‘The most important role of human resource management (HRM) in a fast food restaurant is to maintain a high level of employee morale and welfare.’
Evaluate this view.
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: 9609
‘The most important role of human resource management (HRM) in a fast food restaurant is to maintain a high level of employee morale and welfare.’
Evaluate this view.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
George’s Gym (GG)
George identified a potential niche market for a new gym in his local area. He set up GG as a sole trader business three years ago. GG is a modern gym with the latest equipment.
George has recently gained planning permission to build a new swimming pool. George wants to open the swimming pool because a national competitor is planning to open a new gym close by and he wants GG to remain competitive. The swimming pool will cost $400 000 and George has yet to decide on the best source of finance. He has $50 000 in savings that he could use and he does not have any mortgage or loans. George is thinking about seeking a private investor but is unsure of the risks involved.
The local population is wealthy. Last year (2012), GG had 300 members who each paid a membership fee of $60 per month. George is thinking about new ways of increasing revenue such as offering additional ‘keep fi t’ classes. He also plans to increase the monthly fee he charges members to $66. His accountant has told him he needs to think about the price elasticity of demand before making a pricing decision.
Table 3 – Annual revenue and profit for the year for the previous 3 years ($000)
2010 | 2011 | 2012 | |
Annual revenue | 120 | 160 | X |
Profit for the year | 20 | 50 | 80 |
George hopes that the information in Table 3 will help show any potential lender how attractive the gym is as an investment.
GG has a problem of a high labour turnover of personal trainers. Three of them have left in the last six months. He has just employed a new personal trainer, Sally. George needs to issue her contract of employment. George thinks that the reasons for the high labour turnover include:
George is always busy and so he can never offer an effective induction training programme for his employees
GG salaries are below average for the industry.
Briefly explain the term ‘contract of employment’ (line 22).
How did you do?
Analyse the disadvantages to GG of a high labour turnover of personal trainers.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Read the following extract before answering
Evaluate the factors that the Human Resources manager should consider before completing the workforce plan for PC’s operations in country X.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Explain one type of training that a business may use.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Define the term ‘workforce planning’.
How did you do?
Explain two advantages to a business of using induction training.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Seaside Hotel (SH)
SH is a large hotel located in a tourist area of country H. SH has 120 rooms and employs 42 workers during the peak (busiest) season which is from April to September. Table 2.1 shows employee data for SH’s peak season.
Table 2.1: Employee data for SH’s peak season
Type | Number | Main tasks |
Manager | 3 |
|
Cleaner | 12 |
|
Customer service | 16 |
|
Marketing | 7 |
|
Other | 4 | • various |
SH makes half of the cleaners and customer service employees redundant at the end of the peak season.
To break even, the hotel must sell 72 rooms per night. The hotel offers good views of the sea and it is very busy in the peak season when the weather is hot. Table 2.2 shows SH’s sales of rooms.
Table 2.2: SH’s sales of rooms 2021–2022
Time period | Average percentage of rooms sold per night |
April 2021 – September 2021 | 95% |
October 2021 – March 2022 | 45% |
SH does not have a restaurant. It has a joint venture with a restaurant close to the hotel where SH’s customers receive a discount on their food and drink. The hotel advertises the restaurant on social media and the restaurant advertises the hotel on its menu.
Tia is one of the managers of SH. She has an autocratic leadership style and is responsible for the cleaners and marketing employees.
The directors of SH aim to increase the value added to the service that SH provides.
Define the term ‘redundant’ (line 16).
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Read the following extract (lines 45-48 and Table 1)
Calculate the:
difference in labour turnover between the Design Division and the Manufacturing Division for January to May 2022
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Benjamin’s Beds (BB)
Benjamin’s Beds (BB) is a large manufacturer of beds and has a strong brand image for quality. Its main channel of distribution is through the producer market (B2B) to national hotel chains. Recently, BB has also entered the consumer market (B2C) by selling online direct to customers.
BB uses flow production. BB’s existing machinery is old and cannot satisfy the increased demand. The directors of BB have decided its existing machinery needs replacing. Table 2.1 shows data for existing and proposed new machinery.
Table 2.1 Data for existing and proposed new machinery
Variable cost per unit | Output per year | |
Existing machinery | 50 | 5000 |
New machinery | 40 | 7500 |
Fixed costs are $500000 per year. Using new machinery would reduce this by 10%.
BB sales data suggests that its market share is growing rapidly. The consumer market (B2C) is becoming more important to BB because online orders are increasing. However, online demand is for a wide range of bed styles. The consumer market requires a substantial marketing budget and some retraining of employees.
