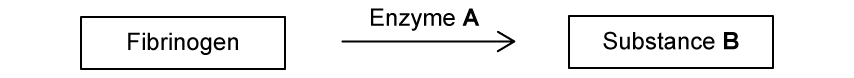When treating more aggressive forms of B lymphocyte cancer, rituximab is often combined with more traditional chemotherapies.
The graph below shows the results of a trial looking at the effects of several different treatments, alone and in combination, on B lymphocytes grown in the laboratory.
Rituximab on its own killed 23% of the B lymphocytes, and when combined with hydroxyurea it killed 82% of the B lymphocytes.
Calculate the percentage increase in effectiveness of rituximab in combination with hydroxyurea, compared to rituximab on its own. Give your answer to three significant figures.