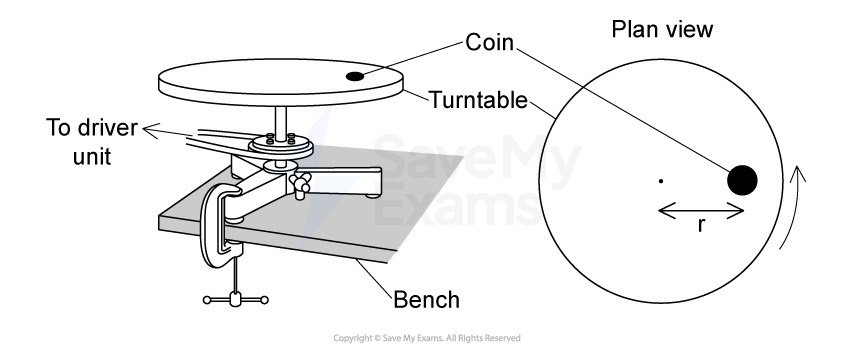
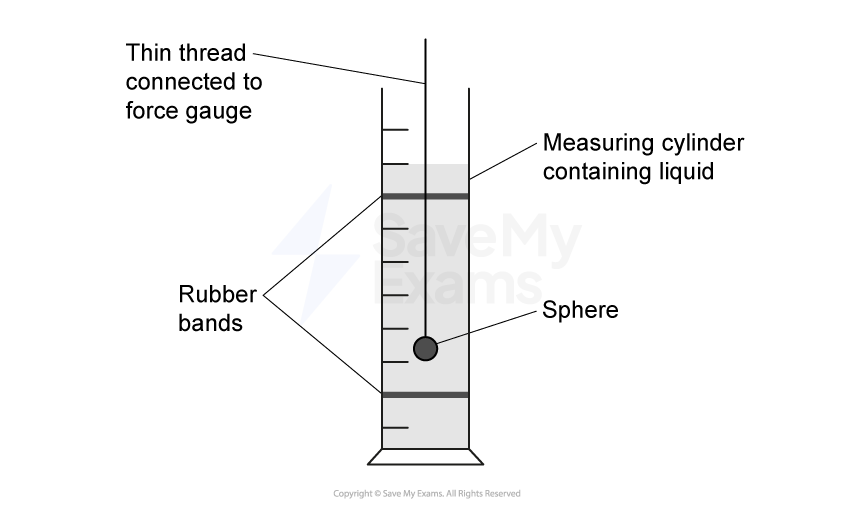
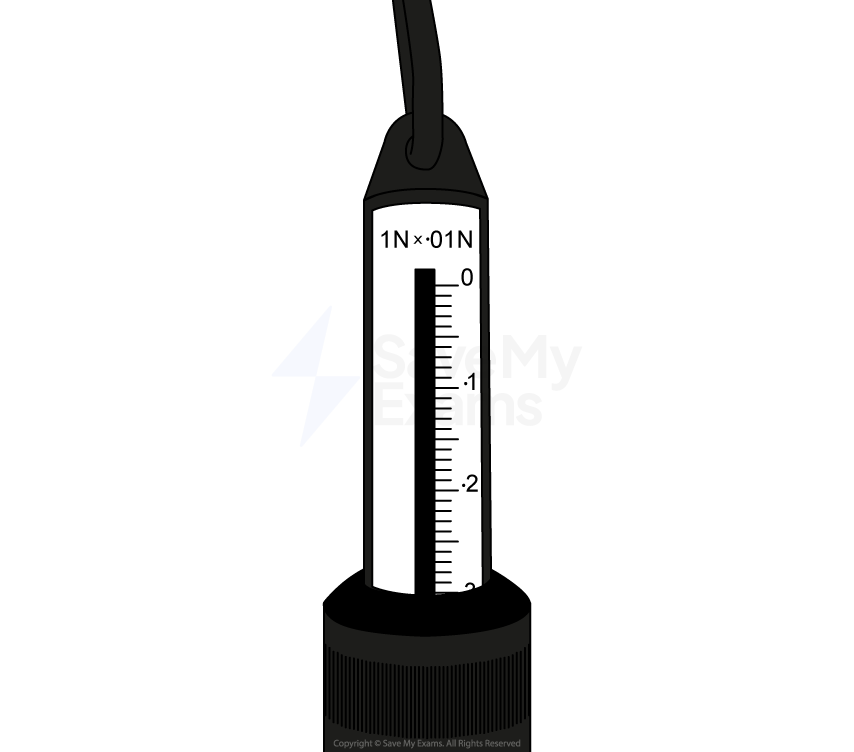
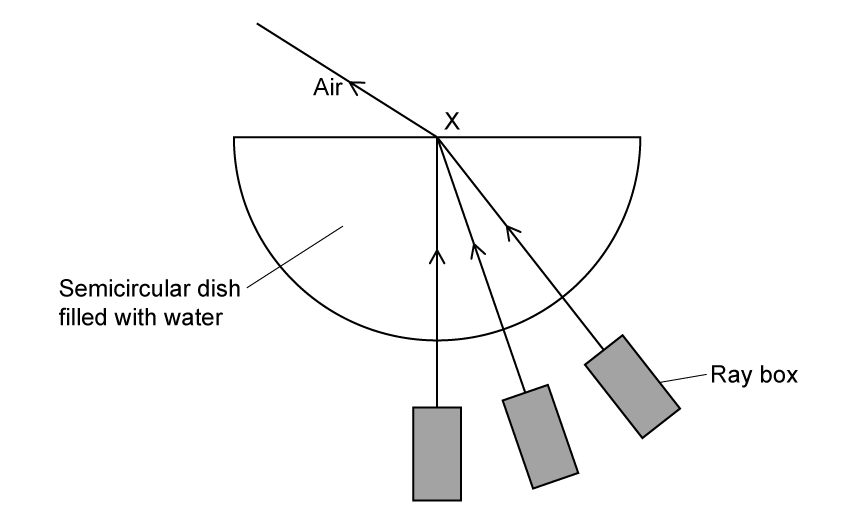
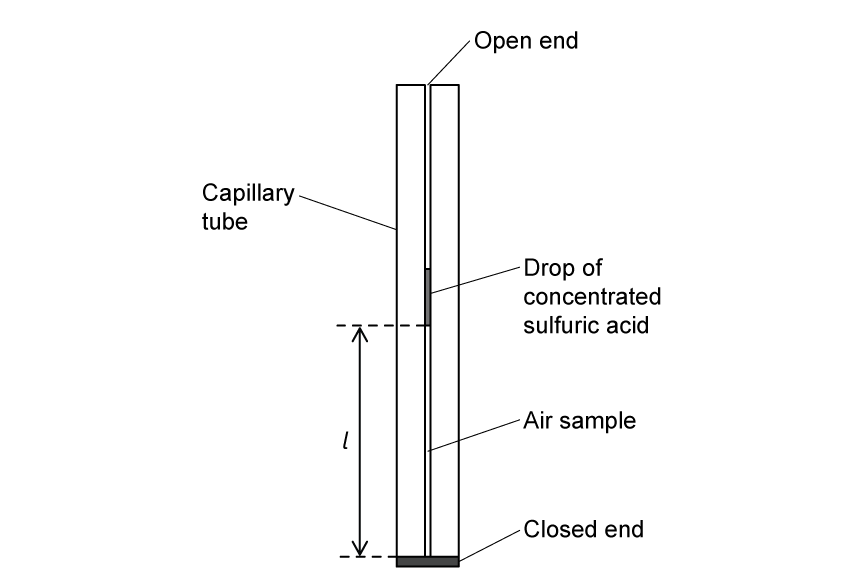
A group of students investigate the rise of a liquid in a capillary tube. The students use a travelling microscope to measure the height reached by the liquid when one end of the capillary tube is immersed into it.
A travelling microscope is a measuring instrument consisting of a simple microscope that can be moved vertically along a vernier scale. The students take measurements of the positions of the top and bottom of the liquid column.
