Properties of Ellipses (Edexcel A Level Further Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 9FM0
Written by: Mark Curtis
Updated on
Properties of ellipses
What is an ellipse?
An ellipse is a stretched circle
is its horizontal half length
is its vertical half length
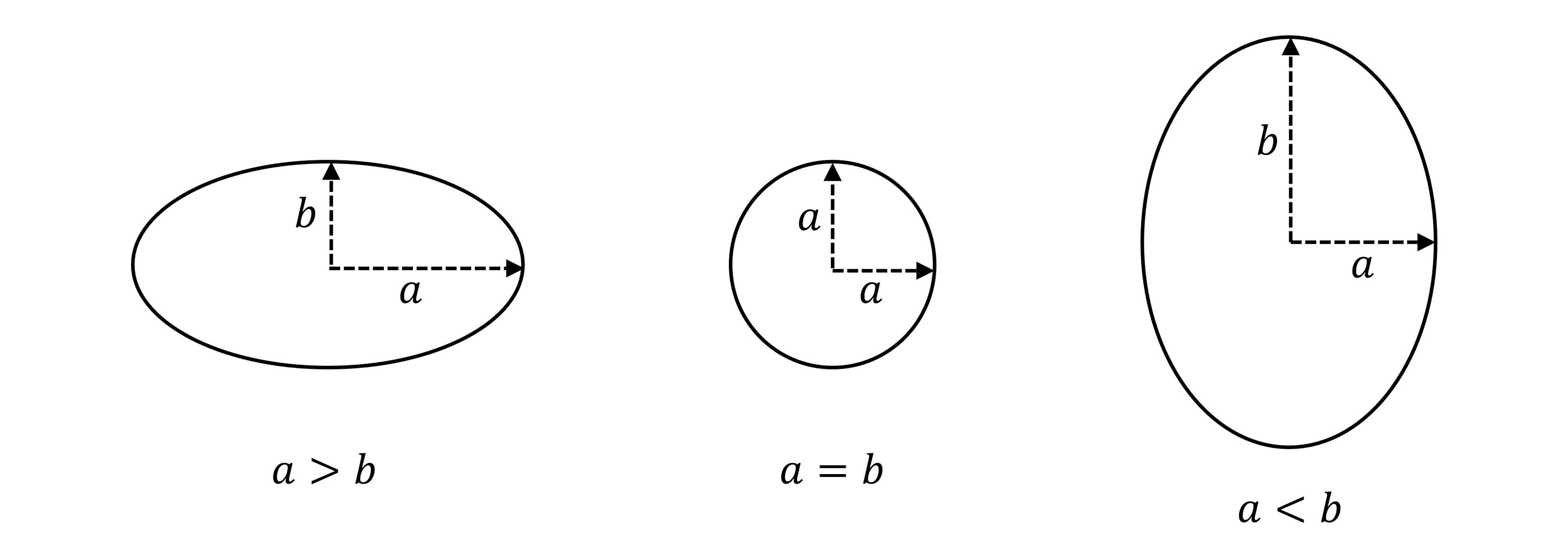
