Properties of Rectangular Hyperbolas (Edexcel A Level Further Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 9FM0
Written by: Mark Curtis
Updated on
Properties of rectangular hyperbolas
What is a rectangular hyperbola?
A rectangular hyperbola is a special hyperbola with the Cartesian equation
where
e.g. the familiar reciprocal graph
when
Its lines of symmetry are
Its asymptotes are the coordinate axes
and
It is rectangular because its asymptotes are perpendicular
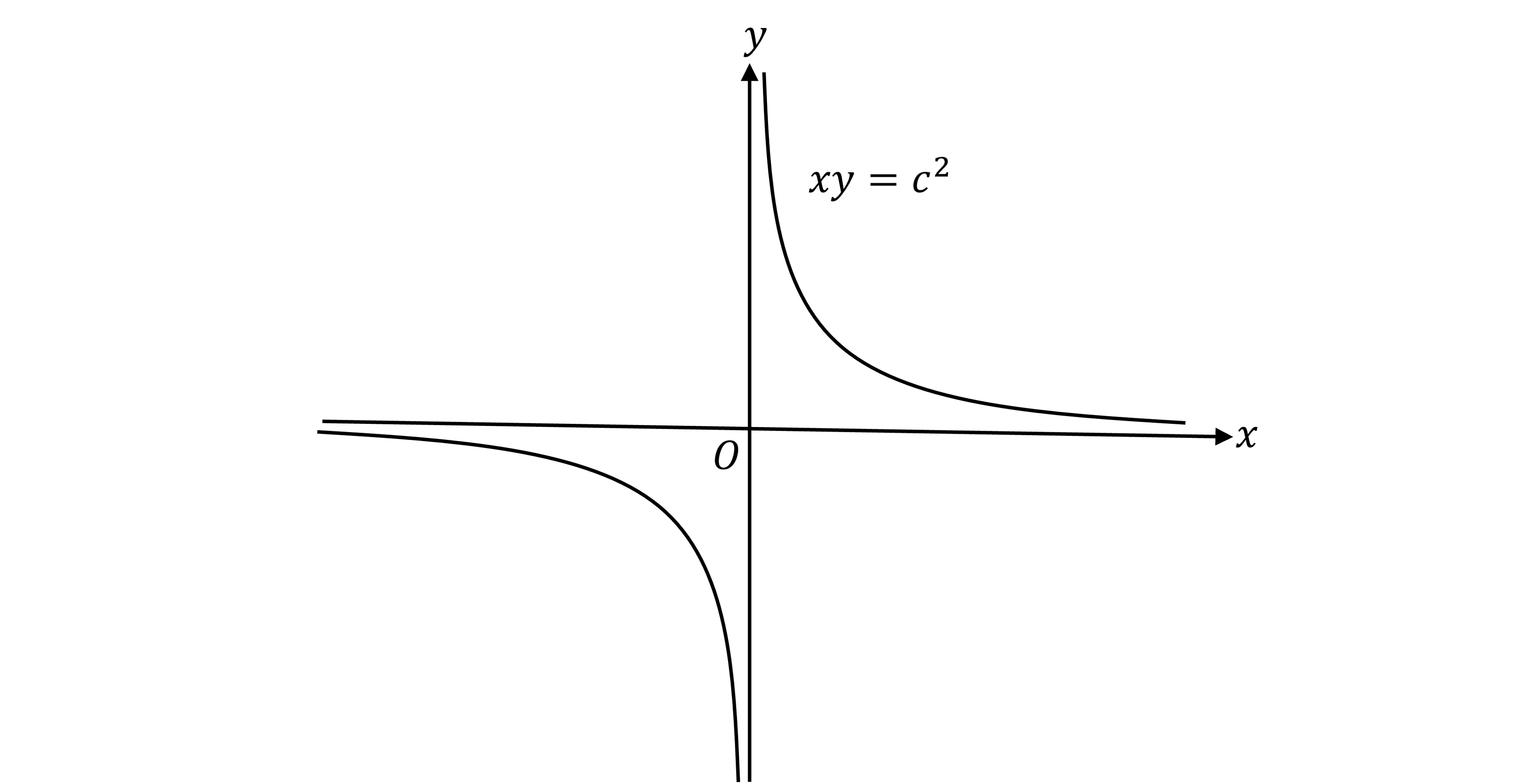
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are given the Cartesian equation of a rectangular hyperbola in the formulae booklet.
