Background Radiation (SQA National 5 Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: X857 75
Background radiation
Background radiation is defined as:
The radiation that exists around us all the time
There are two types of background radiation:
Natural sources from radioactive elements that have always existed on Earth and in outer space
Man-made sources from human activity that adds to the amount of radiation humans are exposed to on Earth
The count rate of detected levels of background radiation can vary significantly from place to place
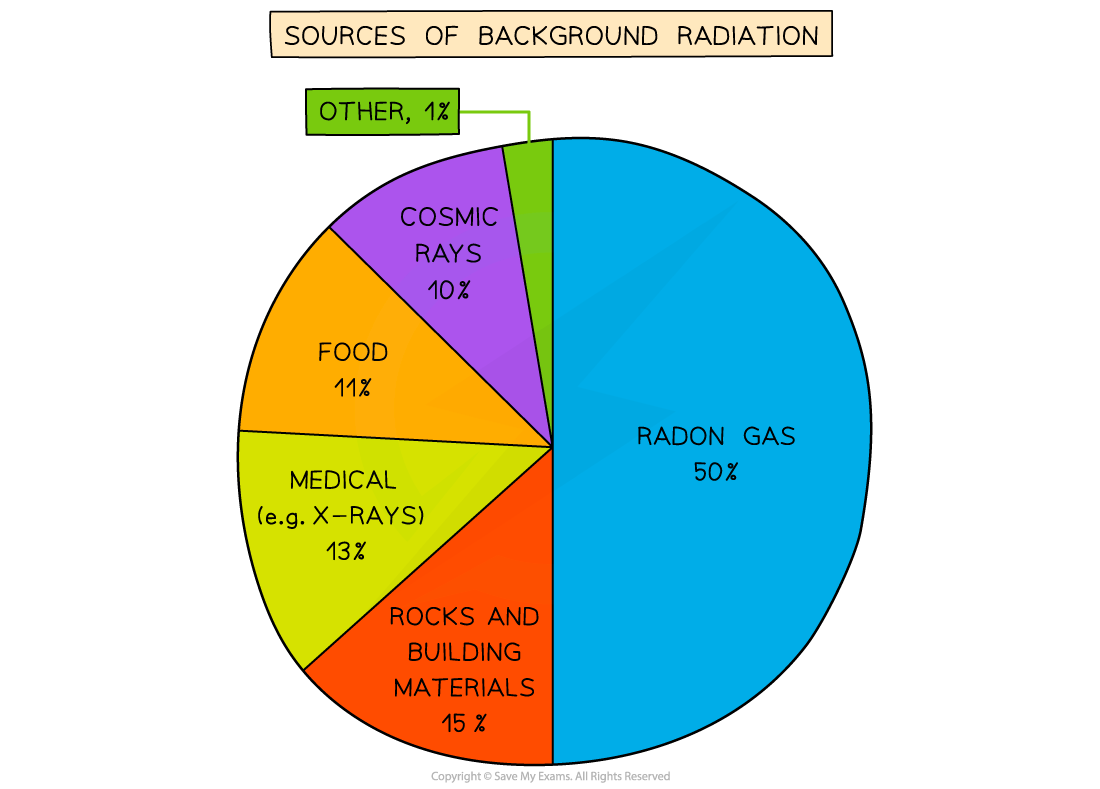
Sources of background radiation
The sources that make a significant contribution to background radiation include:
radon gas (in the air)
rocks and buildings
soil
food and drink
cosmic rays
Background radiation sources pie chart
Natural sources
Rocks and buildings
Natural radioactivity can be found in building materials, including decorative rocks, stone and brick
Heavy radioactive elements, such as uranium and thorium, occur naturally in rocks in the ground
Uranium decays into radon gas
Radon gas (in the air)
Radon gas is an alpha emitter
Radon gas is particularly dangerous if it is inhaled into the lungs in large quantities
The gas is tasteless, colourless and odourless, but it is not generally a health issue unless levels are significantly high
Radioactive material in food and drink
Naturally occurring radioactive elements can get into food and water since they are in contact with rocks and soil containing these elements
Some foods contain higher amounts such as potassium-40 in bananas
However, the amount of radioactive material is minuscule and is not a cause for concern
Cosmic rays from space
The sun emits an enormous number of protons every second
Some of these enter the Earth’s atmosphere at high speeds
When they collide with molecules in the air, this leads to the production of gamma radiation
Other sources of cosmic rays are supernovae and other high-energy cosmic events
Carbon-14 in biological material
All organic matter contains a tiny amount of carbon-14
Living plants and animals constantly replace the supply of carbon in their systems, hence the amount of carbon-14 in the system stays almost constant
Therefore, soil, made from decomposed organic matter is also a source of background radiation
Man-made sources
Medical sources
In medicine, radiation is used frequently
Uses include X-rays, CT scans, radioactive tracers, and radiation therapy
Nuclear waste
While nuclear waste itself does not contribute much to background radiation, it can be dangerous for the people handling it
Nuclear fallout from nuclear weapons
Fallout is the residue radioactive material that is thrown into the air after a nuclear explosion, such as the bomb that exploded at Hiroshima
While the amount of fallout in the environment is presently very low, it increases significantly in areas where nuclear weapons are tested
Nuclear accidents
Accidents such as that in Chernobyl contributed a large dose of radiation into the environment
While these accidents are now extremely rare, they can be catastrophic and render areas devastated for centuries
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The sources that make the most significant contribution are the natural sources:
Radon gas
Rocks and buildings
Food and drink
Cosmic rays
Make sure you remember these for your exam!

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
