The Universe (SQA National 5 Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: X857 75
The universe
The universe is everything that exists - all matter, energy, space, and time
It contains billions of galaxies, each with billions of stars, many of which have their own planets and moons
Astronomical terms
Planet
An object that orbits a star, but does not emit its own light
Dwarf planet
An object that orbits a star and is similar to a planet, but is not large enough to clear its orbital path of debris
Moon
A natural satellite that orbits a planet or a dwarf planet
Sun
The star at the centre of our solar system
Asteroid
A small, rocky, irregularly shaped object that orbits the Sun
Solar system
A star and the objects that orbit it
Star
A large ball of hot gas that is undergoing nuclear fusion and emits heat and light as a result
Exoplanet
A planet outside the solar system
Galaxy
A large collection of stars
Universe
A large collection of galaxies separated by empty space
Our place in the universe
The Milky Way is one of many billions of galaxies making up the universe
The Sun is one of many billions of stars making up the Milky Way
Other stars in the Milky Way galaxy are much further away from Earth than the Sun is
Some of these stars also have planets which orbit them, known as exoplanets
Hierarchy of the universe
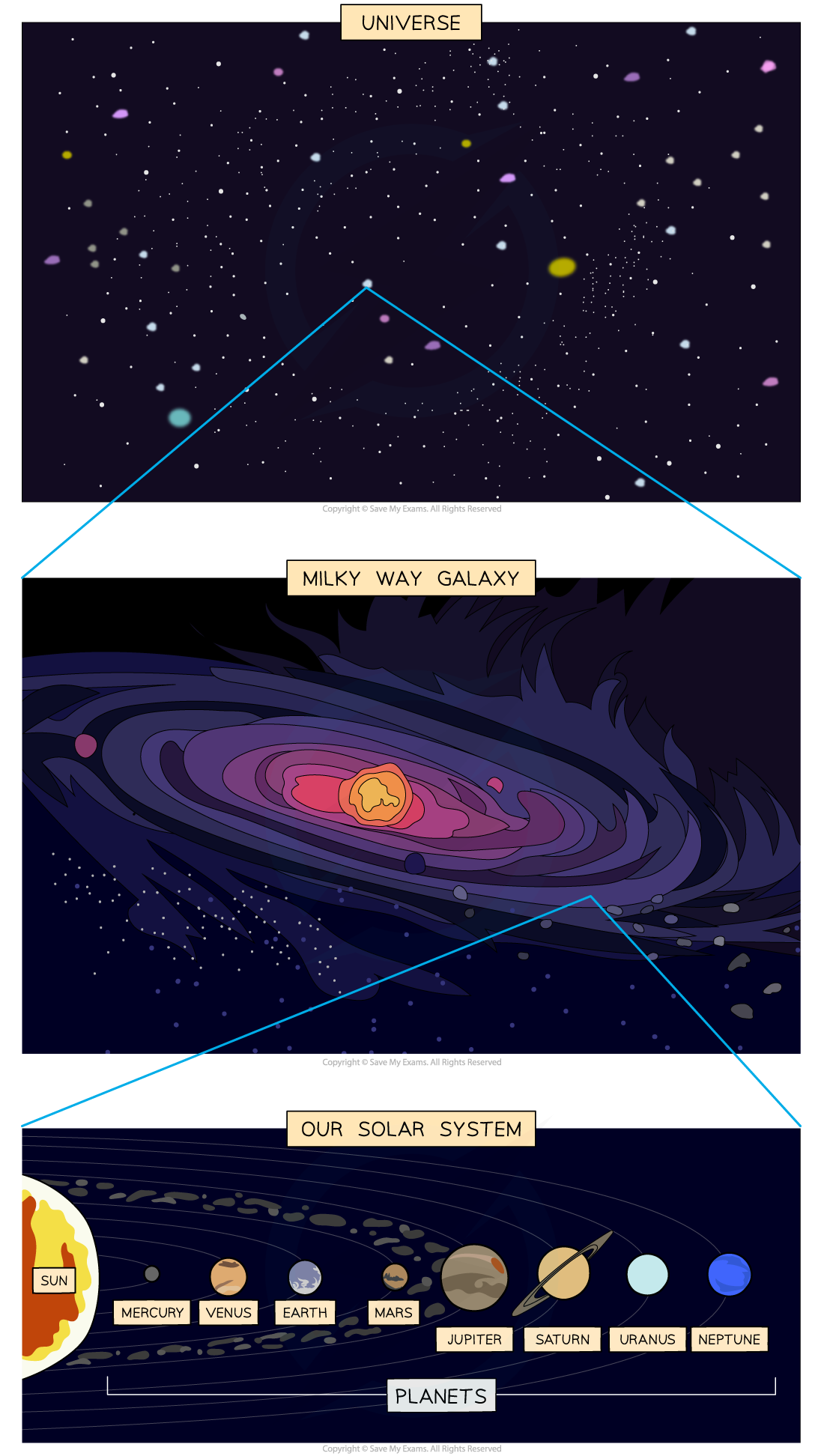
The Solar System
The Solar System consists of:
the Sun
A star which lies at the centre of the solar system and contains 99% of the total mass
eight planets
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
natural and artificial satellites
Natural satellites are objects that orbit planets, e.g. the Moon
Artificial satellites are man-made and can orbit any object in space, e.g. the International Space Station (ISS)
dwarf planets
The gravitational field around a dwarf planet is not strong enough to pull in nearby objects, unlike a planet
asteroids and comets
Both are small objects which orbit the Sun
Asteroids are made of rock and metal and are typically found in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter
Comets are made of dust and ice and typically have highly elliptical orbits
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You need to know the order of the 8 planets in the Solar System. The following mnemonic gives the first letter of each of the planets to help you recall them:
My Very Excellent Mother Just Served Us Noodles
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