What are the parametric equations of a rectangular hyperbola?
The parametric equations of a rectangular hyperbola are
where
Eliminating the parameter,
, gives the Cartesian equation
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are given the parametric equations of a rectangular hyperbola in the formulae booklet.
What are the coordinates of a general point on a rectangular hyperbola?
A general point
on the rectangular hyperbola
has coordinates given by its parametric equations,
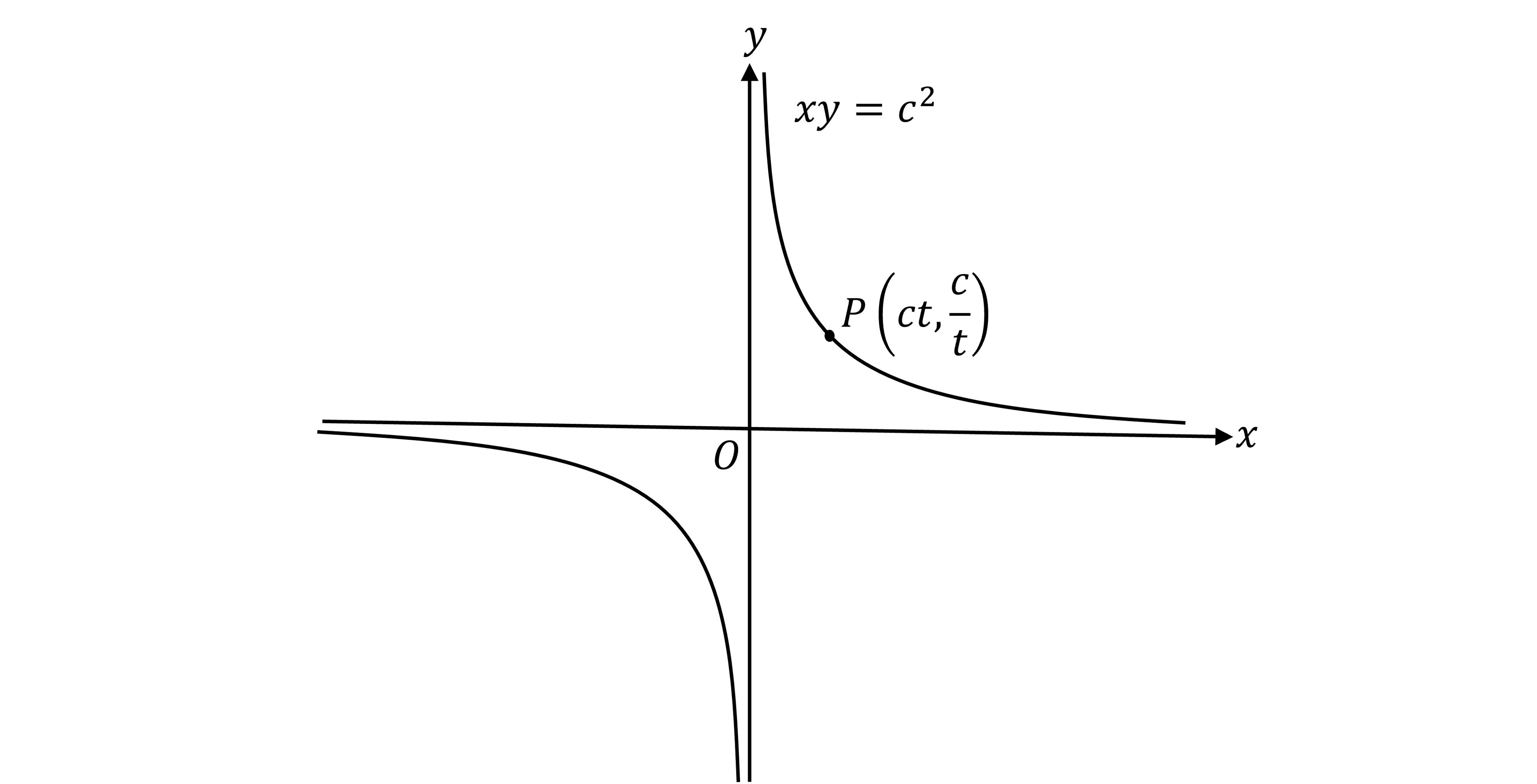
e.g.
is a general point on the rectangular hyperbola
(where
)
It satisfies the equation of the curve
It moves around the curve depending on the value of
This is different to, say,
which is a fixed point on the rectangular hyperbola
What is the eccentricity, focus and directrix of a rectangular hyperbola?
