Kinetic Energy (SQA National 5 Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: X857 75
Kinetic energy
Kinetic energy is defined as:
The energy an object has due to its movement
This means that all moving objects have kinetic energy due to their mass and speed
If an object speeds up, energy is transferred to it as kinetic energy
If an object slows down, its kinetic energy is transformed into a different type of energy
Kinetic energy of a moving object
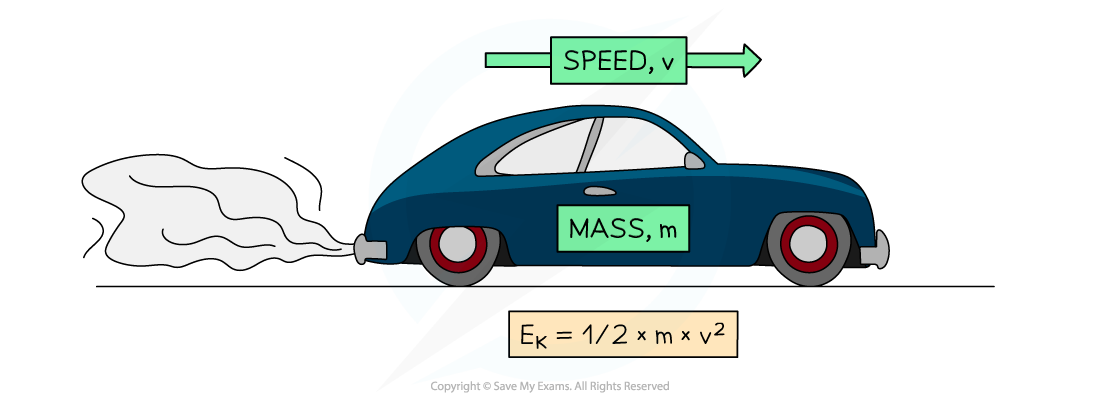
Calculating kinetic energy
The kinetic energy possessed by a moving object can be calculated using the relationship:
Where:
= kinetic energy, measured in joules (J)
= mass of the object, measured in kilograms (kg)
= speed of the object, measured in metres per second (m s-1)
The kinetic energy equation demonstrates that if the mass of an object is doubled for a given speed, then its kinetic energy will double
This is because kinetic energy is directly proportional to mass
If the speed of the object is doubled for a given mass, it will have four times the kinetic energy
This is because kinetic energy is directly proportional to velocity squared
Worked Example
Calculate the kinetic energy stored in a vehicle of mass 1200 kg moving at a speed of 27 m s-1.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Mass of the vehicle,
Speed of the vehicle,
Step 2: Write down the equation for kinetic energy
Step 3: Calculate the kinetic energy
Step 4: Round the final answer to 2 significant figures
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When performing calculations using the kinetic energy equation, always double-check that you have squared the speed. Forgetting to do this is the most common mistake that students make.
You will most likely need to rearrange the kinetic energy equation in your exam. The kinetic energy equation is one of the more difficult rearrangements, so make sure you are comfortable doing it before your exam!

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