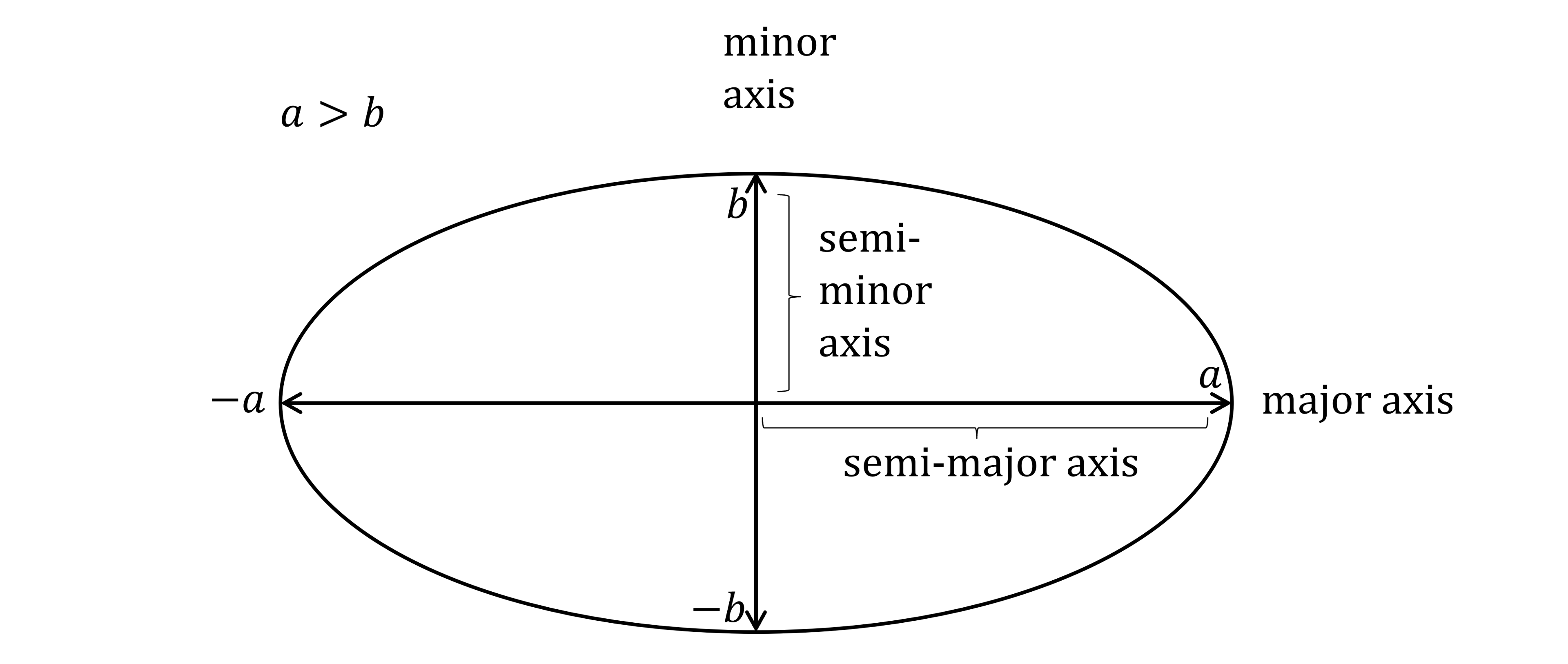
If
the major axis is
of length
the minor axis is
of length
is called a semi-major axis
of length
is called a semi-minor axis
of length
An ellipse is one of the conic curves
with eccentricity
A circle is an ellipse with
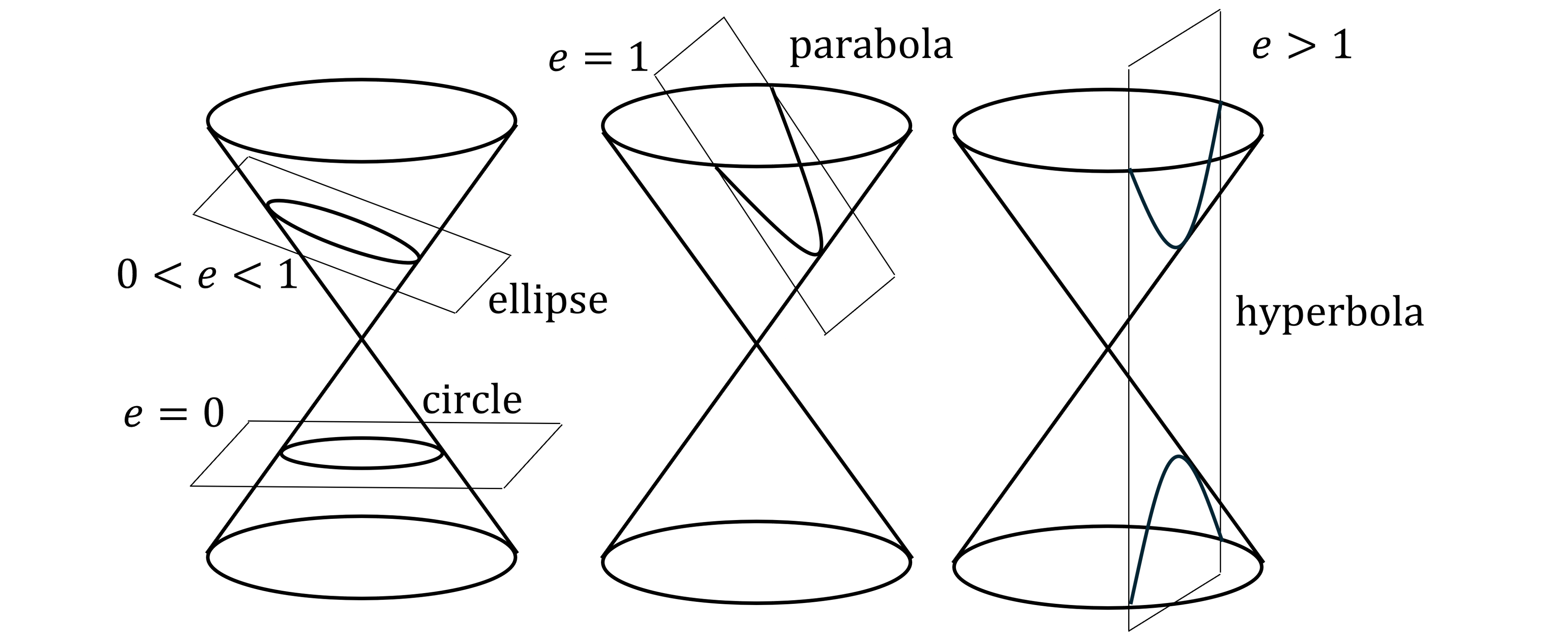
What is the equation of an ellipse?
