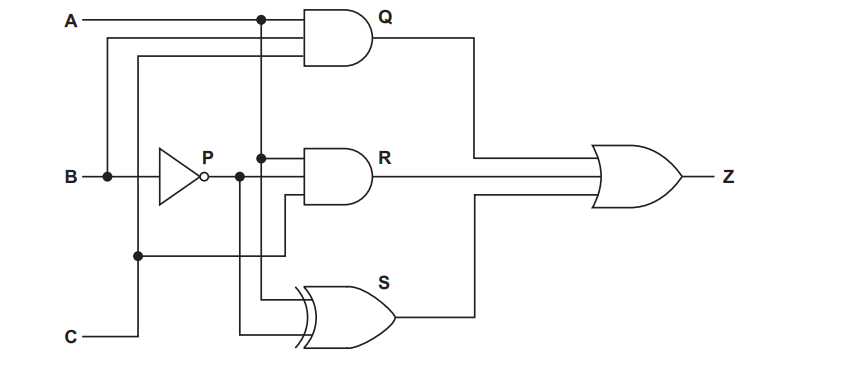
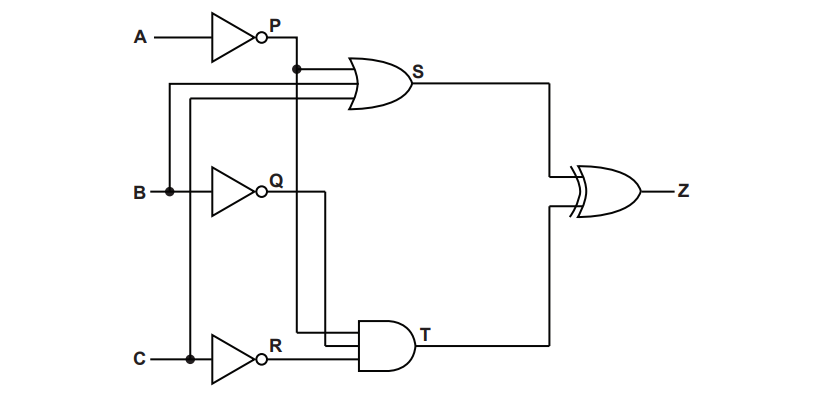
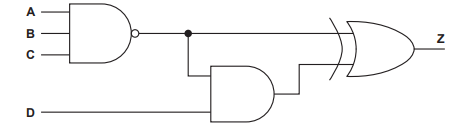
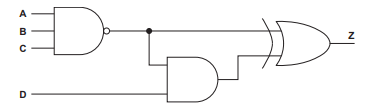
The truth table for a logic circuit is shown.
INPUT | OUTPUT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
A | B | C | D | T |
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Write the Boolean logic expression that corresponds to the given truth table as the sum-of-products.
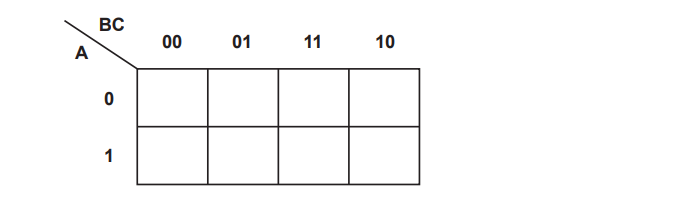
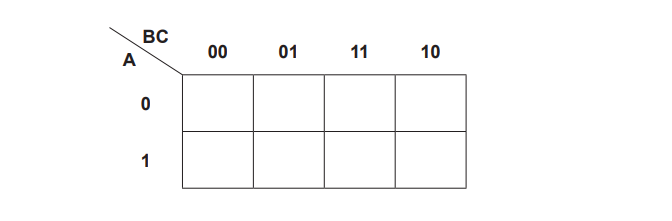
Complete the Karnaugh map (K-map) for the given truth table.
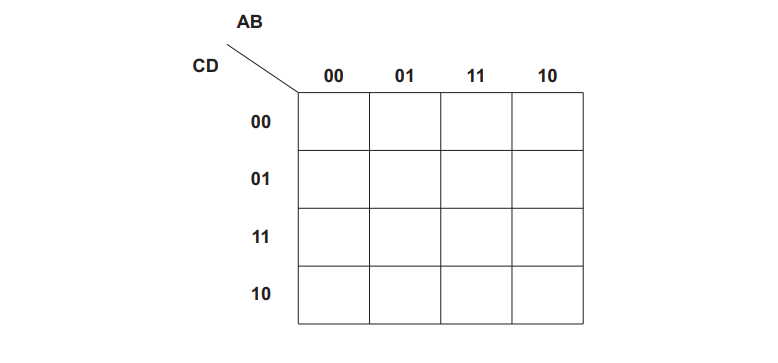
Draw loop(s) around appropriate group(s) in the K-map to produce an optimal sum-of-products.
(i) Write the Boolean logic expression from your answer to part (c) as the simplified sum-of-products.
(2)
(ii) Use Boolean algebra to write your answer to part (d)(i) in its simplest form.
(1)
Was this exam question helpful?