A shop repairs electronic devices, for example mobile phones and tablet computers. The shop owner stores the data about the repairs using a file-based approach.
Give one limitation of using a file-based approach to store the data and explain how a relational database addresses this limitation.
Limitation.......................................................................................................
Explanation.....................................................................................................
The shop owner creates a relational database called FIXIT.
The database stores data about the customers and the devices for repair.
Some devices need new parts that are ordered from suppliers.
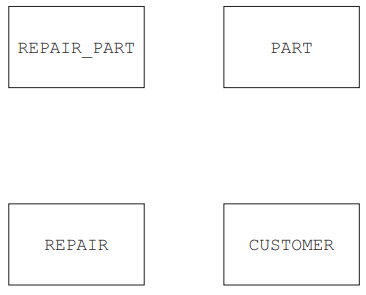
The database FIXIT is designed to include the following tables:
PART(PartID, Description, Price, SupplierID)
CUSTOMER(CustomerID, FirstName, LastName, ContactNumber)
REPAIR(RepairNumber, StartDate, EndDate, CustomerID, Device)
REPAIR_PART(PartID, RepairNumber, Quantity)
Complete the entity-relationship (E-R) diagram for the given tables.
Complete the table by writing a definition for each of the database terms.
Term | Definition |
Referential integrity | ..................................................... |
Candidate key | ...................................................... |
Tuple | ........................................................ |
Was this exam question helpful?