Applications of Nuclear Radiation (SQA National 5 Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: X857 75
Did this video help you?
Applications of nuclear radiation
Radioactivity has many uses, such as:
Smoke detectors (alarms)
Monitoring the thickness of materials
Detecting leaks in pipes
Generating electricity
Medical procedures including diagnosis and treatment of cancer
Sterilising food (irradiating food)
Sterilising medical equipment
Determining the age of ancient artefacts
The properties of the different types of radiation determine which one is used in a particular application
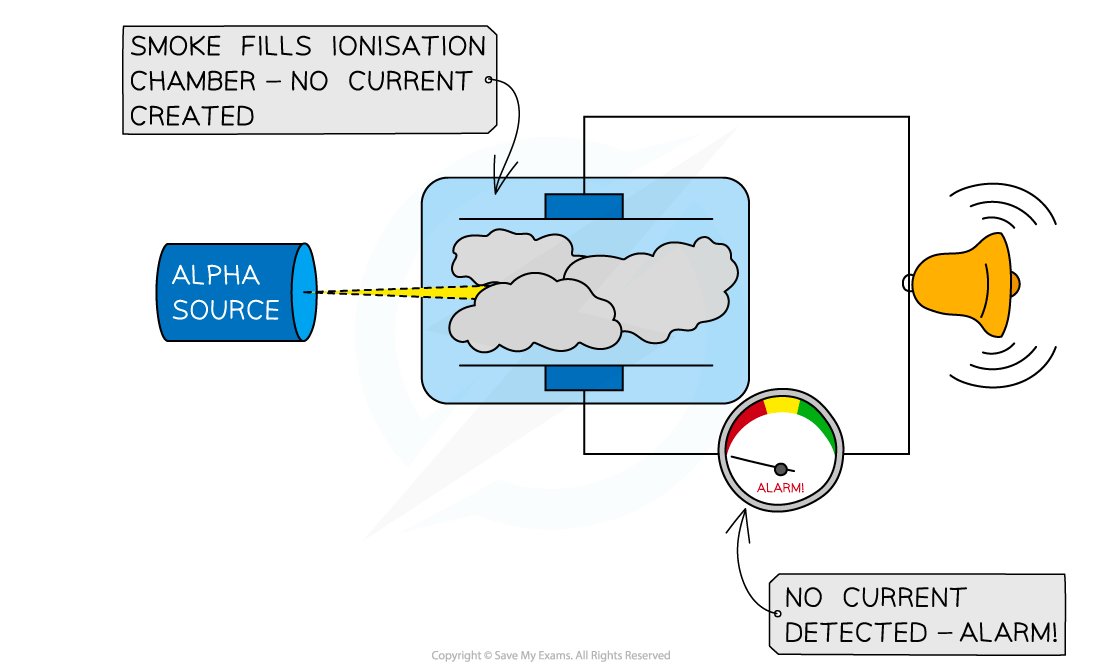
Smoke detectors
Alpha particles are used in smoke detectors
The alpha radiation will normally ionise the air within the detector, creating a current
The alpha emitter is blocked when smoke enters the detector
The alarm is triggered by a microchip when the sensor no longer detects alpha

Measuring the thickness of materials
When a material, such as aluminium foil, moves above a beta source, some beta particles will be absorbed, but most will penetrate
The amount of beta particles passing through the material can be monitored using a detector
If the material gets thicker, more particles will be absorbed, and the count rate will decrease
If the material gets thinner, fewer particles will be absorbed, and the count rate will increase
This allows the manufacturer to make adjustments to keep the thickness of the material constant
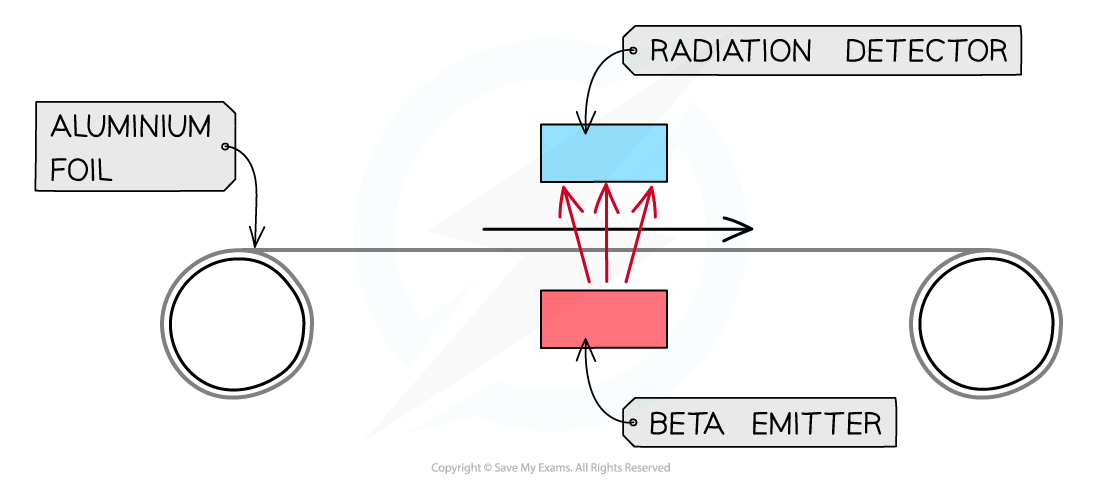
