EM spectrum in Cosmology (SQA National 5 Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: X857 75
EM spectrum in cosmology
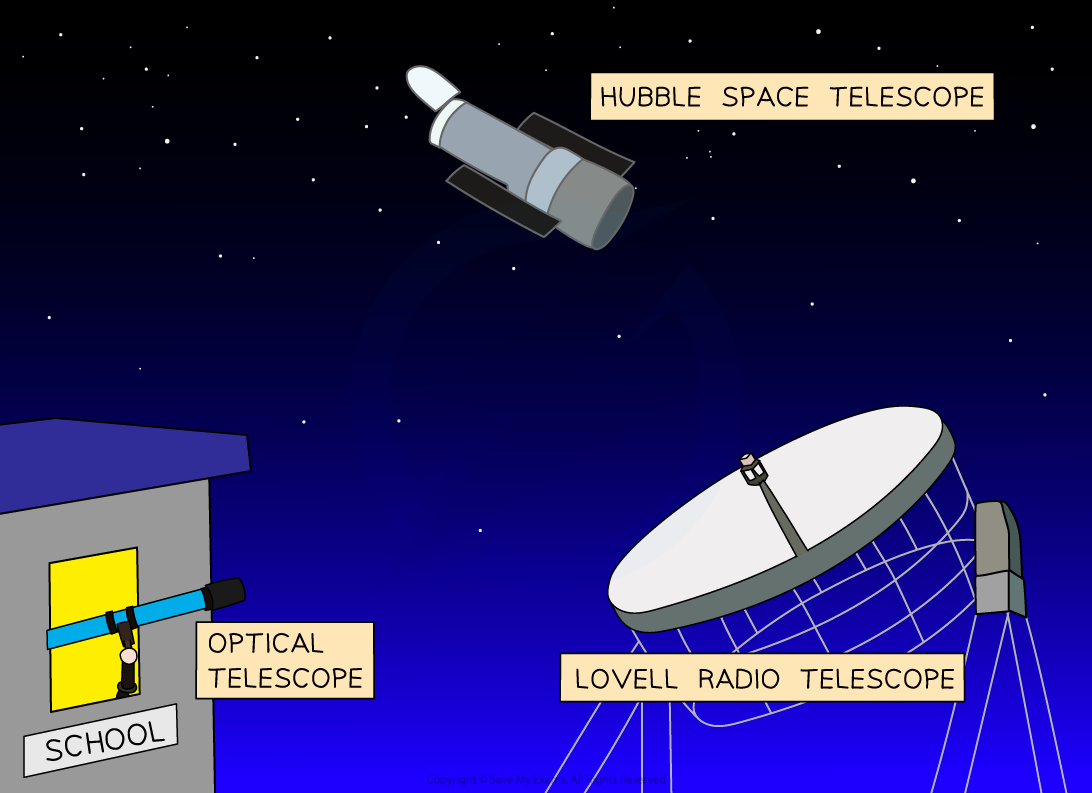
Astronomers use telescopes to obtain information about astronomical objects
Optical telescopes detect wavelengths of light from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum
Telescopes that look at other parts of the electromagnetic spectrum are known as non-optical telescopes, including
radio telescopes
infrared (IR) telescopes
ultraviolet (UV) telescopes
X-ray telescopes
Different types of telescopes
Being able to collect radiation from all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum opens up a whole world of new information for astronomers
For example, different areas of an astronomical object known as the Crab Nebula are found to emit strongly at all wavelengths
In particular, radio waves, X-rays and gamma rays all appear to originate from its centre, whilst the infrared, visible and ultraviolet wavelengths appear to come from the gas and dust that surrounds it
Note: images of astronomical objects are often given 'false colour' to help us visualise wavelengths the human eye cannot see
Observing the Crab Nebula at different wavelengths

Ground-based telescopes
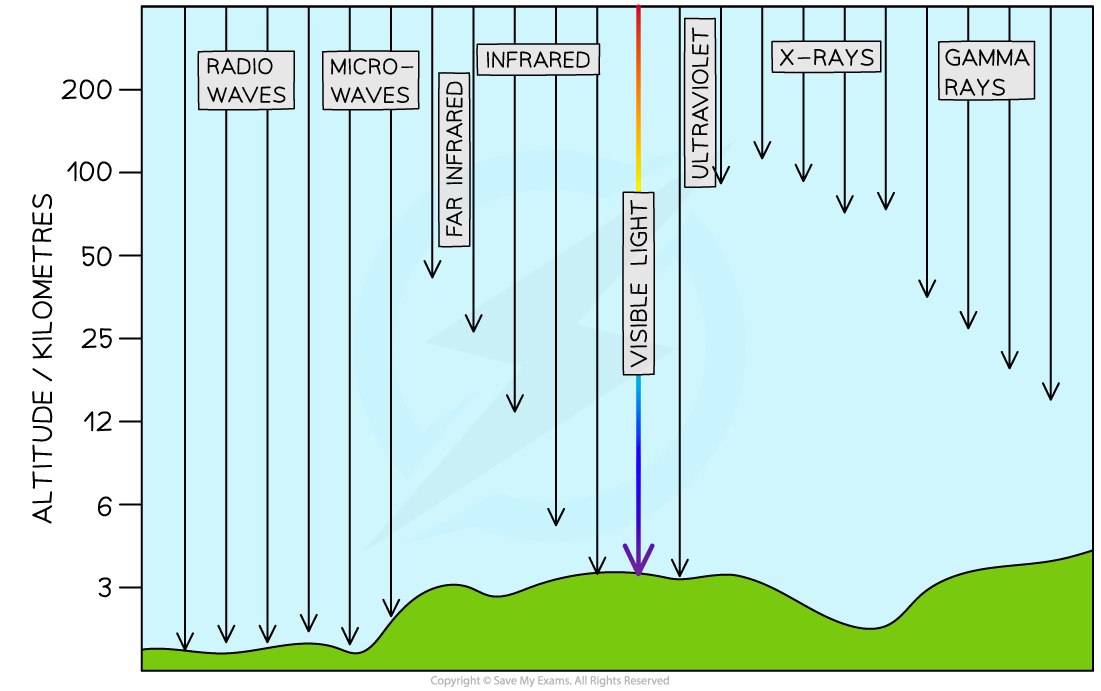
The atmosphere can have a significant impact on the quality of astronomical observations made using ground-based telescopes