The eccentricity of a rectangular hyperbola,
, is
The foci,
and
, are the points
on the line
The directrices are the lines with equations
perpendicular to the line
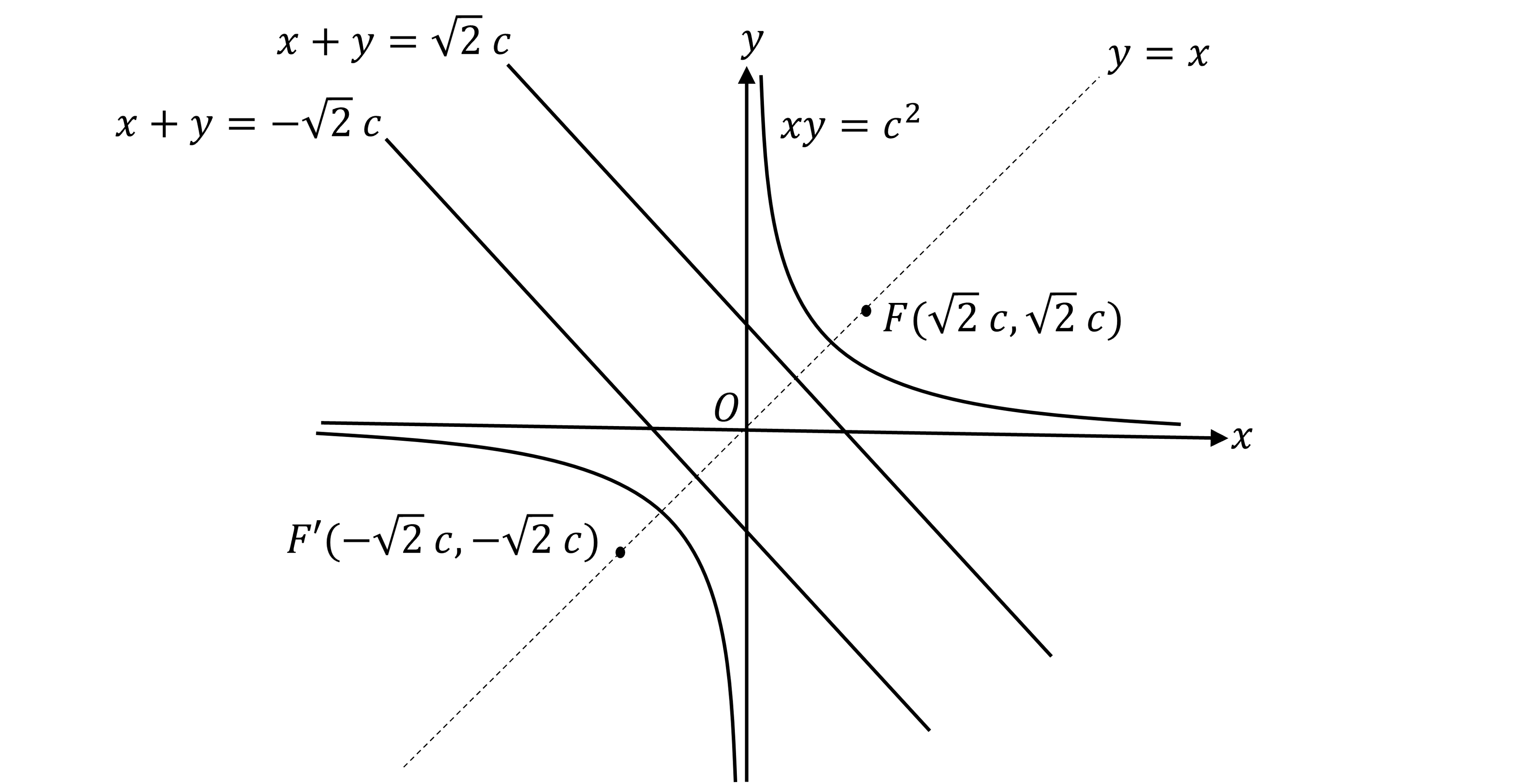
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are given the eccentricity, foci and directrices of a rectangular hyperbola in the formulae booklet.
