Electrical Resistivity (Edexcel AS Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 8PH0
Electrical Resistivity
All materials have some resistance to the flow of charge
As free electrons move through a metal wire, they collide with ions which get in their way
As a result, they transfer some, or all, of their kinetic energy on collision, which causes electrical heating

Free electrons collide with ions which resist their flow
Since current is the flow of charge, the ions resisting their flow cause resistance
Resistance depends on the length of the wire, the cross-sectional area through which the current is passing and the resistivity of the material

Electrical resistance equation
The resistivity equation shows that:
The longer the wire, the greater its resistance
The thicker the wire, the smaller its resistance

The length and width of the wire affect its resistance
Resistivity is a property that describes the extent to which a material opposes the flow of electric current through it
It is a property of the material, and is dependent on temperature
Resistivity is measured in Ω m
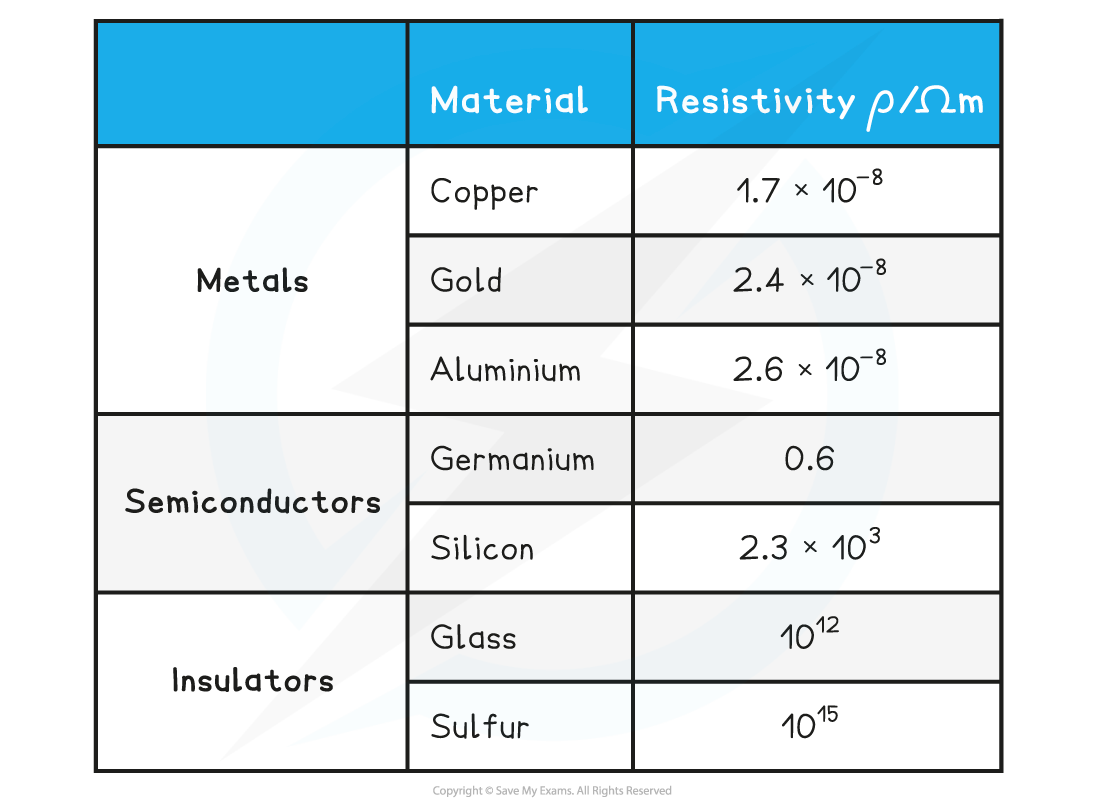
Resistivity of some materials at room temperature
The higher the resistivity of a material, the higher its resistance
Copper has a relatively low resistivity at room temperature, and so is used for electrical wires
This is because current flows through it very easily
Insulators have such a high resistivity that virtually no current will flow through them
Worked Example
Two electrically-conducting cylinders made from copper and aluminium respectively.
Their dimensions are shown below.

Copper resistivity = 1.7 × 10-8 Ω m
Aluminium resistivity = 2.6 × 10-8 Ω m
Which cylinder is the better conductor?
Answer:

Examiner Tips and Tricks
You don’t need to memorise the value of the resistivity of any material; these will be given in the exam question.
Remember if the cross-sectional area is a circle e.g. in a wire, then area is proportional to the radius or diameter squared. This means if the diameter doubles, the area will quadruple. This causes the resistance to drop by a quarter. Considering how changing one property affects the value of the others is a common exam question.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