Orders from national hotel chains in the producer market (B2B) are for a more limited range of bed styles. These orders remain constant with low marketing costs. However, BB is increasingly under pressure to reduce prices to hotels.
BB uses non-financial motivators and until recently had a motivated workforce. Efficiency is falling due to employees having to work longer hours because of increased demand. This is decreasing staff morale and welfare.
Analyse two possible disadvantages to BB of decreased staff morale and welfare.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Explain why businesses invest in the training and development of employees.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Explain why it is important for a business to have effective human resource management (HRM).
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Quality Furniture (QF)
QF is a public limited company in country S. It manufactures furniture for cafés. The number of cafés in country S has increased by more than 50% over the last 5 years. This has meant that QF has been able to expand and achieve internal economies of scale. However, the growth of the café market has attracted new firms supplying café furniture and increased competition for QF.
An extract from QF’s income statement is shown in Table 1.1.
Table 1.1: Extract from QF’s income statement for 2020
$m | |
Revenue | 300 |
Cost of sales | 120 |
Gross profit | 180 |
Expenses | 150 |
Although QF has been successful so far, Javid, the Managing Director, has identified two problem areas: inventory and human resources.
Inventory
QF’s inventory includes raw materials, work in progress and finished tables and chairs. QF buys 80% of its materials from country T and there is a long delivery lead time. This means that QF holds a high level of buffer inventory which has a high value.
Human resources
QF’s production employees are unhappy that they have not received any benefit from the company’s expansion. Profit has doubled over the past three years but employees have not received any pay increases or bonuses. The employees have all been trained by QF and have specialist skills which had ensured that customer expectations were met. However, customers are starting to complain about a fall in the quality of the furniture, which could be the result of the low morale of the employees. Some highly trained employees have left QF to work for competitor firms.
Recommend how QF’s management could improve the morale of its production employees. Justify your recommendation.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Tin Mines (TM)
TM is a private limited company in the primary sector. Tin is found underground and is extracted by mining. TM operates seven mines in country C. There are several job roles at each mine including skilled engineers, managers and miners.
TM has recently discovered a new source of tin in a remote area of country C. TM has permission to develop a tin mine but will have to construct transport links. It will need new buildings such as offices, warehouses and employee housing. The Human Resources Director is developing a workforce plan to recruit miners and managers for the new mine.
TM’s Financial Director has produced a cash flow forecast for the new mine for the next five years. This is shown in Table 2.1.
Table 2.1: Cash flow forecast for the new mine ($m)
Year | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 |
Opening balance | X | -80 | -95 | -85 | 5 |
Sales | 0 | 0 | 25 | 105 | Y |
Development costs | 60 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Operating costs | 0 | 0 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
Closing balance | -80 | -95 | -85 | 5 | 240 |
The remote area of country C where the new tin mine will be located has a high level of unemployment and average incomes are low. TM intends to recruit employees from the local area and buy resources from local suppliers, if they are available. The market for tin is likely to be affected by increased demand for electric vehicles. The batteries in electric vehicles contain tin. The government of country C believes that the tin mine will be of great benefit to both the local community and national economy. However, tin mining can result in pollution of local water supplies.
Analyse two methods of recruitment that TM’s Human Resources Director can use to recruit employees for the new mine.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Define the term ‘job description’.
How did you do?
Explain two advantages to an employer of using a person specification.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
‘Human Resource Management is the most important department in any large manufacturing business.’
Discuss the extent to which you agree with this view.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
The Shop (TS)
Thomas worked for 30 years as a manager of a factory. Although he was very good at his job he was recently made redundant.
Thomas always wanted to open a shop. He thinks he has the qualities an entrepreneur is likely to need for success. He has undertaken some primary market research to identify possible opportunities in city X where he lives (see Fig. 1.1).
