Define the term ‘secondary research’.
Explain one advantage to a business of data collected using primary research methods.
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: 9609
Define the term ‘secondary research’.
How did you do?
Explain one advantage to a business of data collected using primary research methods.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Barbecue House (BH)
BH is a fast food restaurant and takeaway business, which sells a range of burgers, kebabs, pizzas and side orders. BH also has a delivery service to the local area.
BH is owned by Amir who mortgaged his home to finance the start-up of the business. Amir operates BH as a sole trader. His son also works within the business as a chef. Amir has been advised to change the legal structure of BH and to become a private limited company to protect the business and himself.
BH is located on a busy high street. There are many other similar businesses on the high street and in the surrounding area. Amir knows that the continued success of the business requires him to identify a gap in the market and develop a unique selling point (USP). Amir has carried out some market research (see Table 1.1 and Fig. 1.1).
Table 1.1: Market research data about competitors within 2 km of BH
Total number of competitors | 8 |
Number of competitors who offer delivery services | 4 |
Number of competitors who do not sell Asian food | 6 |
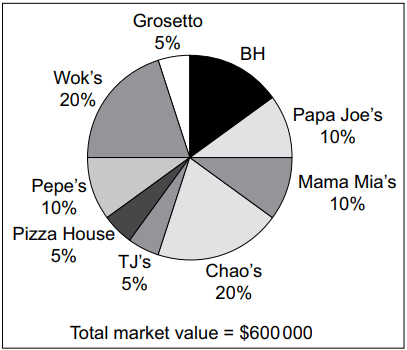
Fig. 1.1: Market share data for competitors within 2 km of BH
The two market leaders are Wok’s and Chao’s. Both businesses specialise in Asian food but neither has a delivery service. Amir would like to increase BH’s market share. He is considering starting to sell Asian food. None of his employees have any experience cooking or selling Asian food but Amir believes that the possible increase in income would be worth any extra costs.
Explain one reason why Amir carried out market research.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Discuss the usefulness of secondary market research to a business planning to launch a new luxury perfume.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Discuss the usefulness to a furniture retailer of using secondary market research when planning to enter a new market.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Discuss whether a successful soft drinks business needs to continue to carry out market research.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Super Candy (SC)
SC is a large public limited company that sells low-sugar candy (sweets) with natural flavourings. The candy is made using flow production in SC’s four large factories in country T.
SC uses psychographic market segmentation when planning its marketing mix.
SC has completed some secondary market research using published accounts. The data is about one of SC’s main competitors, Organic Kandy (OK) and compares the results with data about SC (see Table 2.1). OK is in the same market as SC.
Table 2.1: Secondary market research about OK and SC for 2020
OK | SC | |
Revenue | $60m | X |
Market share by revenue | 40% | 34% |
Different varieties of candy | 12 | 18 |
Main channels of distribution | Wholesalers | Wholesalers |
Target market(s) | Mass market | People with interests in:
|
There have been a number of media reports in country T about the increasing importance of corporate social responsibility (CSR). A large food manufacturing business in country T recently lost many customers due to reports about its use of plastic packaging.
The directors of SC are particularly concerned about this trend because of SC’s use of plastic in its packaging. The marketing department has been told to conduct some primary market research on this issue. The directors are planning to discuss making CSR a new business objective for SC.
Explain one possible disadvantage to SC of using secondary market research.
How did you do?
Analyse two primary market research methods that SC could use.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
The Shop (TS)
Thomas worked for 30 years as a manager of a factory. Although he was very good at his job he was recently made redundant.
Thomas always wanted to open a shop. He thinks he has the qualities an entrepreneur is likely to need for success. He has undertaken some primary market research to identify possible opportunities in city X where he lives (see Fig. 1.1).
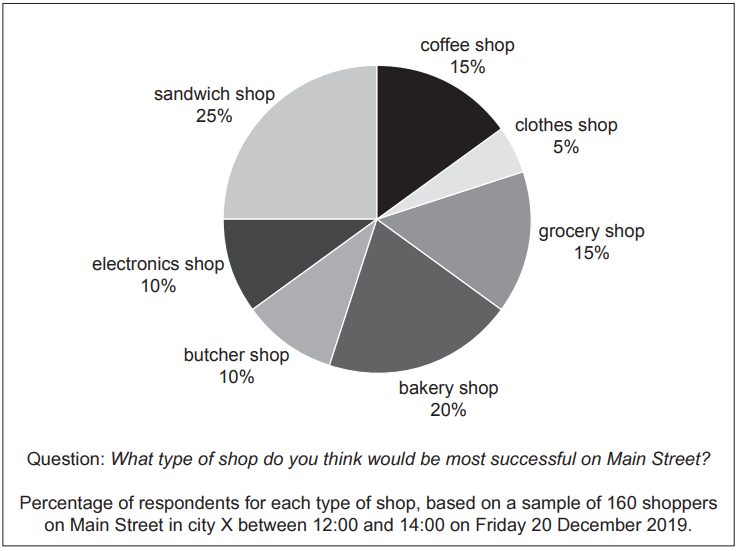
Fig. 1.1: Market research
Thomas now needs to make a decision about which type of shop to open. He has used the data in Fig. 1.1 and some secondary market research to identify two options.
Option 1: Coffee shop
The coffee shop would provide hot drinks that customers could take away and drink elsewhere. It would also sell some bakery items, such as biscuits and doughnuts. There are four other shops selling takeaway hot drinks and bakery items in the city, as well as five cafés. Thomas thinks that the profit margin would be 6% to 8%.
Option 2: Sandwich shop
The sandwich shop would make sandwiches using job production. Customers can choose from a range of sandwich fillings, as well as cold drinks and snacks. There is only one competitor in the city. It is a well-known international franchise that spends a lot of money on promotion. Thomas thinks that the profit margin would be 10% to 15%.
Explain the term ‘primary market research’ (line 4).
How did you do?
(i) Refer to Fig. 1.1. Calculate the number of respondents who think a coffee shop would be most successful on Main Street.
[2]
(ii) Explain two limitations of the sampling used by Thomas.
[4]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Define the term ‘market research’.
How did you do?
Explain two advantages to a business of using primary (field) market research data.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?