Satellite Orbits (SQA National 5 Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: X857 75
Satellite orbits
Artificial satellites are man-made satellites
Uses of satellites include:
GPS
communications
weather forecasting
scientific discovery
Artificial satellites can be put into a
low Earth orbit (LEO) - up to 2000 km
medium Earth orbit (MEO) - between 2000 km and 36 000 km
high Earth orbit (HEO) - up to 36 000 km
geostationary orbit - 36 000 km
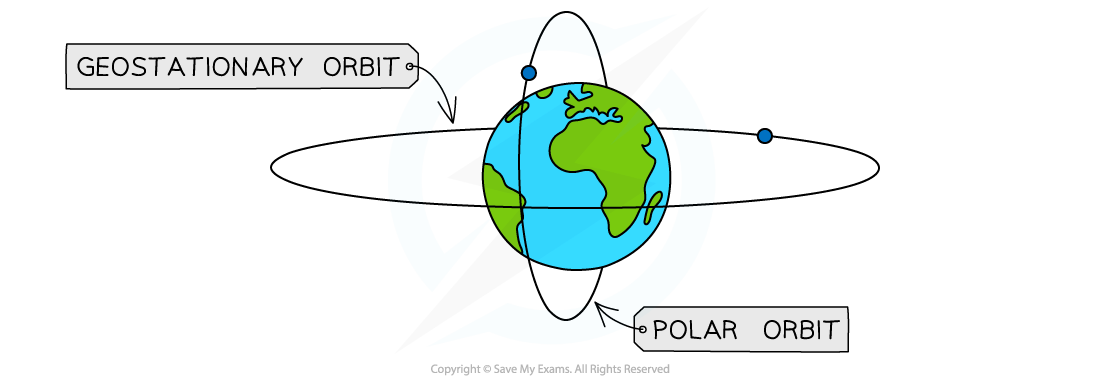
Orbital paths of satellites around the Earth
Geostationary satellites
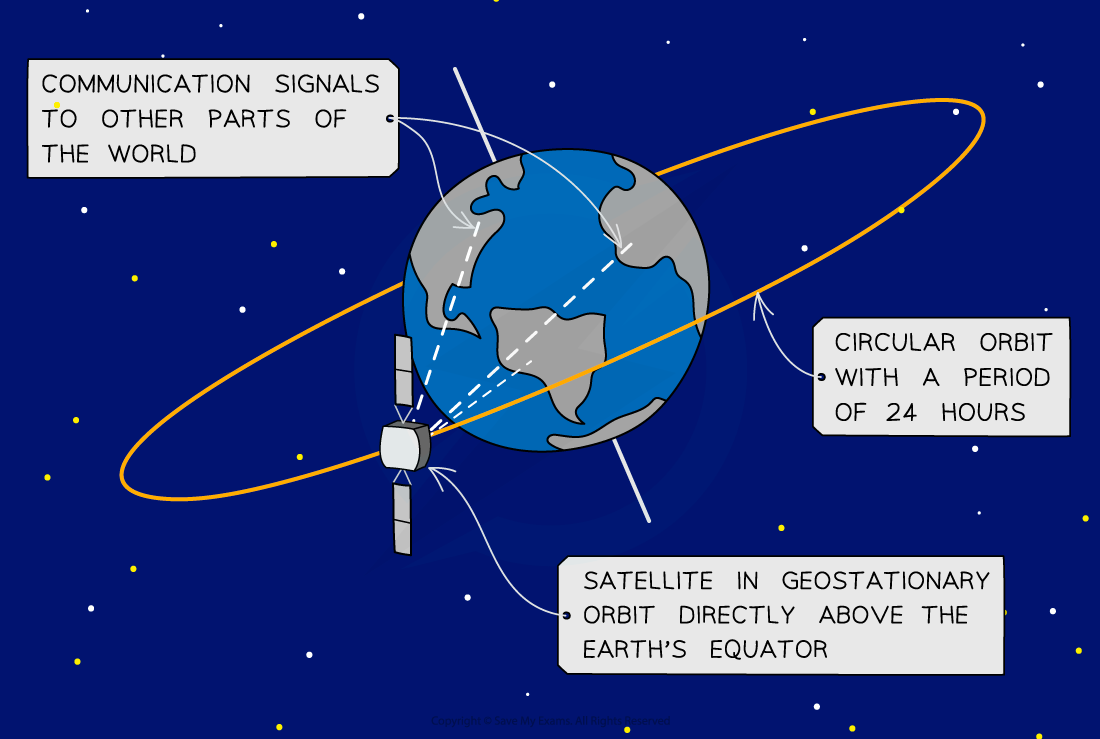
Geostationary satellites orbit above the Earth’s equator
They have an orbital period of 24 hours
They orbit at an altitude of 36 000 km above the Earth’s surface
Used for
radio and TV broadcasting
weather forecasting
Geostationary orbit
Low Earth orbits
Some satellites are in low orbits, which means they orbit closer to the Earth's surface
One example of this is a polar orbit, where the satellite orbits around the north and south poles of the Earth
Low orbits are useful for taking high-quality photographs of the Earth's surface. This could be used for:
weather monitoring
military applications
Low polar orbit

Orbital period of satellites
The orbital period of a satellite depends on its distance from Earth
The closer a satellite is to Earth, the shorter the time it will take to complete each orbit
The period of a satellite in a high altitude orbit is greater than the period of a satellite in a lower altitude orbit
Worked Example
The table shows the orbital heights for three satellites, X, Y, and Z.
Satellite | Orbital height (km) |
|---|---|
X | 4000 |
Y | 20 000 |
Z | 36 000 |
Which row in the table shows possible periods for the orbits of satellites X, Y, and Z?
Period of orbit of satellite X (hours) | Period of orbit of satellite Y (hours) | Period of orbit of satellite Z (hours) | |
|---|---|---|---|
A | 3 | 12 | 24 |
B | 24 | 18 | 12 |
C | 24 | 24 | 24 |
D | 48 | 36 | 24 |
E | 3 | 6 | 12 |
Answer: A
Step 1: Identify the geostationary satellite
Satellite Z is a geostationary satellite as it has an orbital height of 36 000 km
All geostationary satellites have an orbital period of 24 hours to stay fixed over one point on Earth
Therefore, the period of Z must be 24 hours
This eliminates options B and E
Step 2: Use the relationship between orbital height and period to deduce the correct option
Satellites in higher altitude orbits have longer periods than satellites in lower altitude orbits, so
the period of Y must be shorter than the period of Z
the period of X must be shorter than the period of Y
The only option that shows this is A as 3 h < 12 h < 24 h
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure to memorise the key features of a geostationary orbit, since this is a common exam question. Remember:
Orbits above the equator
Altitude of 36 000 km
Period of 24 hours

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
