Tangents & Normals to Ellipses (Edexcel A Level Further Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 9FM0
Written by: Mark Curtis
Updated on
Tangents & normals to ellipses
What is a tangent or a normal to an ellipse at a general point?
The position of the general point
on the ellipse
depends on
It is possible to calculate equations of tangents and normals at
where the coefficients are in terms of
i.e. as
varies, the equations vary
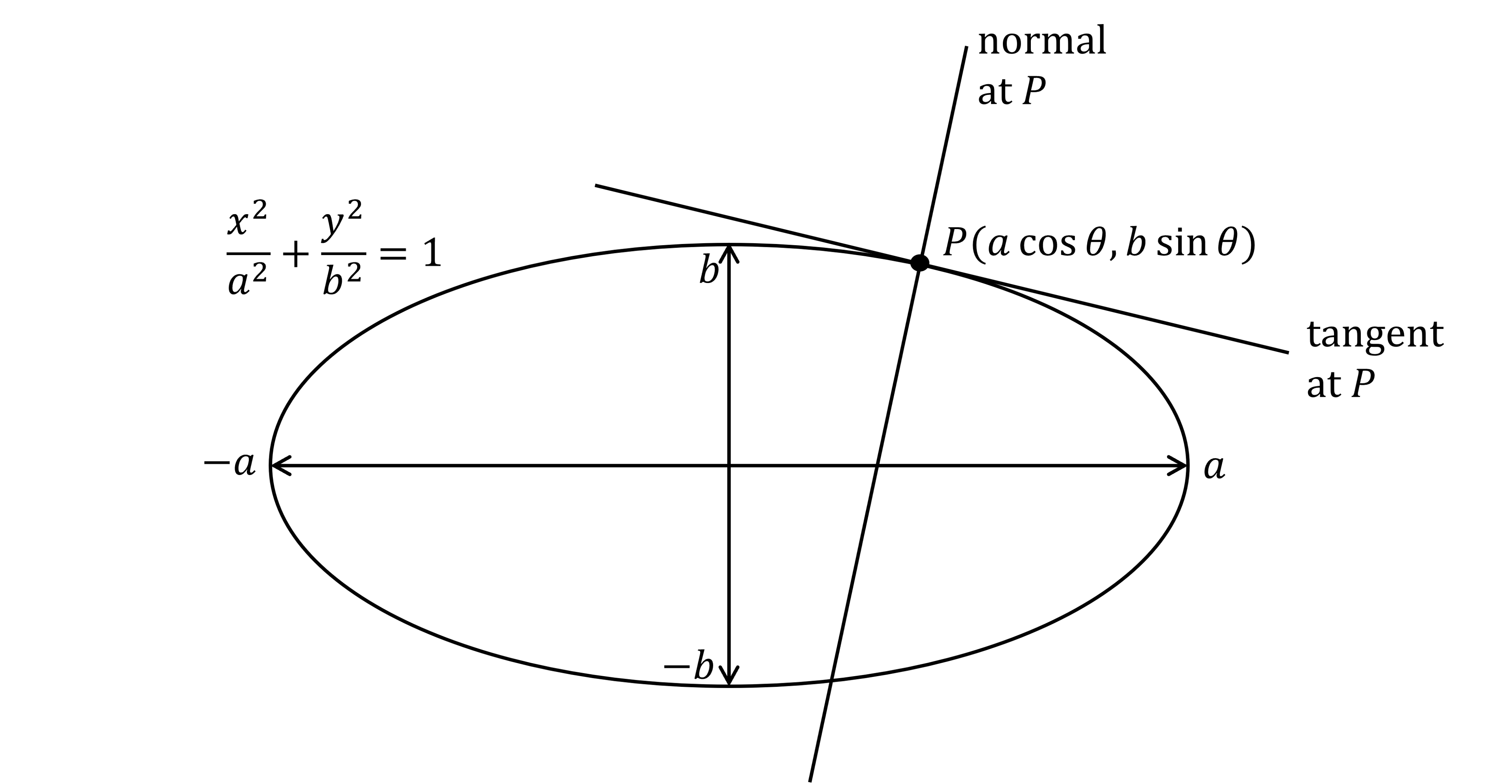
In general
at the point
on the ellipse
is the tangent
is the normal
Be careful with infinite gradients at the vertices
e.g. the equation of the tangent at
is
e.g. the equation of the normal at
is
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are not expected to remember the general formulae for tangents and normals, but you are expected to be able to work them out using the steps below.
How do I find the equation of a tangent to an ellipse?
To find the equation of the tangent to the ellipse
at the general point
:
STEP 1
Find the gradientof the tangent at
in terms of
either by implicit differentiation of
to find
then substituting
and
into the result
or by parametric differentiation of
and
using
STEP 2
Substitute into the equation of a straight linethe following:
in terms of
and simplify using trig identities
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It is possible to make the subject of
to find
, i.e.
, but differentiating this is more messy than implicit or parametric differentiation!
Worked Example
Show that the tangent to the ellipse at the point
has the equation
.
Answer:
The tangent has the equation
Method 1
Use implicit differentiation to differentiate
Substitute and
into the result and rearrange for
Method 2
Use parametric differentiation to find from
and
After either method, substitute ,
and
into
Rearrange into the form given in the question
Use that to get the final answer
What is the tangent condition for an ellipse?
The condition for a straight line
to be a tangent to the ellipse
is that the gradient
and y-intercept
of the straight line must satisfy
You need to know how to prove this condition
by solving
and
simultaneously
and forcing the discriminant to be zero
See the worked example below
Worked Example
Prove that, if is tangent to
, then
.
Answer:
First substitute into the equation
Multiply both sides by , expand and rearrange into a three-term quadratic in
The solutions to this equation are the -intercepts of the points of intersection
Force the discriminant to be zero, as a tangent only touches the ellipse once
It helps to move the second half to the other side, to make expanding easier
Factorise out from both sides, cancel, then expand the brackets and cancel any common terms on both sides
Factorise out and cancel (as
in
)
This rearranges to the answer
How do I find the equation of a normal to an ellipse?
To find the equation of the normal to the ellipse
at the general point
:
follow the previous steps for finding the equation of tangent
but use
as the equation of the normal
where
is the negative reciprocal of the tangent gradient
Worked Example
Show that the normal to the ellipse at the point
has the equation
Answer:
The normal has the equation where the normal gradient is the negative reciprocal of the tangent gradient,
Method 1
Use implicit differentiation to differentiate
Substitute and
into the result and rearrange for
(the gradient of the tangent)
Method 2
Use parametric differentiation to find (the gradient of the tangent) from
and
After either method, convert the tangent gradient into the normal gradient (e.g. find the negative reciprocal, or use )
Substitute ,
and
into
Rearrange into the form given in the question
Factorise out to get the final answer

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
