Which one of these causes plantar flexion at the ankle?
Gastrocnemius
Hamstrings
Quadriceps
Tibialis anterior
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: 8582
Which one of these causes plantar flexion at the ankle?
Gastrocnemius
Hamstrings
Quadriceps
Tibialis anterior
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which bones are found at the shoulder joint?
Femur and tibia
Humerus and radius
Scapula and humerus
Tibia and fibula
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which bones are found at the elbow joint?
Femur and tibia
Humerus and radius
Scapula and humerus
Tibia and fibula
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Flat bones provide a protective function within the body.
Name two flat bones and, using a sporting action of your choice, suggest how these bones provide protection during performance.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Figure 1 Shows a young athlete running. The running action involves the use of many joints within the body.
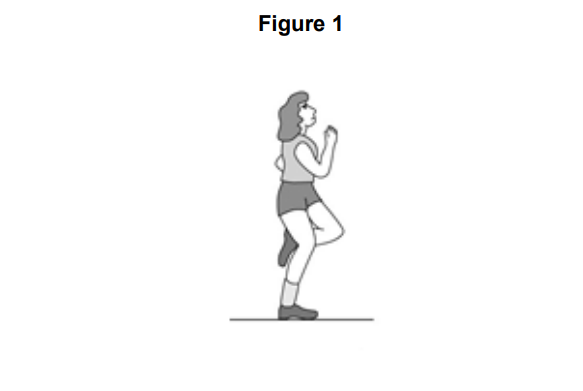
Identify the type of synovial joint working at the shoulder.
How did you do?
Outline how two of the features of the shoulder joint aim to prevent injury occurring
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Figure 3 shows a person kicking a football.
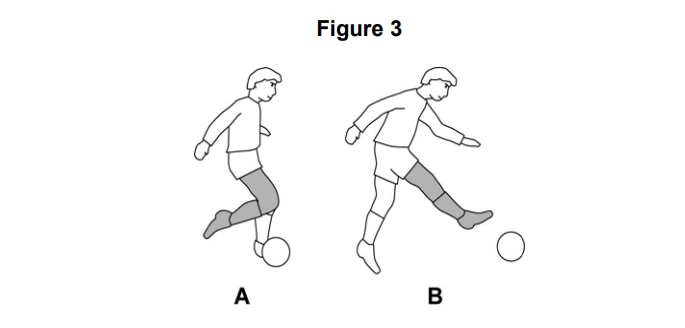
Complete Table 1 to show the joint action occurring at the knee from position A to position B and the agonist muscle group that causes this action.
Table 1
Joint action | Agonist muscle group |
|---|---|
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Before carrying out a weight training session using heavy weights, Robert carries out an appropriate warm up, including stretching of the major muscles that will be used.
Explain what other factors Robert should consider to reduce the chance of injury occurring during the session.
How did you do?
Figure 5 shows a performer weight training. This movement is brought about by the muscular and skeletal systems working together.

Explain how the muscles and bones work together to produce the movement from position A to position B.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Which one of these is the main function of a flat bone?
Allow movement
Blood cell production
Mineral storage
Protection of vital organs
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Figure 2 shows a person performing a wall sit.
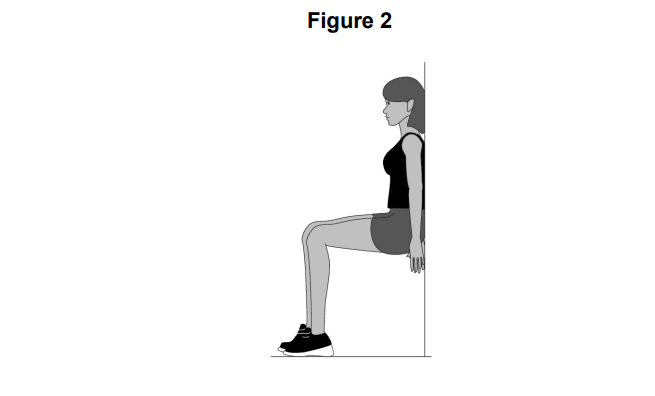
Identify the type of muscular contraction taking place in the legs in Figure 2.