Beta radiation is used because the material will only partially absorb it
If an alpha source were used, all alpha particles would be absorbed regardless of material thickness
If a gamma source were used, almost all gamma rays would be detected regardless of material thickness
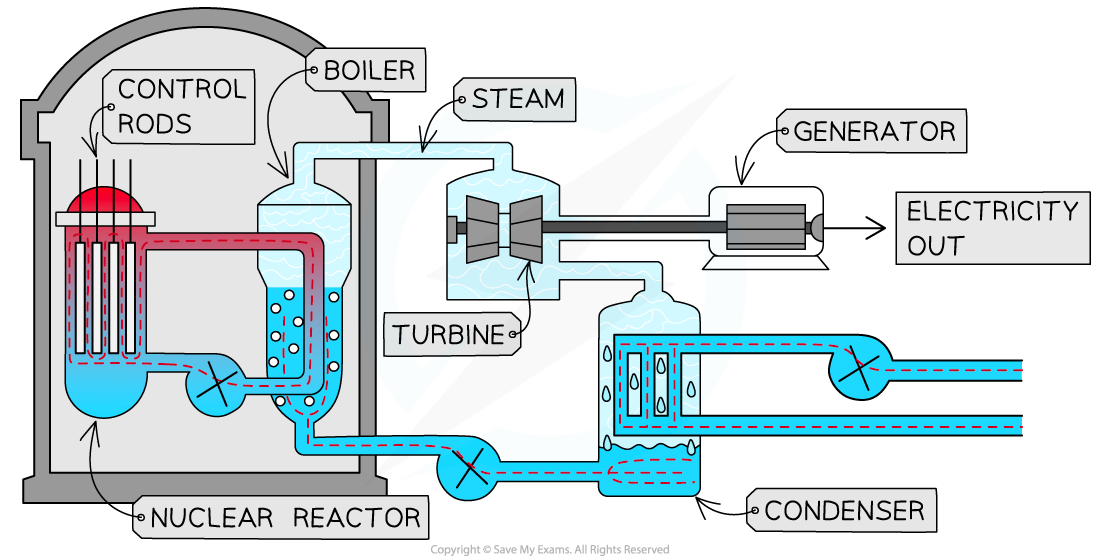
Generating electricity
Nuclear fission is the process of splitting the nucleus of heavy atoms like uranium or plutonium into smaller nuclei
This process releases very large amounts of energy
This energy is used to heat water
The steam produced is used to turn turbines that turn a generator and produces electricity
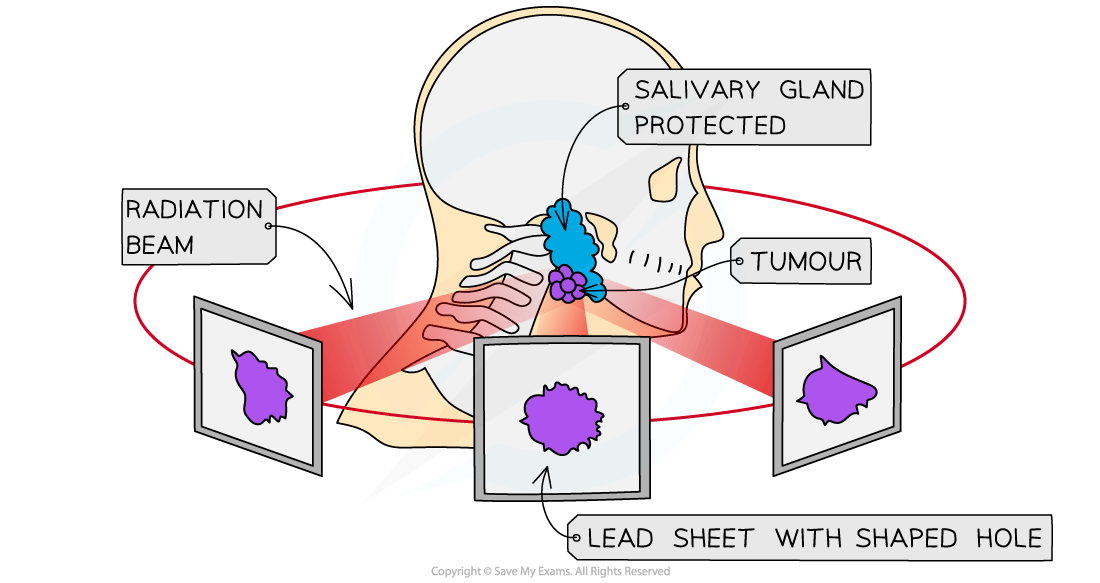
Diagnosis and treatment of cancer
Radiotherapy is the name given to the treatment of cancer using radiation
Note: this is different to chemotherapy, which is a drug treatment for cancer
Although radiation can cause cancer, it is also highly effective at treating it
The relative ionising effect of radiation can kill living cells
Some cells, such as bacteria and cancer cells, are more susceptible to radiation than others
Beams of gamma rays are directed at the cancerous tumour
Gamma rays are used as they can penetrate the body and reach the tumour
The beams are moved around to minimise harm to healthy tissue whilst still being aimed at the tumour
A tracer is a radioactive isotope that can be used to track the movement of substances, like blood, around the body
A PET scan can detect the emissions from a tracer to diagnose cancer and determine the location of a tumour
Sterilising food and medical equipment
Gamma radiation is widely used to sterilise medical equipment
Gamma is most suited to this because:
It is the most penetrating out of all the types of radiation
It is penetrating enough to irradiate all sides of the instruments
Instruments can be sterilised without removing the packaging
Food can be irradiated in order to kill any microorganisms that are present on it
This makes the food last longer and reduces the risk of food-borne infections

Worked Example
Explain why a source of alpha radiation is used in smoke detectors, and not beta or gamma radiation.
Answer:
Step 1: Consider the different properties of alpha, beta and gamma radiation
Alpha is the most weakly penetrating and strongest ioniser
Beta and gamma have stronger penetrating power and weaker ionising power
Step 2: Explain why alpha radiation is the best choice for use in a smoke detector
Alpha radiation is the most suitable as it would be easily absorbed by the smoke and trigger the alarm
Beta and gamma radiation are not suitable as they would pass straight through the smoke and the alarm would not be triggered
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you are presented with an unfamiliar situation in your exam don’t panic! Just apply your understanding of the properties of alpha, beta and gamma radiation. Focus on the range (how far it can travel) and ionising power of the radiation to help understand which radiation is used in which situation.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