The Cartesian equation of an ellipse with its centre at the origin
is
where
The parametric equations of an ellipse
are
where
Eliminating the parameter,
, gives the Cartesian equation
using that
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are given the Cartesian and parametric equations of an ellipse in the formulae booklet.
What are the coordinates of a general point on an ellipse?
A general point
on the ellipse
has coordinates given by its parametric equations,
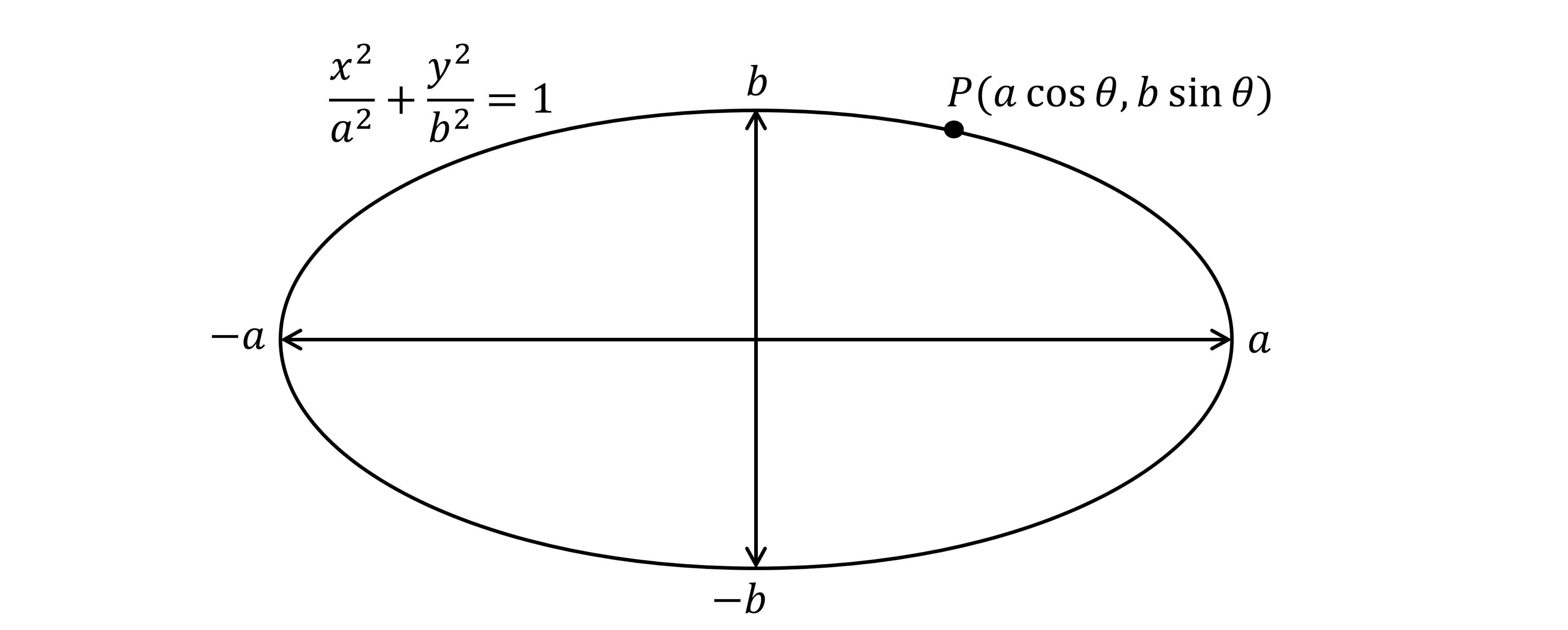
e.g.
