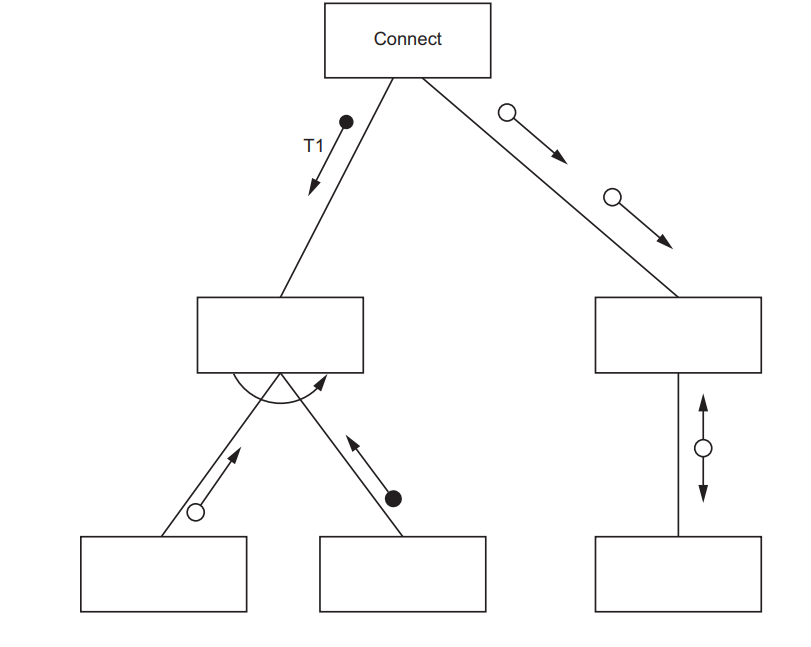
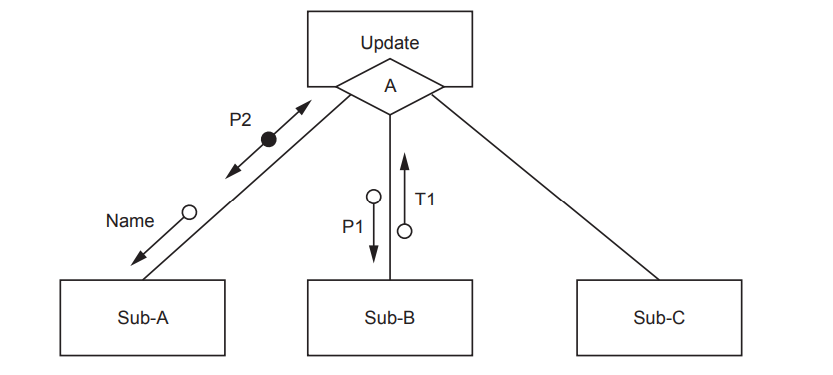
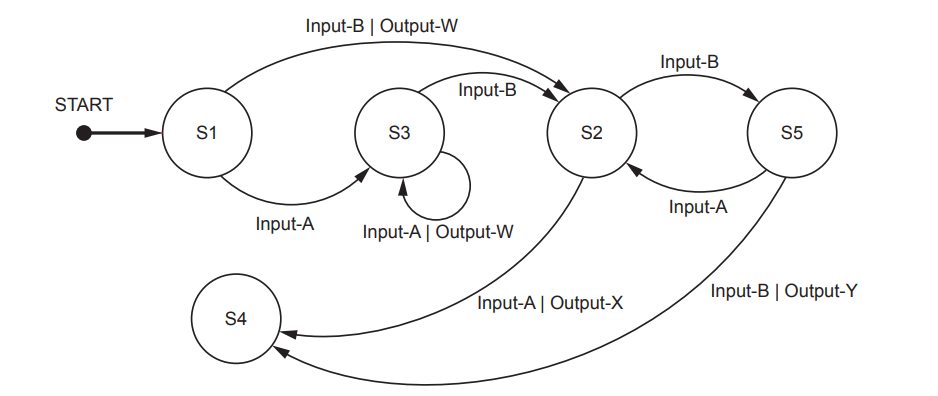
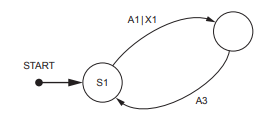
A program includes the following assignment statement:
Result ← STR_TO_NUM(x) / STR_TO_NUM(y)
When the program evaluates the expression in the statement, it performs a calculation.
Variable Result is of type real and variables x and y are of type string.
Two checks are required before the calculation is performed:
The two strings represent valid numeric values.
The numeric value of string
yis not zero.
The designer considers implementing the checks and calculation as a module (a procedure or a function). One reason for this is that the same checks and calculations are performed at several places in the program.
Give another reason why this is a suitable approach and state what is avoided by this approach.
Was this exam question helpful?