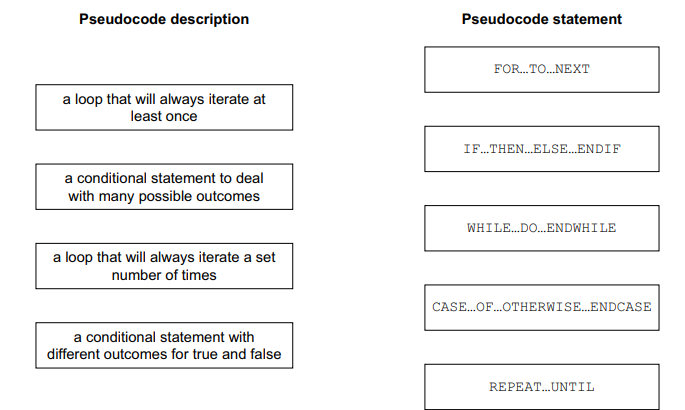
Four pseudocode descriptions and five pseudocode statements are shown.
Draw a line to link each pseudocode description to the most appropriate pseudocode statement.
Some pseudocode statements will not be used
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: 2210
Four pseudocode descriptions and five pseudocode statements are shown.
Draw a line to link each pseudocode description to the most appropriate pseudocode statement.
Some pseudocode statements will not be used

How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Tick (✓) one box to show the named section of a program that performs a specific task.
file
function
parameter
process
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A function is declared using pseudocode.
FUNCTION ConvertToCm(Inches: REAL) RETURNS REAL RETURN Inches * 2.4 ENDFUNCTION
Tick (✓) one box which accurately describes the use of the variable Inches
answer
call
parameter
response
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A database table, 2018MOV, is used to keep a record of movie details

Complete the table to identify the most appropriate data type for each field based on the data shown in the database table, 2018MOV.
Field | Data type |
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
|
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
The variables X, Y and Z are used to store data in a program:
X stores a string
Y stores a position in the string (e.g. 2)
Z stores the number of characters in the string.
Write pseudocode statements to declare the variables X, Y and Z.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Four programming concepts and four descriptions are shown.
Draw one line to connect each programming concept to the most appropriate description

How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Tick (✓) one box in each row to identify the most appropriate data type for each description. Only one tick (✓) per column.
Description | Data type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Boolean | Char | Integer | Real | String | |
a single character from the keyboard | |||||
multiplecharacters from the keyboard | |||||
only one of two possible values | |||||
only whole numbers | |||||
any number | |||||
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
An algorithm has been written in pseudocode to calculate a check digit for a four-digit number. The algorithm then outputs the five-digit number including the check digit. The algorithm stops when –1 is input as the fourth digit.
01 Flag FALSE 02 REPEAT 03 Total 0 04 FOR Counter 1 TO 4 05 OUTPUT "Enter a digit ", Counter 06 INPUT Number[Counter] 07 Total Total + Number * Counter 08 IF Number[Counter] = 0 09 THEN 10 Flag TRUE 11 ENDIF 12 NEXT Counter 13 IF NOT Flag 14 THEN 15 Number[5] MOD(Total, 10) 16 FOR Counter 0 TO 5 17 OUTPUT Number[Counter] 18 NEXT 19 ENDIF 20 UNTIL Flag
Give the line number(s) for the statements showing:
Totalling ...........................................................................
Count-controlled loop .......................................................
Post-condition loop ............................................................
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
The variables P and Q are used to store data in a program. P stores a string. Q stores a character.
Write pseudocode statements to declare the variables P and Q, store "The world" in P and store 'W' in Q
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Describe the difference between a local variable and a global variable.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A function LENGTH(X) finds the length of a string X and a function SUBSTRING(X,Y,Z) finds a substring of X starting at position Y and Z characters long. The first character in the string is position 1.
Write a pseudocode statement to extract the word Computer from P and store it in the variable F.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Explain the difference between a WHILE … DO … ENDWHILE and a REPEAT … UNTIL loop
B ← FALSE INPUT Num FOR Counter ← 1 TO 12 IF A[Counter] = Num THEN B ← TRUE ENDIF NEXT Counter
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Explain the purpose of the library routines DIV and ROUND.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
State two features that should be included to create a maintainable program.
Give a reason why each feature should be used.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
The function LENGTH(Phrase) calculates the length of a string Phrase
The string "The beginning is the most important part" is stored in Phrase
State the output of the pseudocode statements:
OUTPUT LENGTH(Phrase)
OUTPUT UCASE(Phrase)
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
The variables P and Q are used to store data in a program. P stores a string. Q stores a character.
Write a pseudocode algorithm to:
convert P to upper case
find the position of Q in the string P (the first character in this string is in position 1)
store the position of Q in the variable Position
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Using a single loop, write an algorithm in pseudocode to output 50 names that have been stored in the array, Name[]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
The function LENGTH(Phrase) calculates the length of a string Phrase
Write the pseudocode statements to:
store the string "The beginning is the most important part" in Phrase.
calculate and output the length of the string
output the string in upper case.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A program needs to make sure the value input for a measurement meets the following rules:
the value is a positive number
a value is always input
the value is less than 1000.
The program needs editing to include a double entry check for the value input.
The input value needs to be stored in the variable Measurement Write pseudocode to perform the double entry check until a successful input is made.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
An algorithm has been written in pseudocode to calculate a check digit for a four-digit number. The algorithm then outputs the five-digit number including the check digit. The algorithm stops when –1 is input as the fourth digit.
01 Flag FALSE 02 REPEAT 03 Total 0 04 FOR Counter 1 TO 4 05 OUTPUT "Enter a digit ", Counter 06 INPUT Number[Counter] 07 Total Total + Number * Counter 08 IF Number[Counter] = 0 09 THEN 10 Flag TRUE 11 ENDIF 12 NEXT Counter 13 IF NOT Flag 14 THEN 15 Number[5] MOD(Total, 10) 16 FOR Counter 0 TO 5 17 OUTPUT Number[Counter] 18 NEXT 19 ENDIF 20 UNTIL Flag
The algorithm does not check that each input is a single digit.
Identify the place in the algorithm where this check should occur.
Write pseudocode for this check. Your pseudocode must make sure that the input is a single digit and checks for –1
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?