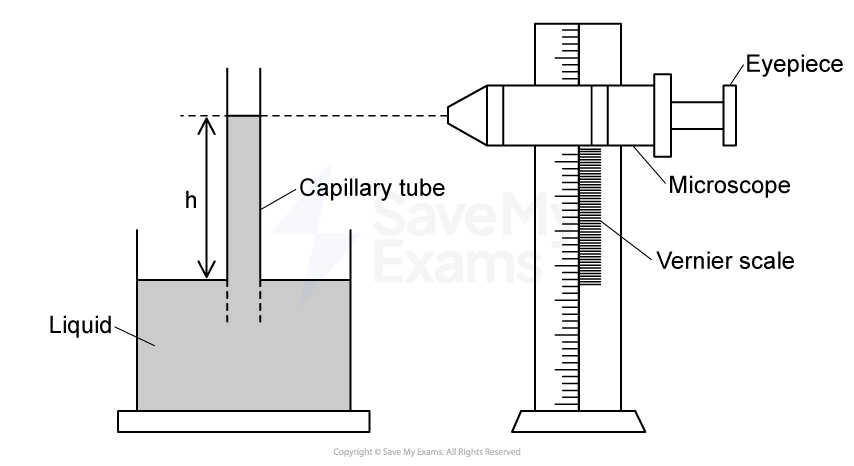
The students used a capillary tube with an internal radius r equal to 0.10 mm and recorded the following readings from the vernier scale.
Bottom of liquid column / cm | Top of liquid column / cm |
12.00 | 27.10 |
(i) State the uncertainty in each of these readings.
[1]
(ii) Calculate the percentage uncertainty in the student’s value of .
[2]
(iii) The students repeated the measurement of for capillary tubes of different radii. The table shows the student’s final data.
0.09 | 11.1 | 16.56 |
0.10 | 10.0 | 15.1 |
0.12 | 8.3 | 12.6 |
0.15 | 6.7 | 10.33 |
Discuss the values that the students have recorded.
[2]
The students suggest the following theoretical relationship between and
where is a constant.
To verify the relationship, the variation of with
is plotted.

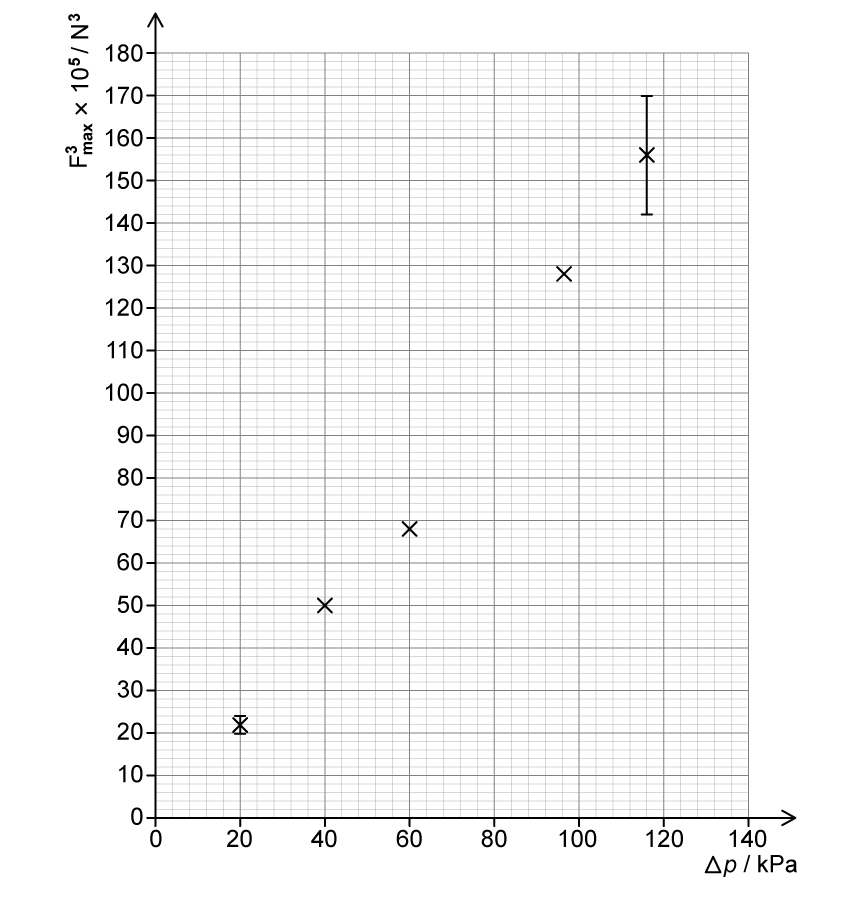
(i) Determine by drawing a line of best fit, and state an appropriate unit for
.
[3]
(ii) Estimate for a tube with internal radius
= 0.11 mm.
[1]
(iii) Suggest whether the student’s data supports the theoretical relationship.
[2]
Was this exam question helpful?