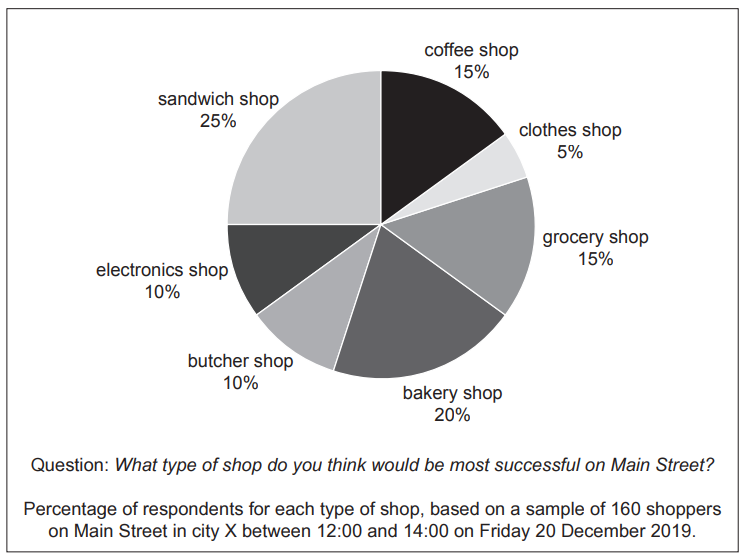
Fig. 1.1: Market research
Thomas now needs to make a decision about which type of shop to open. He has used the data in Fig. 1.1 and some secondary market research to identify two options.
Option 1: Coffee shop
The coffee shop would provide hot drinks that customers could take away and drink elsewhere. It would also sell some bakery items, such as biscuits and doughnuts. There are four other shops selling takeaway hot drinks and bakery items in the city, as well as five cafés. Thomas thinks that the profit margin would be 6% to 8%.
Option 2: Sandwich shop
The sandwich shop would make sandwiches using job production. Customers can choose from a range of sandwich fillings, as well as cold drinks and snacks. There is only one competitor in the city. It is a well-known international franchise that spends a lot of money on promotion. Thomas thinks that the profit margin would be 10% to 15%.
Define the term ‘redundant’ (line 2).
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Market Solution (MS)
MS is a public limited company in the tertiary sector. MS advises businesses on elements of the marketing mix. Most of its customers are small businesses who cannot afford their own marketing department. MS designs marketing materials for these businesses to use.
Although MS uses computer aided design (CAD), the business is labour intensive. MS employs specialist marketing workers as well as administrative support workers.
Table 2.1 shows some data about employees of MS.
Specialist marketing workers | Administrative support workers | |
Average number of workers in 2019 | 40 | 88 |
Payment method | Salary plus bonus | Performance related pay plus bonus |
Number of workers who left in 2019 | 2 | 11 |
Average pay (compared to national average) | High | Low |
Main need of the workers | Achievement | Affiliation |
Main hygiene factors |
|
|
Is a bonus expected in 2020? | Yes | No |
MS has recently employed Hetti as the new Human Resources Manager. Hetti thinks that the ideas of the motivational theorists are important when managing employees. She is particularly worried about the labour turnover of the administrative support workers.
MS has recently taken on a new customer, named Books Outlet (BO). BO has an objective to increase its revenue by targeting a younger market segment. BO has provided MS with the following information about its current marketing mix (see Table 2.2).
Table 2.2: Current marketing mix for BO
Product
| Price
|
Promotion
| Place
|
Refer to Table 2.1. Calculate the difference between the labour turnover of the specialist marketing workers and the labour turnover of the administrative support workers.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Super Heroes (SH)
SH is a leisure (theme) park aimed at 10–18 year olds. It is owned by two companies, X and Y, which started SH as a joint venture. Company X owns many leisure centres and swimming pools. Company Y owns many brands based on superheroes.
SH employs 200 full-time workers and an extra 50 seasonal workers during the busiest times of the year. The park has 10 large rides which take up 2km2 of land. There are also many smaller rides, restaurants, toilets and shops. The price of an entrance ticket is $11 per customer. Table 1.1 shows the costs for SH in 2019.
Table 1.1: SH costs for 2019
Total fixed costs (per year) | $12m |
Variable costs (per customer) | $3 |
Total costs | $42m |
One of the larger rides at SH is the Iron Blaster. The number of customers who use this ride has decreased each year for the last three years. This has led the management of SH to consider its options for internal growth.
Option 1 – A new virtual reality (VR) ride
This option would involve developing the Iron Blaster into a VR ride. Most of the structure of the Iron Blaster could be used but customers would be given a VR headset to wear during the ride. The cost of developing the VR ride would be $2m. The Iron Blaster ride would be closed for a three month period during the off-peak season for the development to be carried out. No employees would be made redundant or dismissed.
Option 2 – A new hotel
SH does not currently have a hotel. It could demolish the Iron Blaster to provide the space to build one. Many of the competitors of SH have a hotel near or within their leisure parks. Hotel customers would pay a high price for a room but have free access to the leisure park’s facilities. Market research suggests that the average hotel customer would spend twice as long in the leisure park than a non-hotel customer. The cost of developing the hotel would be $15m and take a year to build. All of the employees currently working on the Iron Blaster ride would face redundancy or dismissal.
