Skeleton Structure (AQA GCSE Physical Education (PE)): Revision Note
Exam code: 8582
Structure of the skeleton
The skeleton is a framework of bones; its role is to:
support the body
allow movement
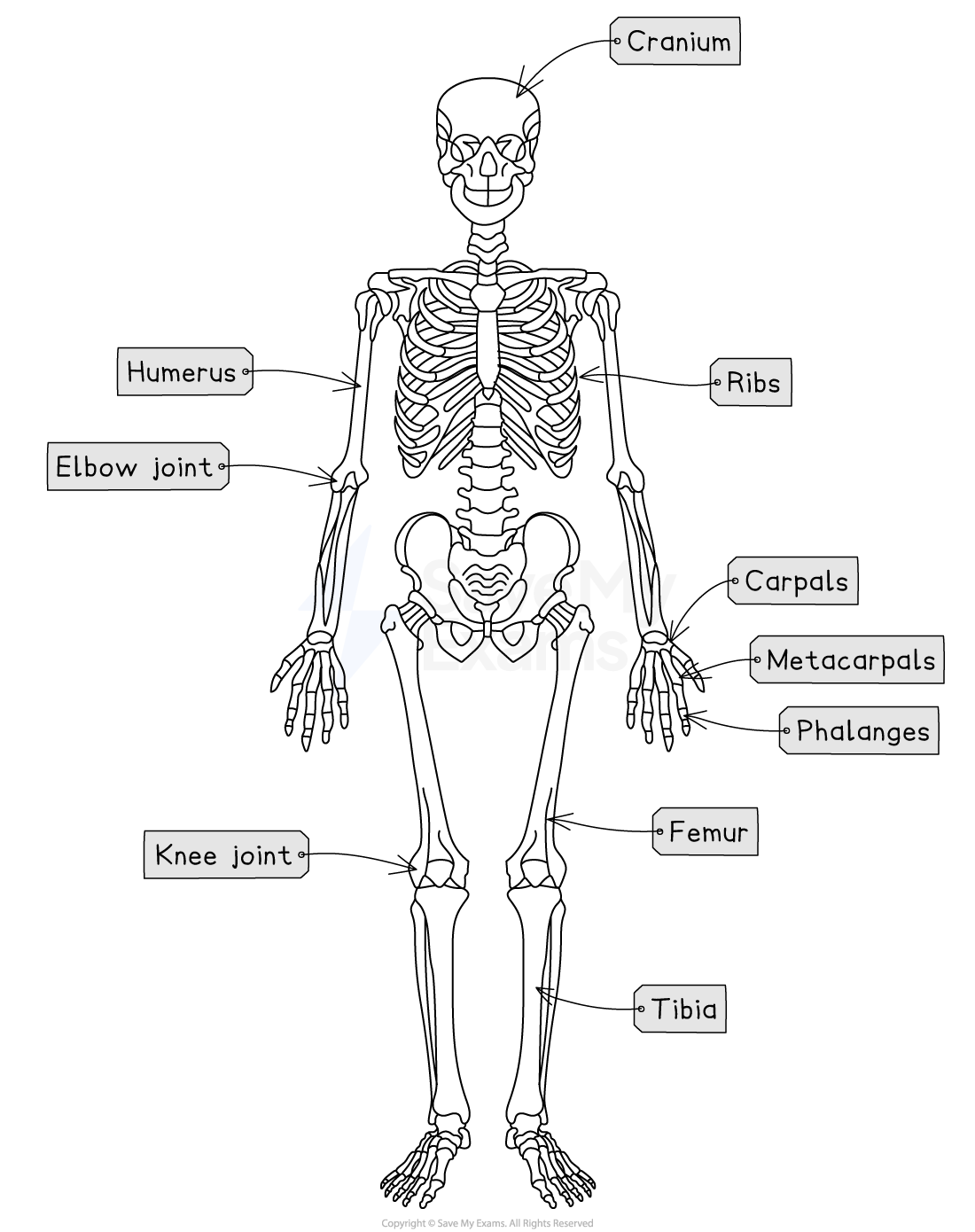
Joints are points of connection between two or more bones, e.g. the elbow joint connects the bones of the arm, and the knee joint connects the bones of the leg
At a joint, bone ends are covered with smooth cartilage and held together by ligaments, while tendons attach nearby muscles to move the joint
There are different types of joints, each allowing different kinds of movement
The shape and size of the bones play an important role in their function
Long bones enable gross, or large-scale, movements such as running or standing up, e.g.:
the femur and tibia in the leg
the humerus in the arm
Short bones enable finer, controlled movement
E.g. the carpals, metacarpals and phalanges in the hand
Flat bones protect organs from damage, e.g.:
the ribs protect the lungs
the cranium protects the brain

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