is a general point on the ellipse
It satisfies the equation of the curve
It moves around the curve depending on the value of
This is different to, say,
which is a fixed point on the ellipse
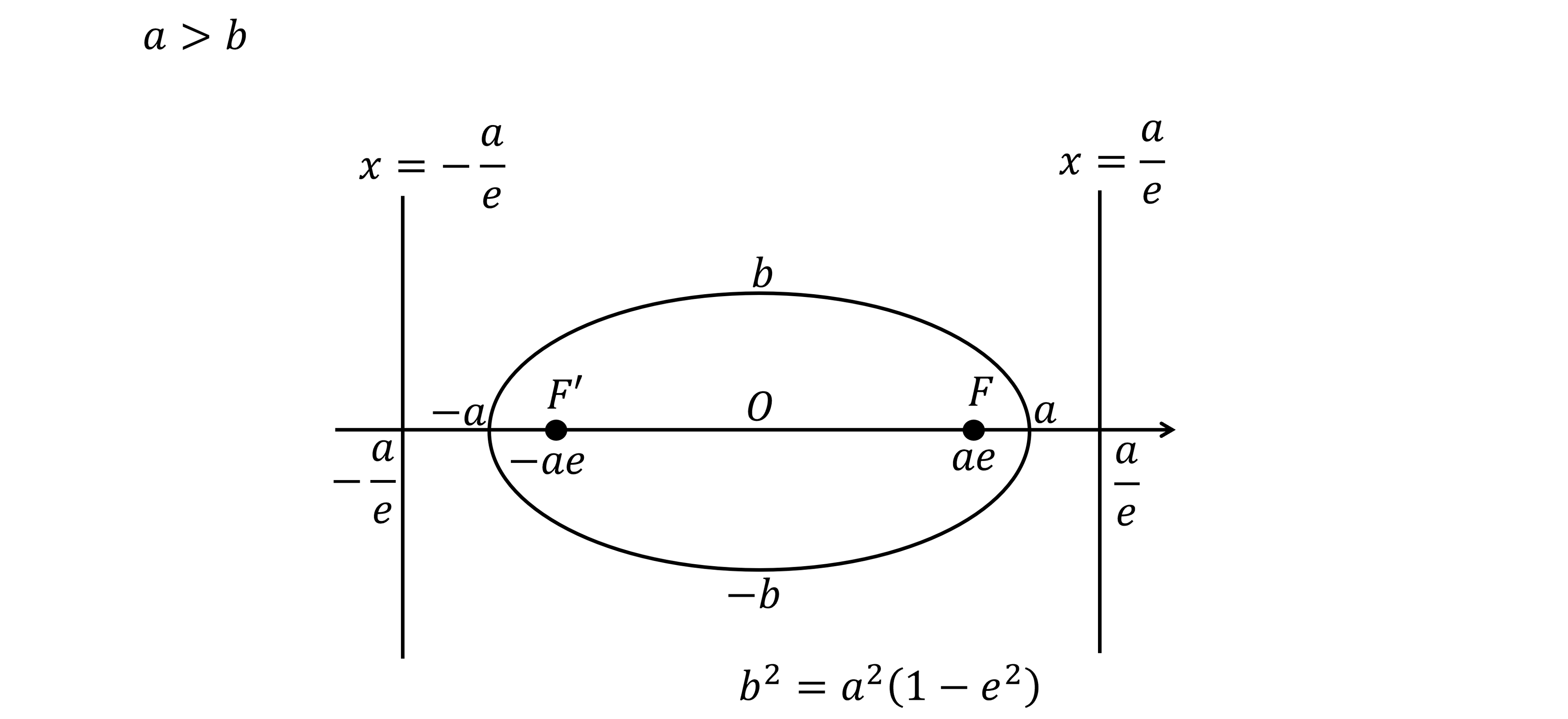
What is the eccentricity, focus and directrix of an ellipse?
The eccentricity of an ellipse,
, where
, is a measure of how stretched the ellipse is
gives a perfect circle
gets flatter and flatter
If
the eccentricity is found be rearranging the following formula
the foci,
and
, are two symmetric points inside the ellipse on the major axis
with coordinates
the directrices are the two vertical lines positioned symmetrically outside of the ellipse
with equations
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are given the eccentricity formula, foci and directrices of an ellipse in the formulae booklet.