Worked Example
A rectangular hyperbola has the equation .
Calculate
(a) the coordinates of the foci,
(b) the equations of the directrices.
Answer:
(a)
Find by comparing to the general equation
Substitute into
The foci have coordinates and
(b)
Substitute into the equations of the directrices,
The directrices have equations and
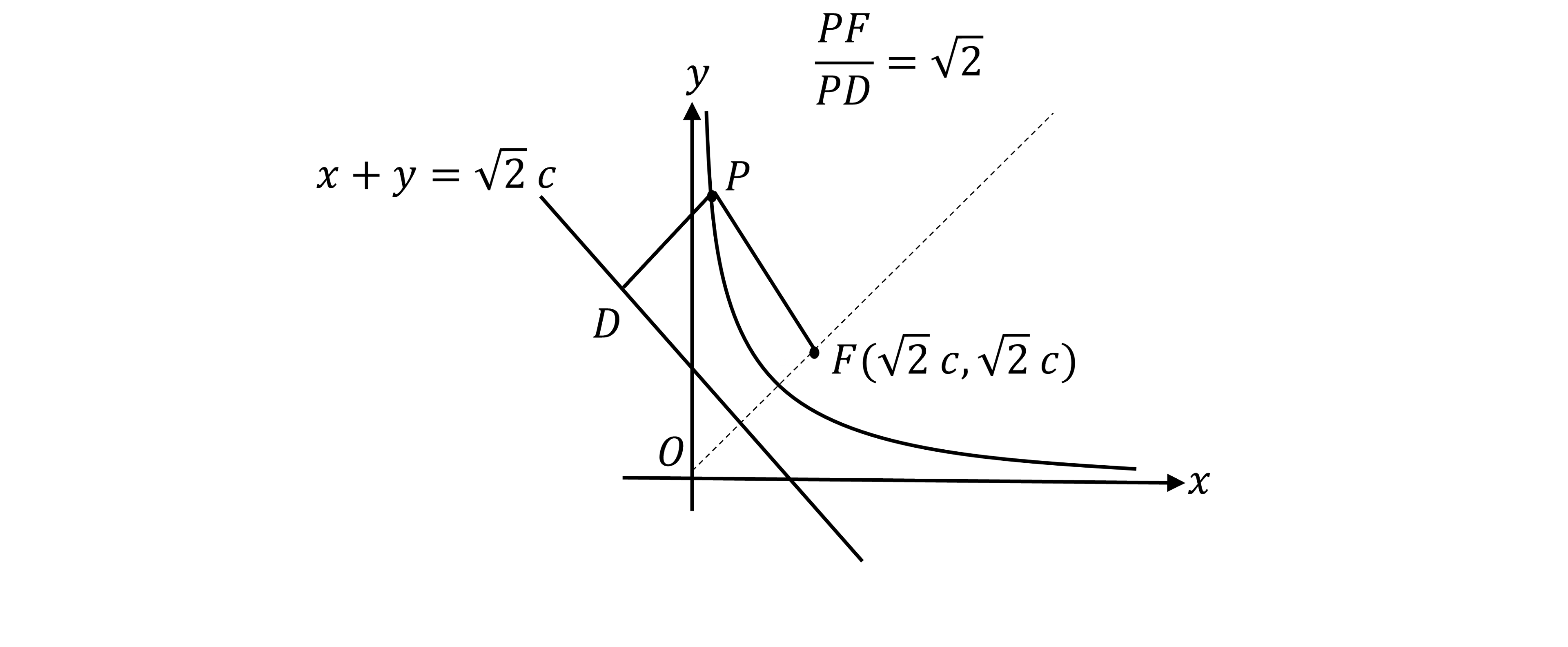
What is the focus-directrix property of a rectangular hyperbola?
The focus-directrix property says that, if you take any point
on a rectangular hyperbola, then
the distance from
to the focus,
divided by the shortest distance from
to the directrix (at point
)
is always equal to
, the eccentricity, where
i.e.
sometimes rearranged to
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are not given the focus-directrix property in the exam (you must learn it).

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
