Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2018
Last exams 2026
Wage Determination (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Economics): Revision Note
Exam code: 2281
Factors That Influence The Demand for Labour
The labour market is composed of sellers of labour (households) and buyers of labour (firms)
Workers supply their labour and firms demand labour
The demand for labour is a derived demand
This means that it depends on the demand for goods/services
If demand for goods/services increases then the demand for labour will increase - and vice versa
Factors That Influence the Demand for Labour
The price of the product being produced | The demand for the final product |
|---|---|
|
|
The ability to substitute capital (machinery) for labour | The productivity of labour |
|
|
Factors Influencing the Supply of Labour
There are numerous factors that influence the amount of labour supplied to a particular industry
Factors Influencing the Supply of Labour
Training period | Wages in other occupations | Changes in migration policy |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Income tax levels | Working conditions | Trade union power |
|
|
|
Level of welfare benefits | Social trends |
|
|
|
|
Diagrammatic Analysis of the Labour Market
The labour market is a type of factor market
Factor markets follow exactly the same rules as product markets
They are affected by changes to price, demand and supply
They are affected by the price elasticity of demand and supply.
Labour market equilibrium occurs where the demand for labour (DL) is equal to the supply of labour (SL)
The DL is the demand by firms for workers - firms demand more labour as the wage rate decreases which results in a downward sloping demand curve
The SL is the supply of labour by workers - workers supply more labour as the wage rate increases which results in an upward sloping supply curve
Individual firms are price takers in the labour market as they have to accept the wage rate that workers are being paid in the industry
If they offer a lower wage, they will likely struggle to recruit workers
If they offer a higher wage there will be a large number of workers applying to work there

Diagram analysis
The market for graphic designers is in equilibrium where DL = SL
The equilibrium wage is W and the quantity of labour is Q
There is no excess supply of labour
There is no excess demand for labour
Analysing the PED and PES of Labour
Price inelastic demand and supply
Consider the labour market for NBA basketball players
In 2022, LeBron James received a salary of $45m
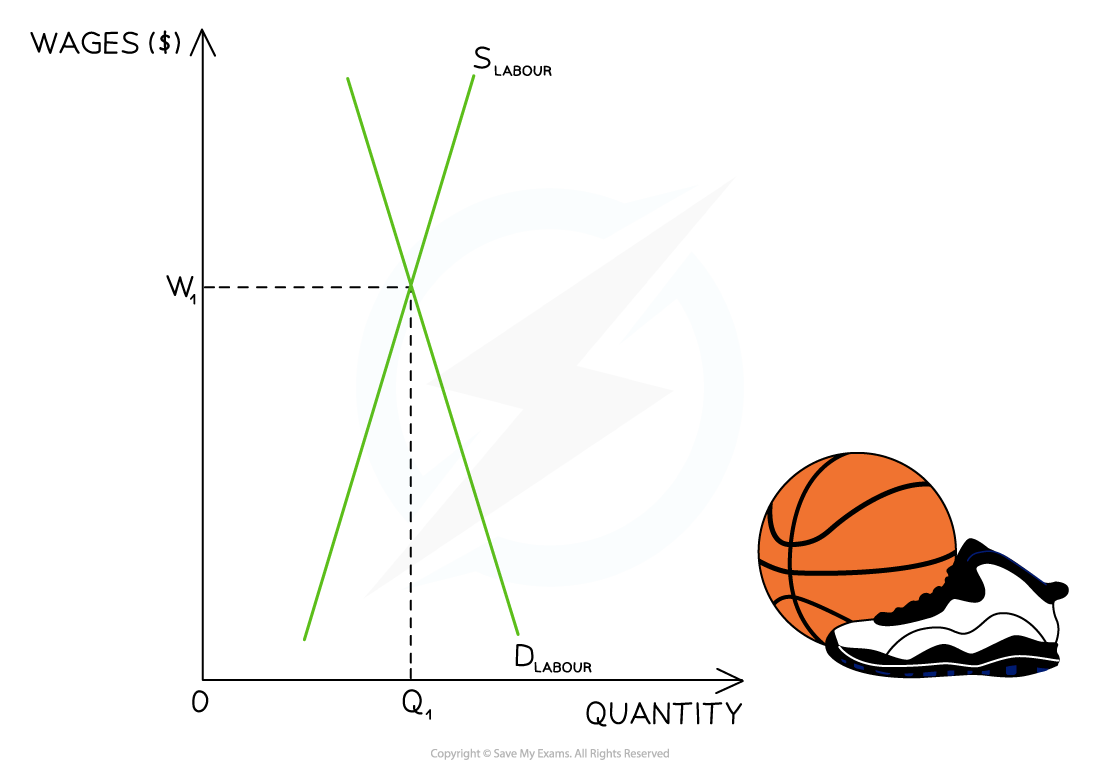
Diagram analysis
DL is the demand for labour from the basketball clubs
SL is the supply of labour by the basketball players
The demand for highly skilled players is very price inelastic
Clubs want the very best players, almost irrespective of what they cost
The supply of highly skilled players is also very price inelastic
A significant increase in price will have little impact on the quantity of labour supplied in the market as it takes years to develop LeBron James type skills
The market equilibrium is found at W1Q1 - a high price and relatively low quantity
Price elastic demand and supply
Consider the labour market for labourers on a building site

Diagram analysis
DL is the demand for labour from the building company for labourers
SL is the supply of labour by people willing to work on a building site
The demand for workers is very price elastic
If wages dropped a little, then firms would respond quickly by employing more workers
The supply of workers is also very price elastic
Due to it being an unskilled job, there would quickly be an increase in the supply of labour if wages were to increase
The market equilibrium is found at W1Q1 - a low price and relatively high quantity
Relative Bargaining Power
Workers have different degrees of bargaining power when it comes to negotiating wage increases with their employers
The following factors influence their bargaining power
Membership of a trade union: trade unions represent the interests of the workers in negotiations with employers and members frequently enjoy higher wages than non-union members
Age and experience: young, inexperienced workers have less bargaining power then older, more experienced workers. As workers grow older their age often begins to count against them and this reduces bargaining power
Level of education: education provides higher levels of skill and specialisation to a worker. This increases their bargaining power relative to unskilled workers
Current supply conditions: the supply of labour in many industries can change due to socio-political conditions e.g prior to Brexit, workers in the hotel industry had very little bargaining power. Brexit created a shortage of labour willing to work in hotels and so the bargaining power of workers has increased, resulting in higher wages in the industry
Government Policy: Minimum Wages
Government's often intervene in the labour market by setting a minimum wage
They do this in order to improve equity and avoid the exploitation of worker
A minimum wage is a legally imposed wage level that employers must pay their workers
It is set above the market rate
The minimum wage/hour often varies based on age

Diagram analysis
The market equilibrium wage and quantity for truck drivers in the UK is seen at WeQe
The government imposes a national minimum wage (NMW) at W1
Incentivised by higher wages, the supply of labour increases from Qe to Qs
Facing higher production costs, the demand for labour by firms decreases from Qe to Qd
This means that at a wage rate of W1 there is excess supply of labour and the potential for unemployment equal to QdQs
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When evaluating national minimum wages, do not assume that they will automatically increase unemployment.
Many studies have shown that unemployment does not increase - and in some instances employment increases. This is likely due to the fact that workers are receiving higher wages and choose to consume more. This increases total demand in the economy which in turn increases the demand for labour by firms - thus reducing/eliminating any potential unemployment.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