If
the eccentricity is found be rearranging the following formula
the foci,
and
, are the symmetric points on the major axis
with coordinates
the directrices are the two symmetric horizontal lines
with equations
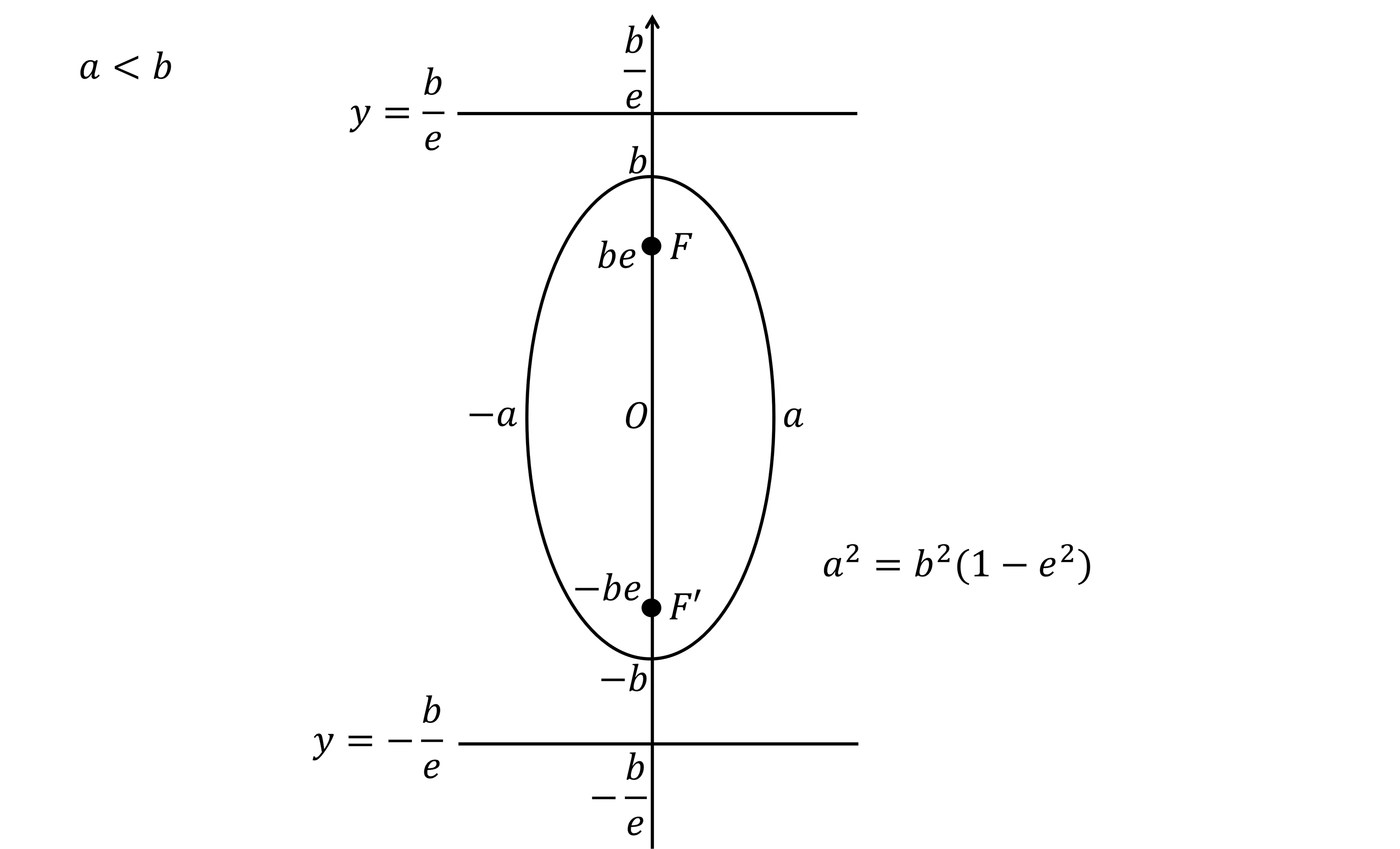
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are not given any formulae for the case, but you can work them out by swapping 'horizontal to vertical' and '
to
'.
Worked Example
An ellipse has the equation .
(a) Calculate the coordinates of the foci.
(b) Calculate the equations of the directrices.
Answer:
(a)
Find and
by comparing to the general equation
Check that
Rearrange the relationship to find
and check that
Calculate the foci using
The foci have coordinates
(b)
Calculate the equations of the directrices using
The directrices have equations
What is the focus-directrix property of an ellipse?
The focus-directrix property says that, if you take any point
on an ellipse, then
the distance from
to the focus,
divided by the shortest distance from
to the directrix (at point
)
is always equal to
, the eccentricity
i.e.