How did you do?
Justify your answer to Question 8.1.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Name two major muscles that allow the foot to move at the ankle.
How did you do?
Name two bones found at the elbow.
How did you do?
Name the type of synovial joint at the elbow.
How did you do?
Name three structures of a synovial joint that help to prevent injury
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Name the type of joint where circumduction can take place.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Figure 3 shows a basketball player in two different positions (A and B) as they perform the jump shot.
Use Figure 3 to help you answer Questions 13.2 & 13.3
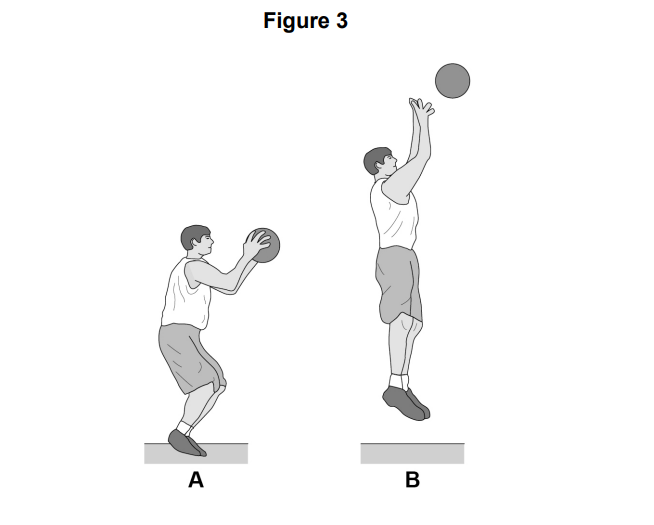
Identify the main agonist at the knee as the basketball player moves from A to B
How did you do?
Identify the type of muscle contraction that is taking place at the knee as the basketball player moves from A to B.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Which one of these structures attaches muscles to bones?
Cartilage
Ligaments
Membranes
Tendons
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which one of these muscles is found in the leg?
Deltoid
Gastrocnemius
Latissimus dorsi
Rotator cuffs
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which one of these describes an isometric contraction?
The muscle expands in size
The muscle increases in length
The muscle remains the same length
The muscle decreases in length
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Figure 1 shows a human skeleton.
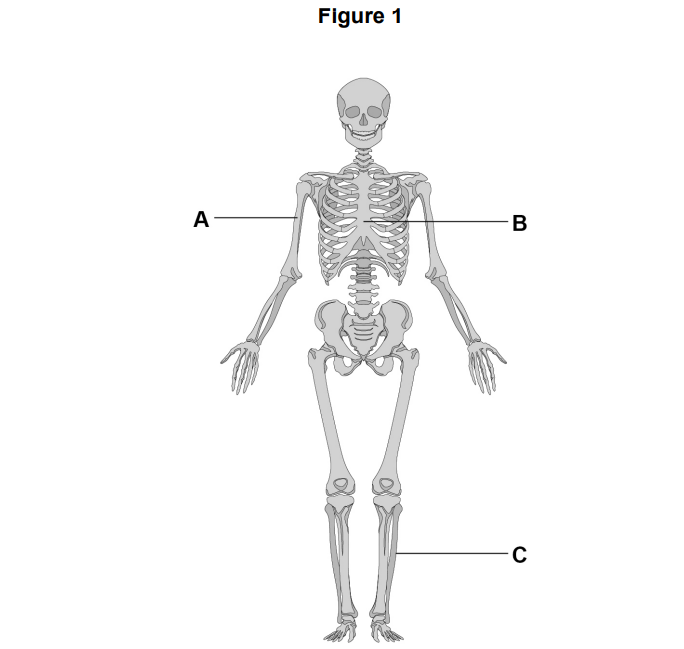
Identify the bones labelled A, B and C in Figure 1.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Figure 2 shows an athlete in two different positions (A and B) as the athlete performs a tricep dip.
