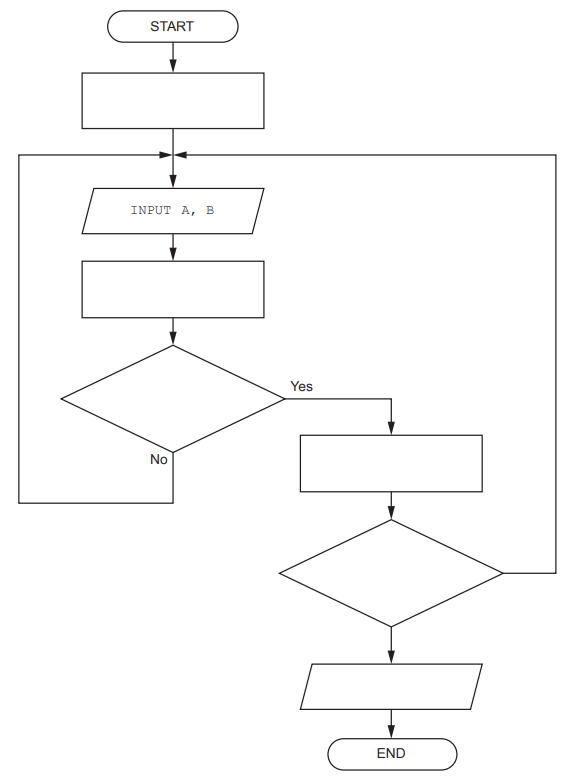
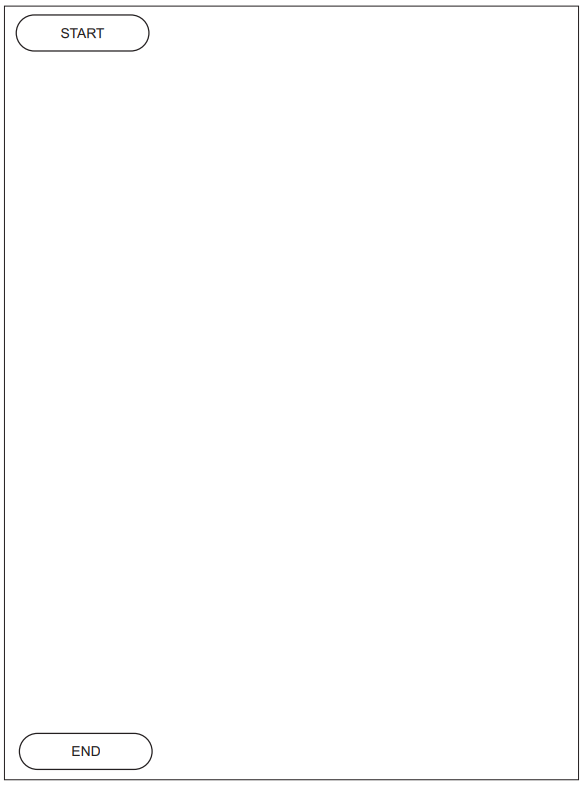
An algorithm will output the last three lines from a text file Result.txt
The lines need to be output in the same order as they appear in the file.
Assume:
Three variables
LineX,LineYandLineZwill store the three lines. These are of type string and all three variables have been initialised to an empty string.The file exists and contains at least three lines.
The algorithm to output the lines is expressed in eight steps.
Complete the steps.
1. Open the file ...........................................................................
2. Loop until ...........................................................................
3. ........................................................................... and store in ThisLine
4. Assign LineY to LineX
5. Assign LineZ to LineY
6. Assign ThisLine to LineZ
7. After the loop, ...........................................................................
8. Output LineX, LineY, LineZ
Explain the purpose of steps 4, 5 and 6 in the algorithm from part (a).
Was this exam question helpful?