sometimes rearranged to
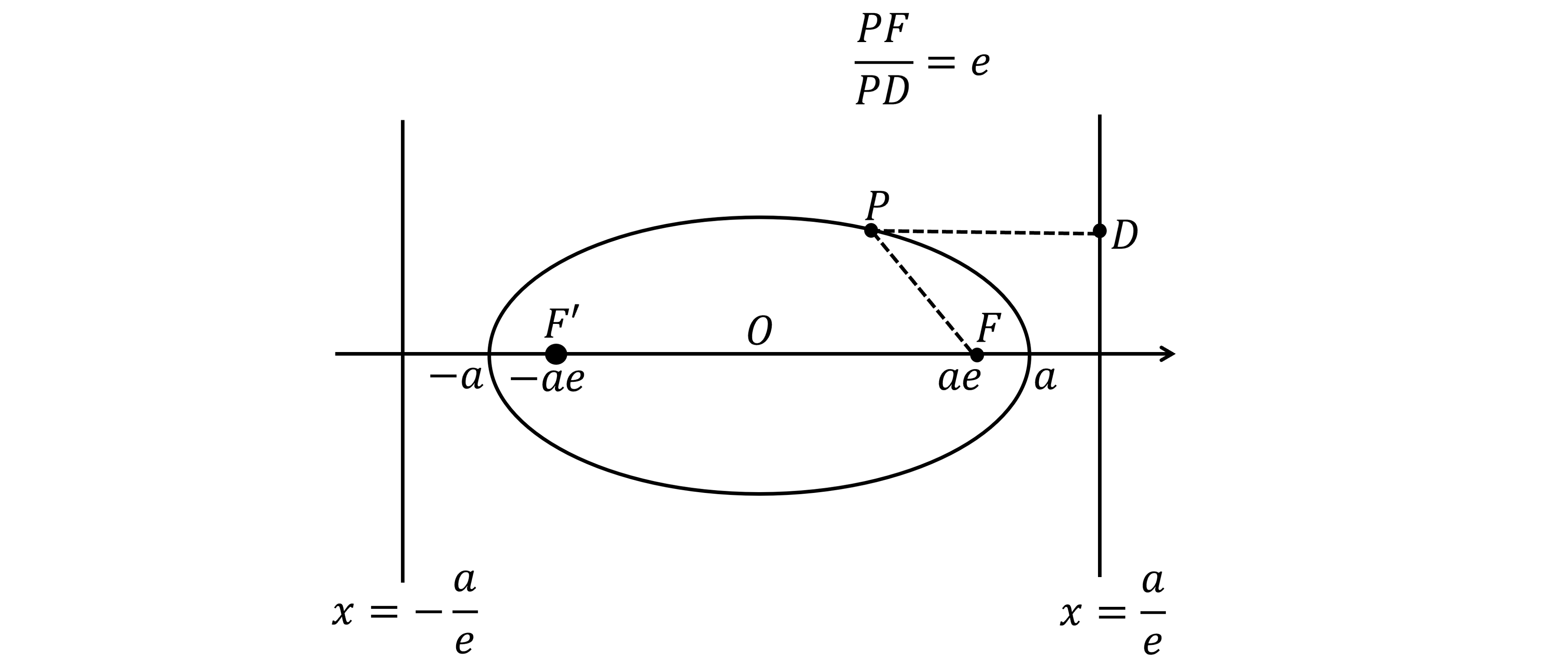
The focus-directrix property works from
to the other focus,
, and directrix,
where
is the same eccentricity
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are not given the focus-directrix property in the exam (you must learn it).
Worked Example
An ellipse with foci and
and directrices
is shown below.
The point on the ellipse has coordinates
and the points
and
are on the directrices, at the same height as
.