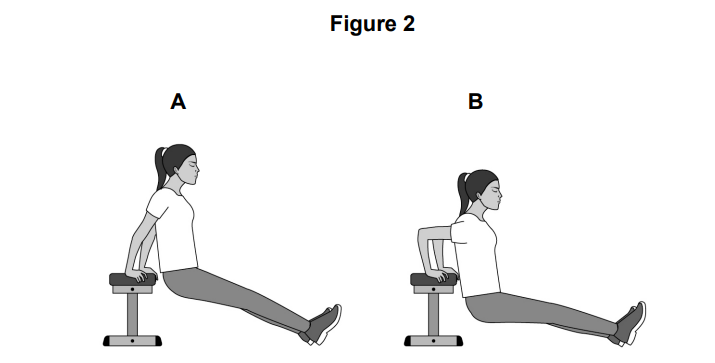
Identify the joint action taking place at the elbow as the arm moves from A to B
How did you do?
Identify the main antagonist at the elbow as the arm moves from A to B.
How did you do?
Identify the type of isotonic muscle contraction that is taking place at the elbow as the arm moves from A to B.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Name the type of joint where abduction can take place.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Figure 1 shows muscles in the body.
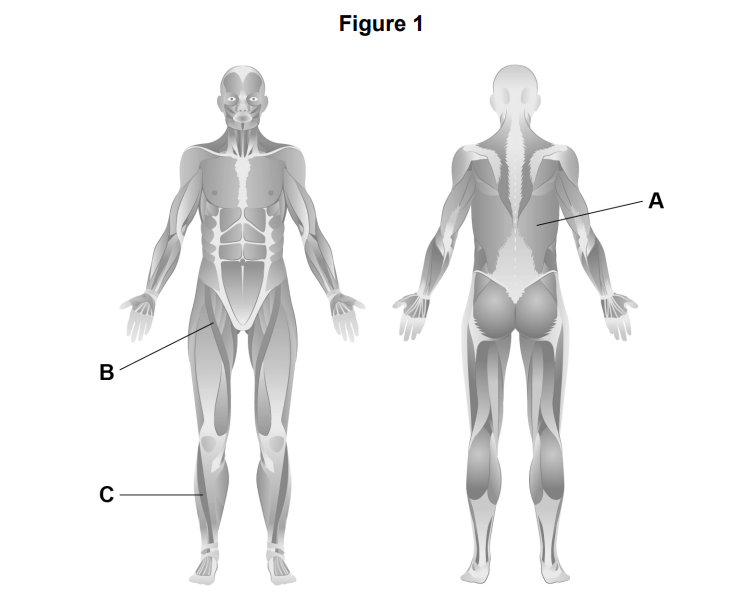
Identify the muscles labelled A, B and C in Figure 1
How did you do?
Name two bones located at the head/neck.
How did you do?
Explain how muscles and bones work to produce movement.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Figure 3 shows an individual performing a push-up
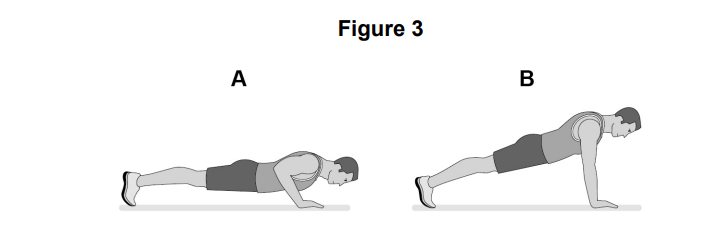
Identify the main agonist at the elbow during the upward phase (A to B) of the push-up.
How did you do?
Identify the type of isotonic muscle contraction taking place at the elbow during the upward phase (A to B) of the push-up.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Analyse how different types of bones help an individual taking part in a sporting activity of your choice.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?