Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Legal Controls Over Employment Issues (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 0450, 0986 & 0264, 0774
Introduction to legal controls
Legislation refers to laws and regulations passed by governments that require businesses to conduct their behaviour in a particular manner
Many countries have passed laws that determine the required behaviour of employers towards their workers
Legal controls over business
Unfair dismissal
Dismissal takes place when an employer ends an employee’s contract of employment with the business
Dismissal can be fair for a number of reasons
The job no longer exists, which means the employee is made redundant
An employee cannot do the job properly, e.g., they may lack the right skills
Long-term illness
Gross misconduct, such as theft or violence at work
For other “substantial” reasons, such as the employee has been sent to prison
Unfair dismissal is when an employee of a business has their employment terminated without a valid reason or against government legislation
Reasons for unfair dismissal include discrimination or avoidance of paying compensation for redundancies
In cases where there is unfair dismissal, the worker may take his/her complaint to a court called an industrial tribunal to decide whether there is a case to answer
If the independent tribunal finds that the worker was wrongfully dismissed, then the worker receives compensation and their job is offered back to them
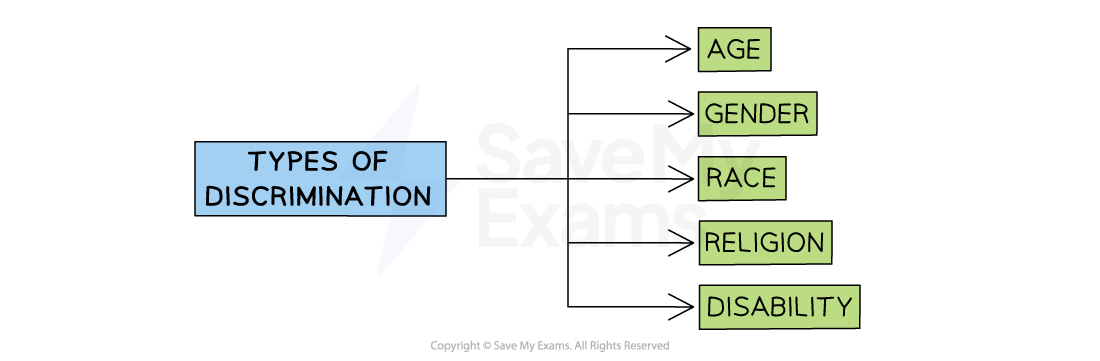
Discrimination
Discrimination at work occurs when the employer treats employees with protected characteristics such as gender or race less favourably than one without these characteristics
In many countries, discrimination based on these characteristics is illegal
The main forms of discrimination
Employees who are victims of discrimination in the workplace can take legal action against the employer
Trade unions often support employees with legal claims against employers and provide legal advice and support
Businesses can miss out on recruiting the best applicant if recruitment policies are discriminatory
Reputational damage may result if a business is found to have discriminated against employees
Health and safety
Health and safety legislation requires businesses to operate in a way that protects the physical and mental well-being of its employees, contractors and customers
Health and safety legislation covers areas including
The provision of adequate breaks and rest periods
Temperature and noise levels
The provision of safety equipment
Hygienic, safe and sanitary conditions
Preventing stress
Implementation of procedures and equipment required to maintain healthy working conditions are likely to incur financial and time costs, such as
Staff training and supervision
Changes to working hours and rest provisions
Arrangement of manuals, signage and safety documentation
Purchase and maintenance of safety equipment
Drawing up and implementing a code of practice
Serious health and safety breaches can lead to fines or investigations by the Health and Safety Executive and, in some cases, prison sentences
Legal minimum wage
A national minimum wage (NMW) is a legally imposed wage level that employers must pay their workers
It is set above the market rate of pay
In some countries, the minimum wage varies by age
A minimum wage makes it illegal for an employer to pay an hourly rate below the minimum wage set
The impact of a legal minimum wage
On employers | On employees |
|---|---|
|
|
Businesses in some countries are free to pay their workers very low wages, leading to much lower business costs
Businesses are often questioned about this decision, as it compromises business ethics
Effects of legal controls over employment issues on employers and employees
Employers need to understand the impact of employment laws to stay legal, avoid fines and manage their staff fairly and effectively
For employees, understanding their legal rights can help them feel more confident and supported in their jobs
Impact on employers
Increased responsibilities
Employers must follow legal rules when hiring, managing and dismissing staff
This includes giving written contracts, fair pay and safe working conditions.
Extra costs
Legal controls may lead to higher costs, such as paying minimum wage, providing sick leave or making workplaces safe
Avoiding legal trouble
By following the law, employers reduce the risk of being taken to court by employees, which could damage their reputation and finances
Improved staff relations
Fair treatment and clear policies can lead to better motivation and lower staff turnover, saving money in the long term
Impact on employees
Greater protection
Employees are protected from unfair treatment, such as being dismissed without reason or being underpaid
Safer working environment
Legal controls help ensure that workplaces are safe and that employees are properly trained to avoid accidents
More job security
Employees are less likely to lose their jobs unfairly or face discrimination, which gives them more confidence at work
Better working conditions
Laws encourage fair pay, rest breaks, equal treatment and protection from bullying or harassment
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Always link legal controls (like unfair dismissal or minimum wage) to their impact on both employers and employees – examiners look for this two-sided analysis

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
