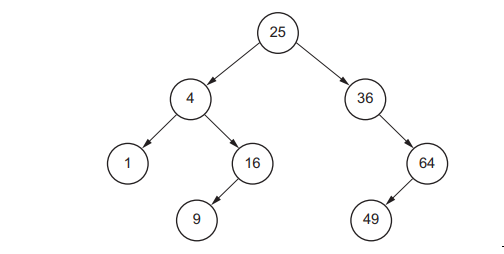
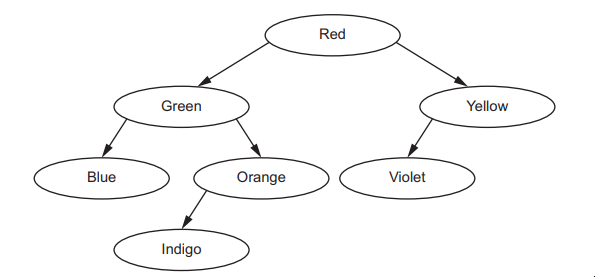
The following diagram shows an ordered binary tree.
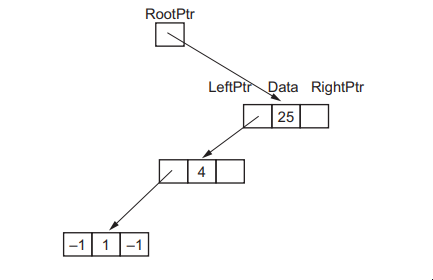
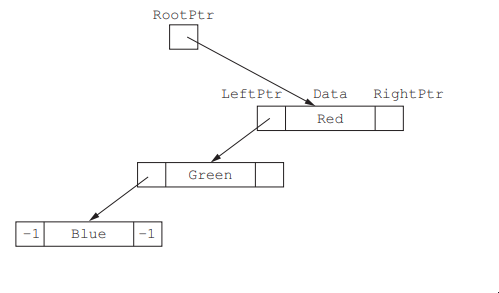
A linked list of nodes is used to store the data. Each node consists of a left pointer, the data and a right pointer.
–1 is used to represent a null pointer.
Complete this linked list to represent the given binary tree.
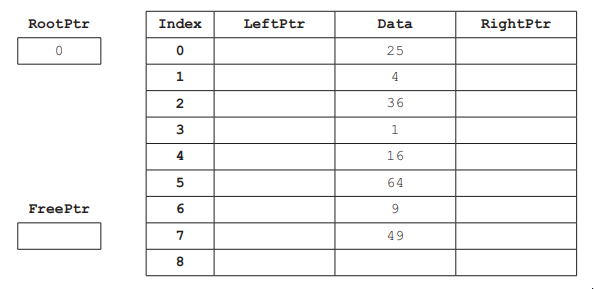
A user-defined record structure is used to store the nodes of the linked list in part (a).
Complete the diagram, using your answer for part (a).
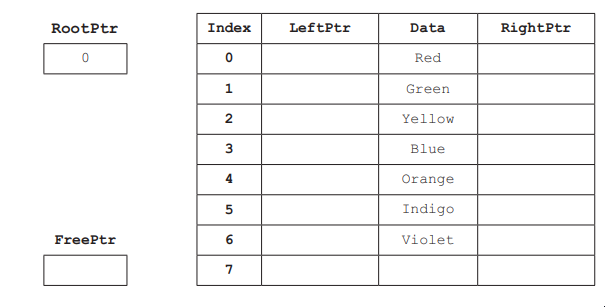
The linked list in part (a) is implemented using a 1D array of records. Each record contains a left pointer, data and a right pointer.
The following pseudocode represents a function that searches for an element in the array of records BinTree. It returns the index of the record if the element is found, or it returns a null pointer if the element is not found.
Complete the pseudocode for the function.
FUNCTION SearchTree(Item : STRING) ........................................................................
NowPtr .........................................................................................................................
WHILE NowPtr <> -1
IF ..................................................................................................................... THEN
NowPtr BinTree[NowPtr].LeftPtr
ELSE
IF BinTree[NowPtr].Data < Item THEN
.................................................................................................................
ELSE
RETURN NowPtr
ENDIF
ENDIF
ENDWHILE
RETURN NowPtr
ENDFUNCTION
Was this exam question helpful?