Corporate Social Responsibility and Elkington's Triple Bottom Line (Cambridge (CIE) AS Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9609
An introduction to corporate social responsibility
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) refers to the concept that businesses have a responsibility to consider and positively impact society beyond their economic interests
It is a framework through which companies voluntarily integrate social and environmental concerns into their business operations and interactions with stakeholders

CSR involves taking into account the impact of business activities on various stakeholders, including employees, customers, communities, the environment, and society at large
CSR goes beyond legal compliance and strives for companies to actively contribute to sustainable development and societal well-being
Examples of socially responsible activities
Sustainable sourcing of raw materials and components
Japanese fashion retailer Uniqlo has moved towards an eco-friendly strategy in recent years, focusing on technologies that make the production of new clothing from recycled materials possible
Responsible marketing
Marks and Spencer ensures that it never actively directs any marketing communications to children under the age of 12 and does not directly advertise any products high in fat, sugar or salt to children under the age of eighteen
Protecting the environment
Multinational coffee chain Starbucks offers discounted coffee for customers
with a branded multi-use cup
Responsible customer service
John Lewis's famous 'Never Knowingly Undersold' slogan refers to the company's commitment to checking competitor prices regularly to ensure that the price its customers pay is the lowest available in the local area at that time
Reasons for implementing CSR
Business set ethical or socially responsible objectives for a range of sound commercial reasons
Common reasons that support setting CSR objectives include:
Improved reputation
CSR can enhance the business image and reputation and improve its attraction to many stakeholders
Operating in a socially responsible way is likely to be attractive to both existing and potential customers
It should lead to positive media coverage
The business may be able to retain and attract quality workers to fill job roles
It may be looked upon favourably by investors, especially those who prefer ethical investment
Added value
CSR can be very profitable as it adds value
In competitive markets, CSR can provide a differentiating USP that may mean the business can use premium pricing
E.g., Tony's Chocolate's, whose mission is to be commercially successful whilst being committed to using cocoa only from slavery-free sources, is able to charge around 200% more for its products than its mass market rivals
Employee morale and motivation
CSR may improve employee motivation and productivity
Workers are more likely to feel connected to a business that 'does the right thing' and may be more inclined to work hard to ensure that the business is a success
Employees are also less likely to leave the business or take time off work
Solve social problems
CSR may help to solve social problems, e.g. resource depletion
Businesses that adopt CSR objectives are likely to understand that they can play a key role in solving some of the emerging social, ethical and environmental problems faced by communities around the world
E.g., Businesses that look to minimise the use of fossil fuels in production processes will be making a small contribution to global efforts to combat climate change
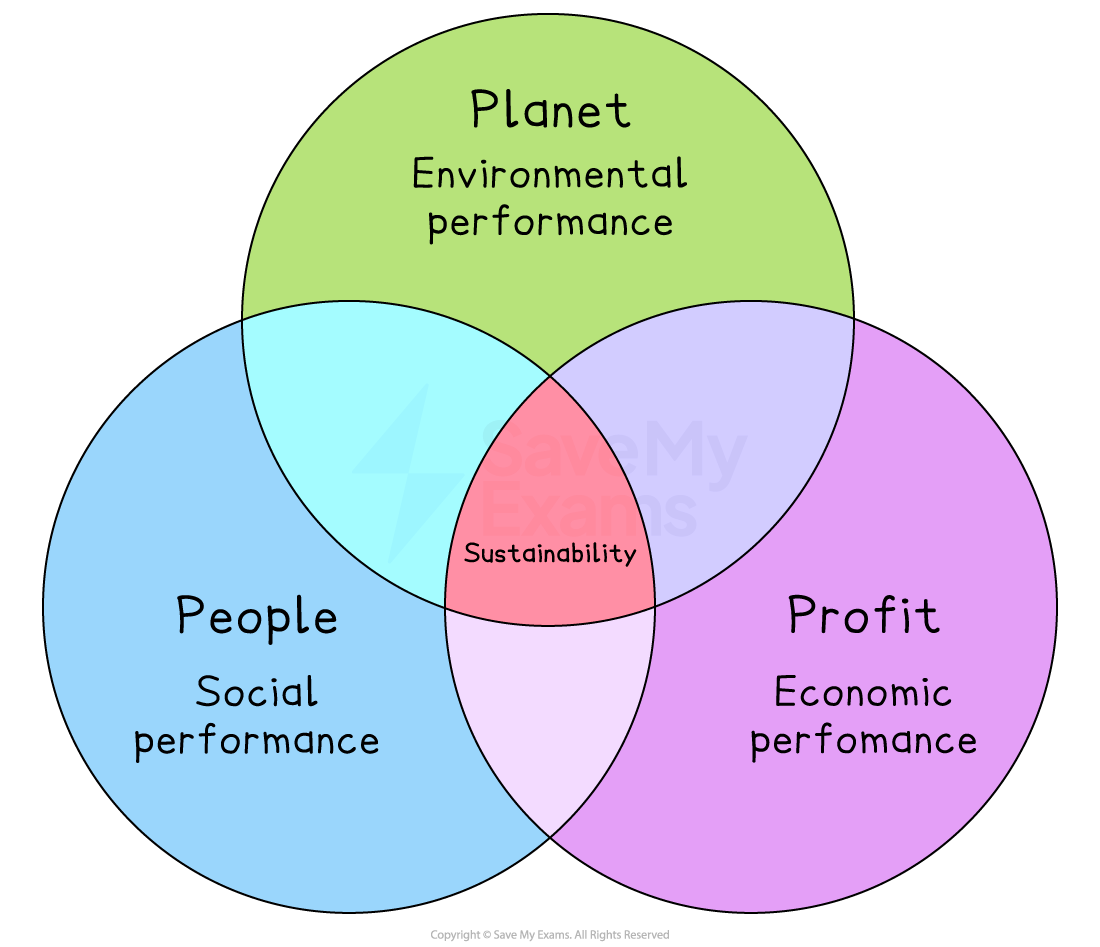
Elkington's triple bottom line
The Triple Bottom Line model highlights that business performance may be measured in a number of ways in relation to
Its finances (Profit)
Its environmental impact (Planet)
How socially responsible it is in relation to employees (People)
Elkington argued that only a company that was measuring performance in all three areas of people, profit and planet was considering the full costs of its activities
If all these areas are measured, business owners and employees are likely to pay attention to them and change their behaviour accordingly, rather than just focusing on profit
As a result, sustainability both within the business and, if adopted widely, across the economy as a whole, should be improved
Elkington's triple bottom line
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You should consider both the short-term and long-term impacts of adopting a socially responsible approach. Whilst costs of implementing socially responsible policies may be significant in the short term and cause disruption as change is implemented, business sustainability is likely to be improved, and, over time, a better business reputation can be a key factor in increasing sales.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