Explain the difference between ‘redundancy’ and ‘dismissal’ (line 28).
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
‘Limited investment in employee training and development in a primary sector business will lead to poor business performance.’
Discuss the extent to which you agree with this view.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
UPlane Components (UC)
UC is a private limited company providing engine parts for commercial aircraft. It uses batch production in factory A and flow production in factory B. As part of UC’s commitment to corporate social responsibility (CSR), it provides a training scheme for the long-term unemployed, based in factory A.
UC’s products are sold to aircraft engine manufacturers. Demand for aircraft engines has increased by 45% over recent years. The aircraft engine manufacturers want inventory just when needed and are demanding a reduction in prices.
In 2017, UC opened factory B which is 5km away from factory A. Factory B has a high level of automation, resulting in low unit costs for the parts produced there. Production is capital intensive. UC has a plan to automate factory A. The production workers are not happy about this proposal and have asked for more details. The workers’ representatives have asked for a meeting with the human resource manager.
In December 2019 a fault was discovered in one of the engine components supplied by UC and produced in factory A. UC had to recall 2000 parts at a cost of $200000. This has had an impact on part of its triple bottom line and UC is unlikely to meet its targets. Table 1.1 shows some financial data for UC.
Table 1.1: Financial data for UC
Year ending 30 November 2019 | Year ending 30 November 2020 | |
Revenue | 5.8 | 6.4 |
Cost of sales | 2.3 | 3.4 |
Expenses | 1.3 | 1.6 |
Cost of recall | - | 0.2 |
Amjit, the human resource manager, believes that the fault was caused by the negligence of Jack, one of the production supervisors. Jack claims that he was made to work overtime to try and meet production targets. This caused him to become tired and make a mistake in one batch of parts. Amjit wants to dismiss Jack.
Analyse two likely effects on the other employees if Jack is dismissed.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Gemini Theatre (GT)
GT is a private limited company fully owned by the Gemini family. It owns a small theatre. This building is used to show live stage performances. Some of the performances are created by GT and some are created by visiting groups who rent the theatre. Table 2.1 shows the planned performances for January 2021.
Table 2.1: Planned performances for January 2021
Name of performance | Created by | Number of performances | Ticket price | Percentage of tickets sold |
A Summer Dream | Visiting group | 9 | $40 | 100% |
Wise Owl | GT | 14 | $15 | 60% |
La Poeme Ballet | GT | 5 | $20 | 40% |
GT gains all the revenue from performances created by GT. Visiting groups must pay 50% of their total ticket revenue to GT. The theatre has a maximum of 250 tickets that can be sold for each performance.
GT uses cost-based pricing to set each ticket price for its own performances. Each performance makes a profit but the company often experiences cash flow problems.
GT needs to recruit a new Theatre Manager. The person hired will have many duties, including the responsibility for all of GT’s administration as well as some accounting. The Directors are considering two people who were both recently interviewed. Table 2.2 contains information gained from the interview process.
Table 2.2: Information gained from the interview process
Nick | Portia |
|
|
Recommend whether GT should employ Nick or Portia for the position of Theatre Manager. Justify your recommendation.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Braid Runner (BR)
Lewis is a hairdresser. He rents a small shop which he uses as a hairdressers called Braid Runner (BR). Lewis is a sole trader and he set up BR 25 years ago.
BR is the smallest of all the hairdressers in city Y. Lewis works on his own. He has repeat customers who have been using BR for many years. However, there are many large franchises in city Y which offer a much cheaper haircut than BR.
Lewis is considering increasing the price of a haircut and he has outlined the costs and revenue of the business in Table 2.1.
Table 2.1: Costs and revenue of BR
Variable costs per customer | $3.50 |
Fixed costs per week | $675 |
Price | $8 |
Lewis would like to employ another hairdresser so that he can work fewer hours in BR. The new employee would have to be able to work in BR on their own. They would be responsible for taking bookings, dealing with customers and some financial transactions. Lewis has drawn up a person specification (see Fig. 2.1) that will be placed on a job website.
Characteristic | Essential | Desirable |
Qualifications |
|
|
Physical |
|
|
Experience |
|
|
Personal qualities |
|
|
Fig. 2.1: Person specification created by Lewis
Refer to Fig 2.1 and any other relevant information. Evaluate the usefulness of the person specification when recruiting another hairdresser.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Read the following extract before answering
Evaluate the importance of workforce planning to C4T’s future success.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?