The reflection of light from moisture in the atmosphere can cause light pollution
Air currents can cause atmospheric distortion (this is what makes stars appear to 'twinkle')
The atmosphere absorbs certain wavelengths of electromagnetic waves
This means that not all electromagnetic radiation coming from space reaches the Earth’s surface
As a result, ground-based telescopes are able to observe:
all visible wavelengths (although there is often some distortion)
very narrow ranges of infrared wavelengths
most microwave & radio wavelengths
Absorption of wavelengths by the atmosphere
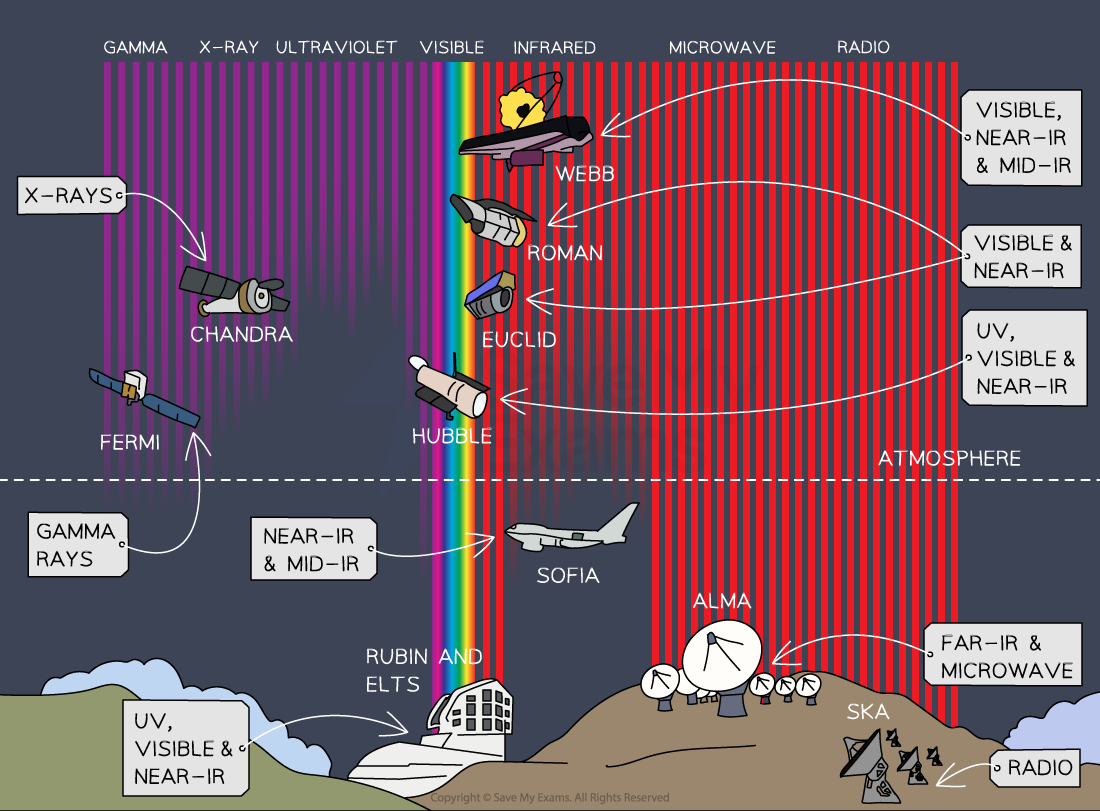
Space-based telescopes
Above the atmosphere, space-based telescopes can detect all wavelengths, making it possible to clearly observe:
gamma rays, X-rays & ultraviolet rays
all infrared wavelengths
Some benefits of space-based telescopes are:
They lead to the discovery of objects not detectable by visible light
More information and data can be collected
Different EM waves can give different types of information about astronomical objects
They can produce much more detailed and magnified images
They produce clearer images, which are unaffected by distortion from the atmosphere and light pollution
Some downsides of space-based telescopes are:
They are much harder to repair
They cannot be made too large since they need to fit into a rocket to be launched
They are much more expensive
Ground & space-based telescopes

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
