Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Enterprise & Entrepreneurship (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 0450, 0986 & 0264, 0774
Characteristics of successful entrepreneurs
An entrepreneur is a person who is willing and able to create a new business idea or invention and takes risks in pursuing success
Successful entrepreneurs can identify and pursue opportunities, create value for customers and build thriving businesses
Entrepreneurs require a unique set of characteristics and skills

Successful entrepreneurs tend to be very persuasive in their communication and decisive in their decision-making
Characteristics of successful entrepreneurs
Characteristic | Explanation |
|---|---|
Creativity |
|
Hard working |
|
Resilience |
|
Initiative |
|
Self confidence |
|
Risk taker |
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When writing about entrepreneurs, don’t just list their characteristics – always link these to why they are important for business success, e.g. risk-taking helps in launching new products
Purpose and importance of a business plan
A business plan is a document, produced by the owner of a business, which provides forecasts of sales, costs and cash flow and details key objectives
Why is a business plan important?
The main aim of producing a business plan is to reduce the risk associated with starting a new business and help the owners raise finance
Having carried out research to support the plan, the business will be well-informed about the potential problems and chance of success
A well-written business plan can help a business obtain finance
Lenders (e.g. banks) and other investors will be able to explore the plan and make an informed decision about whether the business is credible and worth the financial risk
Investors (e.g. venture capitalists) will use the business plan to explore whether there is an opportunity to increase the value of their investment and make a worthwhile profit
A clear action plan provides direction for the business and helps lenders and investors have confidence in the future success of the business
Most high street banks can provide a detailed template for business owners to complete when applying for finance
Key elements of a business plan
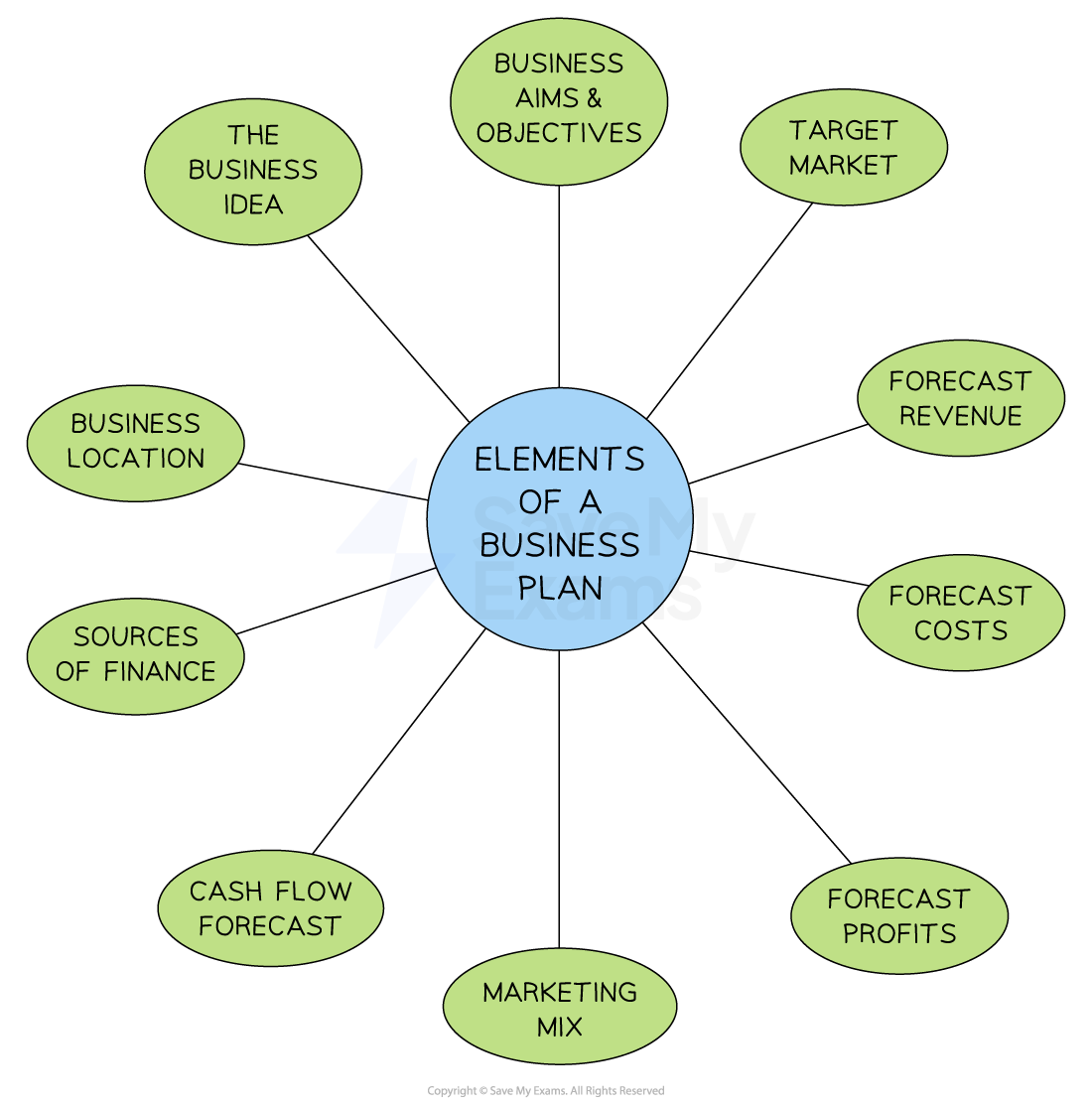
Elements of a business plan
The business idea
A clear explanation of the goods or services provided by the business, helping to attract investors
May also include the history of the business idea
Business aims and objectives
What the business wants to achieve in the medium and long term
Aims can be both financial and non-financial depending on the business
Target market
Explains who the business aims to serve, including age, gender, and income
Forms part of the firm's marketing strategy
Forecast revenue
Projects the business’s anticipated income from sales
Calculated as: Sales Revenue = Price x Quantity Sold
Helps plan for break-even levels of output
Forecast costs
Predicts fixed, variable, and total costs to manage spending effectively
New businesses often have high startup costs, such as initial stock
Profit forecasts
Investors review profit forecasts to assess the business’s ability to repay borrowed funds, such as bank loans
Marketing mix
Outlines the marketing strategy for attracting customers
Includes Product, Place, Price, and Promotion
Cash-flow forecast
Explains management of cash inflows and outflows monthly to prevent liquidity issues
Sources of finance
Details funding sources for the new business, such as loans, owner’s funds, or venture capital
Business location
Describes the proposed business location, including a map and advantages like good transport links or customer proximity
Government support of business start-ups
Governments often provide support to entrepreneurs
This encourages them to set up new businesses or take steps to grow their business
Reasons for providing government support include:
Increase the country's level of output to achieve economic growth
Reduce the level of unemployment as new or growing businesses create jobs
Improve choice for consumers by providing competition for existing businesses
Encourage entrepreneurs to set up social enterprises which may support disadvantaged groups or improve communities
How do governments support business start-ups?
Training and support sessions
Advice regarding finance, operations and marketing can often be accessed through local authorities
Support sessions offered by business mentors allow entrepreneurs to ask specific questions related to their business
Enterprise zones
Enterprise zones are geographic areas which provide tax breaks and Government support to help businesses grow
Enterprise Zones can provide access to low-cost premises and incentives such as reduced business rates
They are often linked with universities that share expertise and facilities, especially in less economically-developed regions
Finance
Some governments provide low-interest start-up loans and grants for new or growing businesses that create jobs or invest in training workers

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