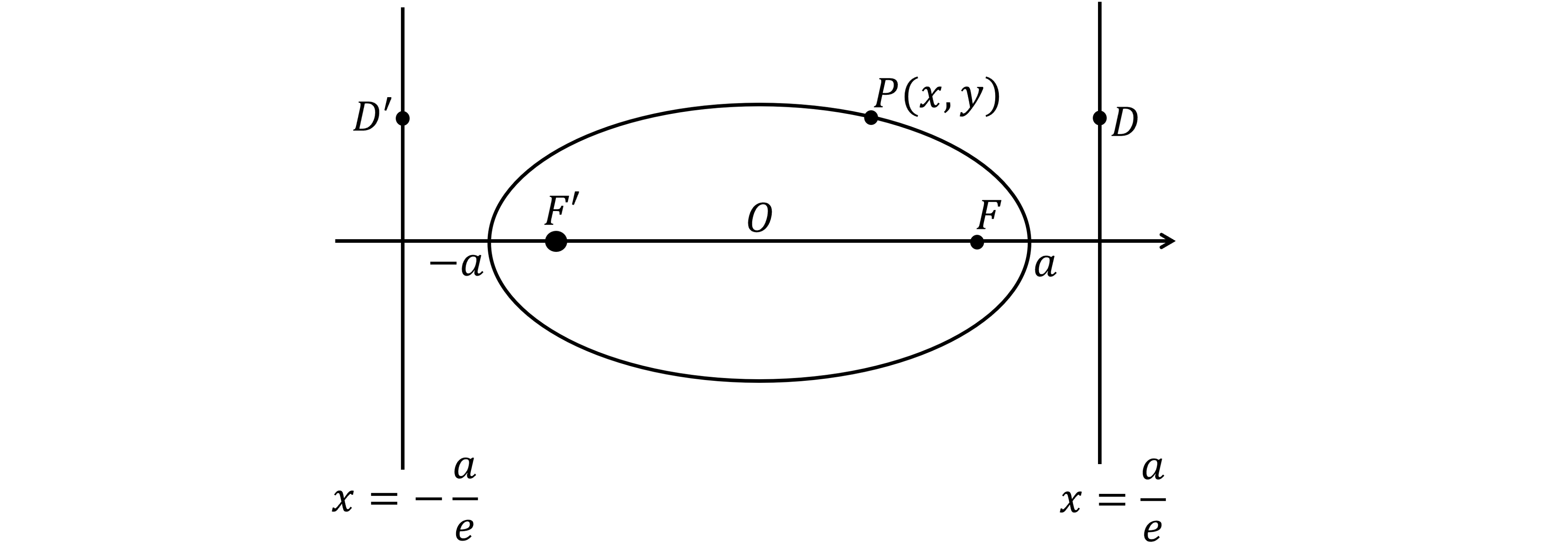
Using only the focus-directrix property,
(a) prove that
(b) derive the Cartesian equation of an ellipse, , where
Answer:
(a)
Use the focus-directrix property on ,
and
and again on
,
and
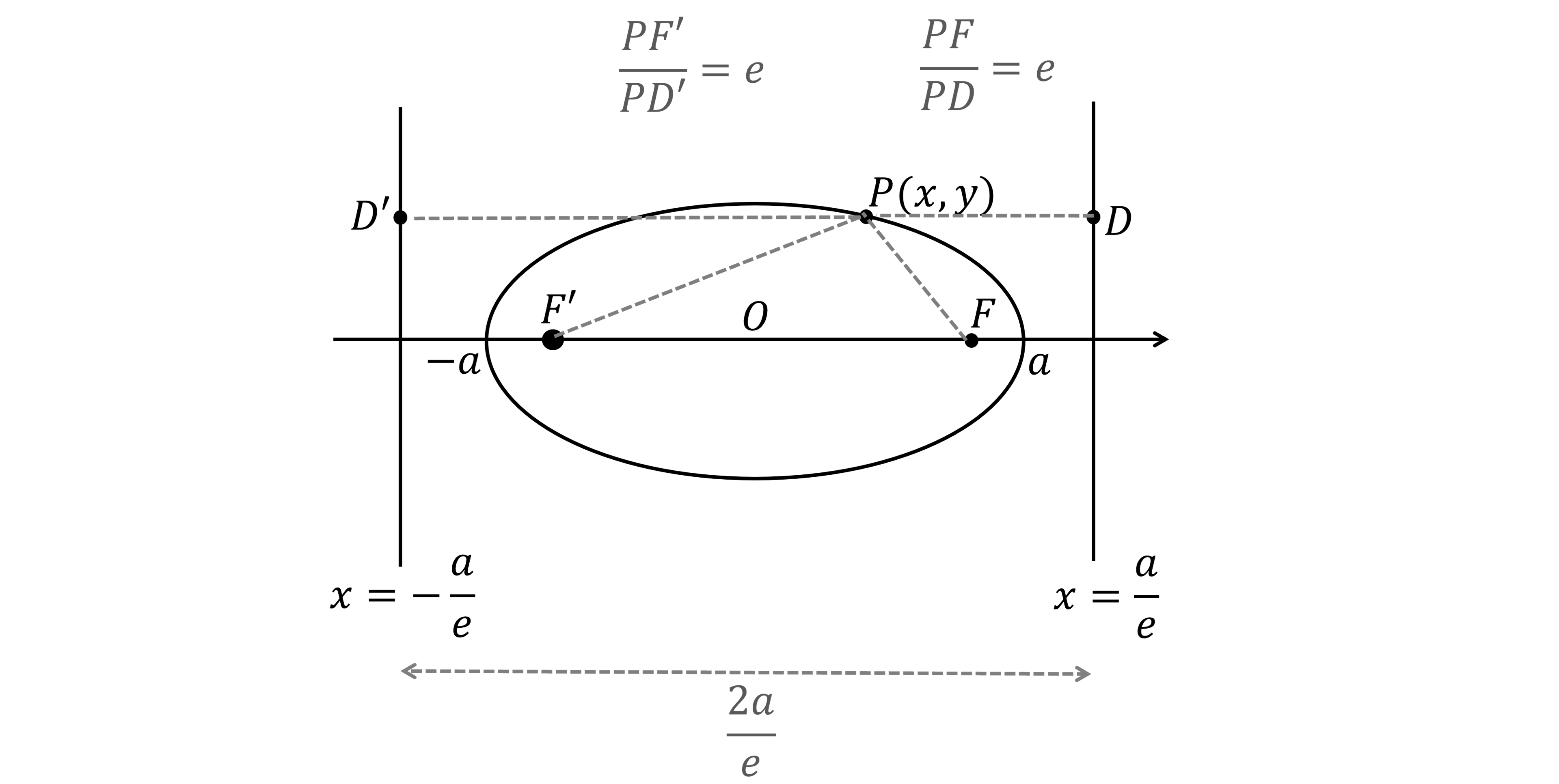
Rearrange to make and
the subjects
Add together and
Factorise out
Use that is the total distance between the two directrices
Substitute this back into
Simplify
(b)
Use the focus-directrix property on ,
and
(draw on lines
and
)
