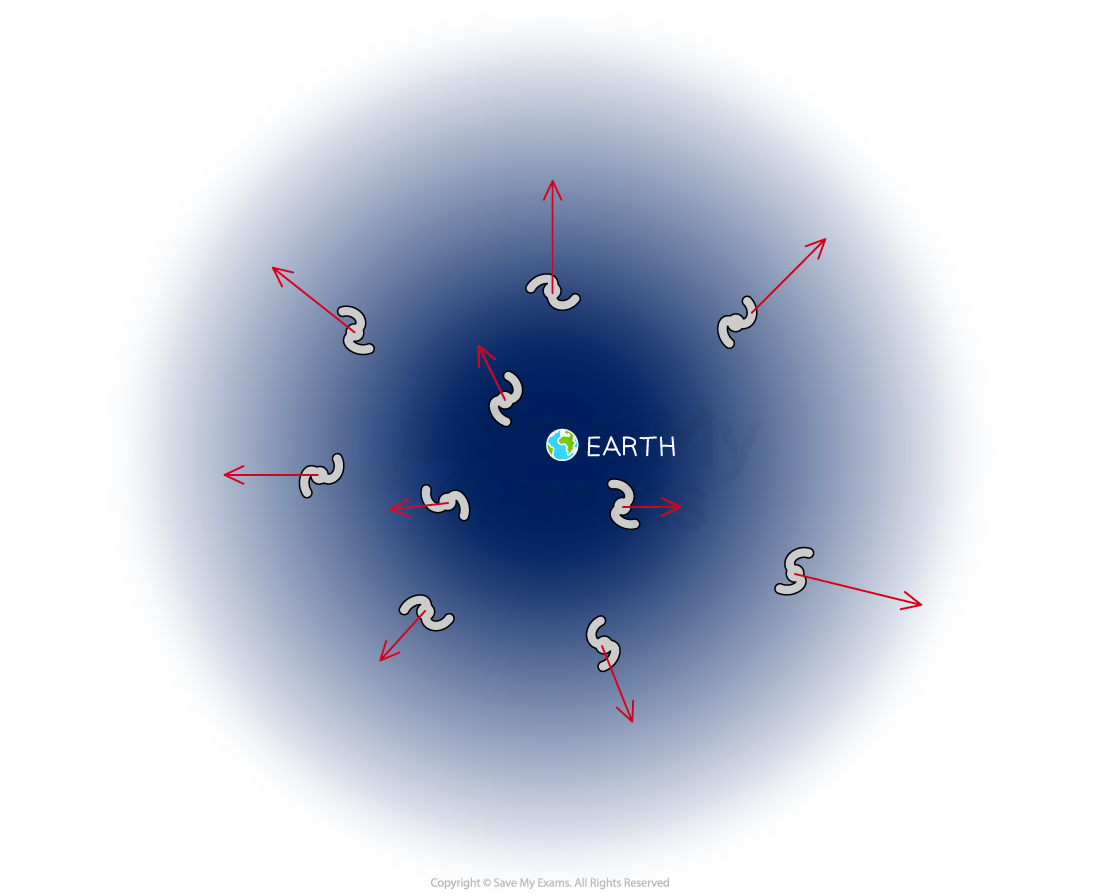
Galactic redshift indicates that distant galaxies are moving away from us
If galaxies are moving away from us, this means the Universe must be expanding
Expansion of the universe
Redshift provides evidence for the Big Bang because:
Observations show that distant galaxies are all moving away from us
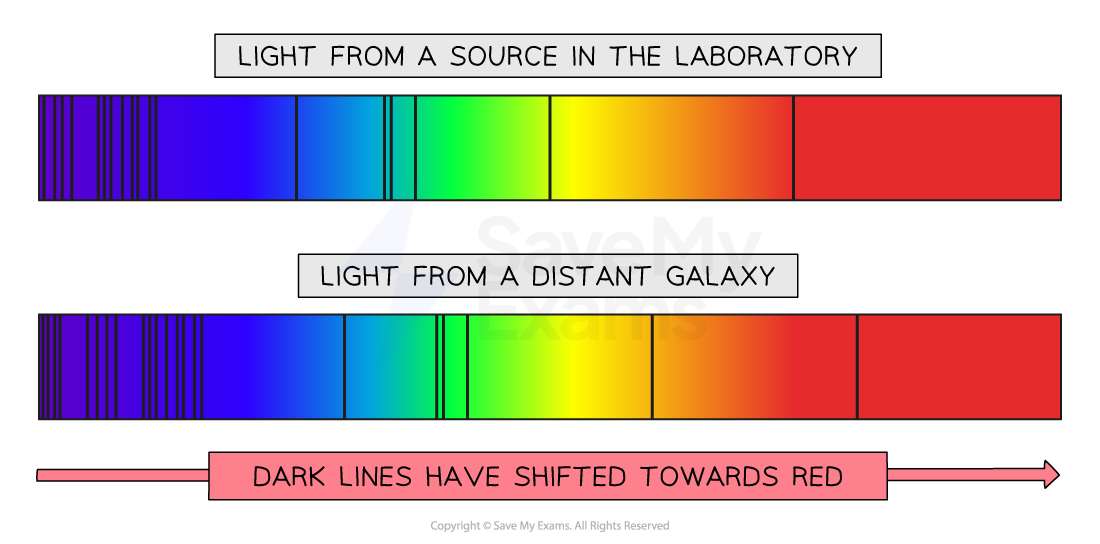
We see that light from glowing hydrogen in stars from distant galaxies is redshifted in comparison with light from glowing hydrogen on Earth
Observations show that the further away a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away from us
The spectra of light from more distant galaxies are more redshifted than closer galaxies due to the expansion of space itself
Galactic redshift spectra
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure that you understand that the stretching of the wavelength of light is due to the expansion of the universe, not the motion of stars and galaxies themselves.
This can be visualised by imagining a balloon with equally spaced points on it. The balloon represents space, and the points represent galaxies.

When the balloon is deflated (i.e. the universe was smaller), the points (galaxies) are closer together and are at an equal distance apart.
As the balloon (universe) expands, all the points (galaxies) become further apart by the same amount.
This is because the space between the galaxies itself has expanded.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