It helps to draw lengths and
from
on the diagram and the foci
Create a right-angled triangle whose hypotenuse is with base
and height
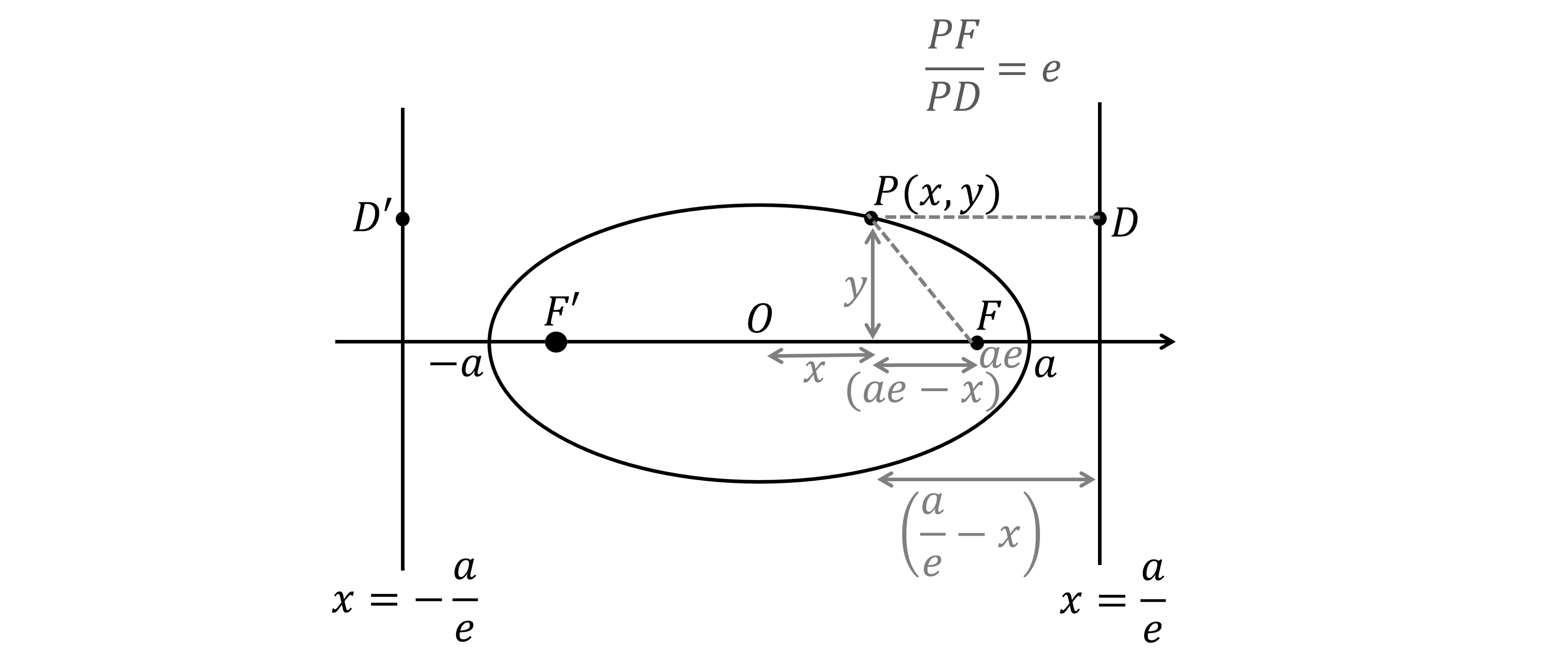
Use Pythagoras' theorem to find
Find the length from
to the directrix
Rearrange to make
the subject
Substitute in expressions for and
from above
Expand, cancel and factorise
Divide both sides by
This is now in the correct form of an ellipse
The Cartesian equation is , where

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
